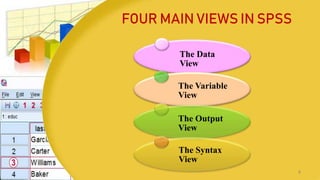
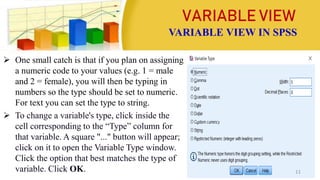
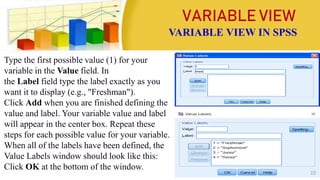
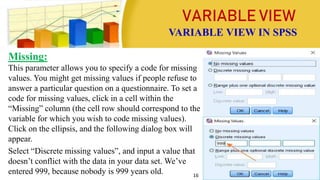
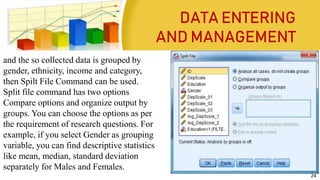
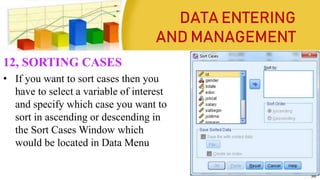
This document provides information on coding data and managing data using SPSS. It defines data coding as the process of converting verbal data into numeric variables and categories that can be analyzed by computers. Data management in SPSS involves viewing, editing, sorting, splitting, identifying duplicate or unusual cases, selecting cases, and inserting new cases or variables. The four main views in SPSS are the Data View, Variable View, Output View, and Syntax View. Steps for entering, editing, and importing data from Excel are also outlined.