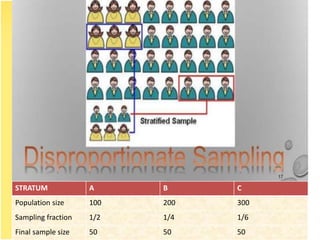
This document discusses various sampling methods used in research. It defines sampling as selecting a subset of individuals from a larger population to gather information about that population. Probability sampling methods like simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, and systematic random sampling aim to provide an unbiased representation of the population. Non-probability methods like purposive sampling and snowball sampling are used when random selection is not feasible. Key factors that influence sampling like sample size, bias, and population characteristics are also reviewed. The document provides examples and compares advantages and disadvantages of different sampling techniques.