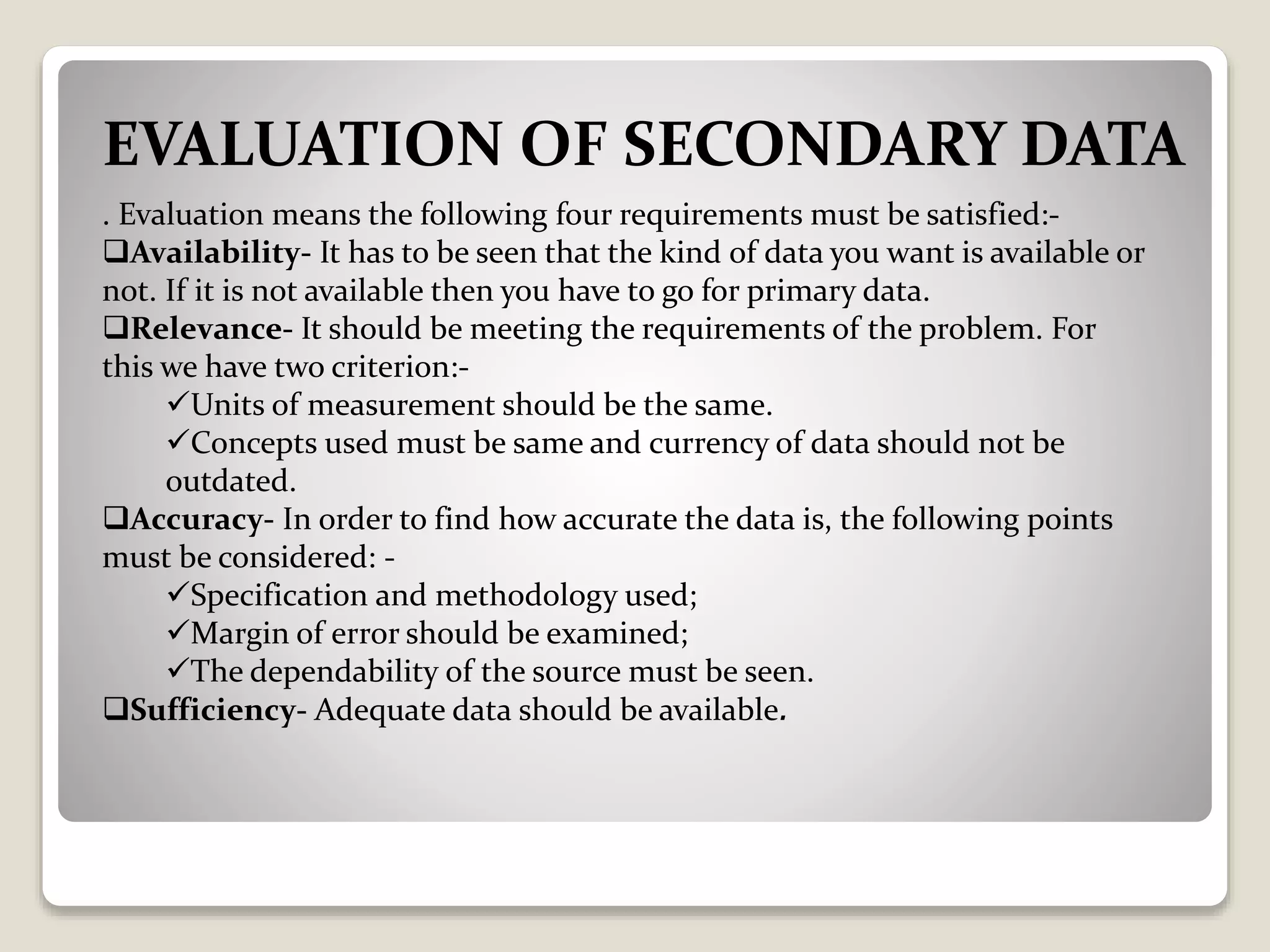
Secondary data refers to data that has already been collected by others and then re-used by researchers. There are several types of secondary sources, including published printed sources like books and journals, published electronic sources like e-journals and websites, and unpublished personal records and government records. While secondary data saves time and money compared to primary data, it can be difficult to find accurate secondary data that fully meets the needs of the present study. Researchers must evaluate secondary data based on its availability, relevance, accuracy, and sufficiency for the research problem.