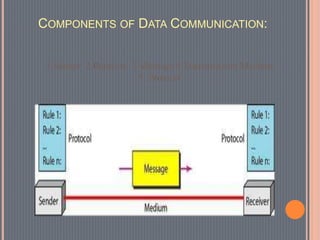
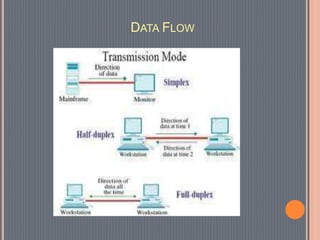
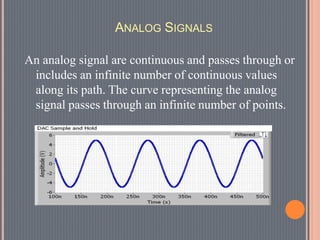
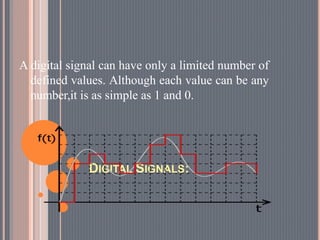
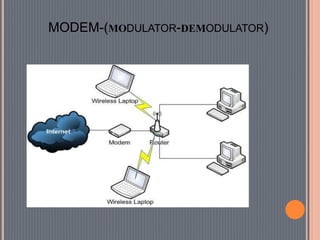
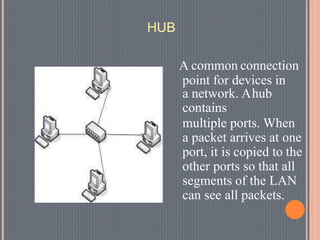
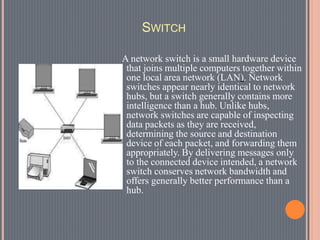
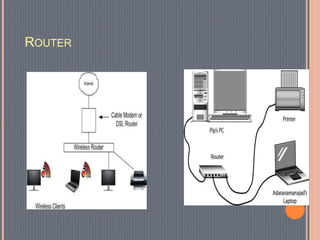
This document provides an overview of data communications. It discusses the key components of data communication systems including senders, receivers, messages, transmission mediums, and protocols. It describes different types of data flow such as simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex. It also discusses analog and digital signals and different transmission mediums including guided mediums like coaxial cable and fiber optics, as well as unguided wireless mediums. Finally, it provides information on common networking devices including modems, hubs, switches, and routers.