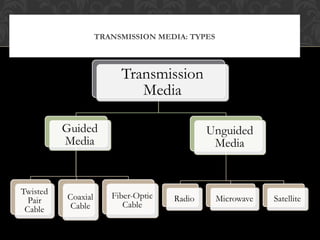
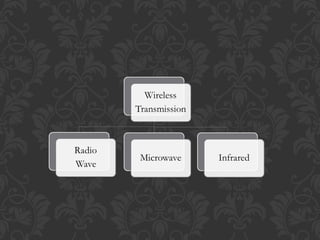
Computers and devices use electromagnetic signals to transmit data through transmission media. Transmission media can be divided into guided and unguided categories. Unguided media, also called wireless communication, transports signals through the air without a physical conductor. Unguided signals can travel from source to destination in several ways, including ground propagation along the earth's surface, sky propagation reflecting signals off the ionosphere, and line-of-sight propagation transmitting signals directly between antennas.