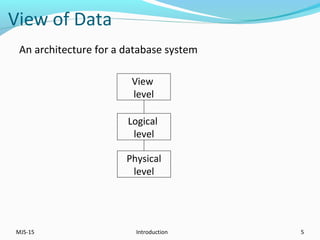
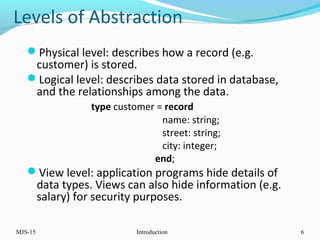
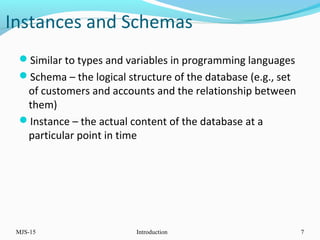
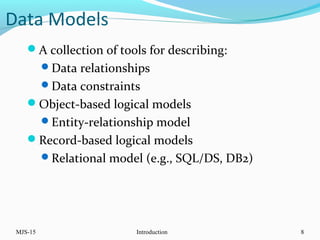
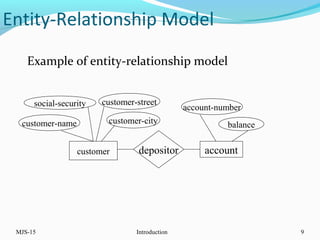
This document provides an overview of database management systems (DBMS). It defines what a database is and discusses the purpose of DBMS compared to traditional file systems. The document outlines several key DBMS concepts including data models, the relational model, and query languages like DDL, DML, DCL, and TCL. Examples are provided for each concept to illustrate database schemas, tables, queries, privileges and transactions.




![Data Control Language (DCL)
A DCL is a language used to control privilege in
Database
DCL Commands:
•Grant
•Syntax: REVOKE [permission] ON database.table FROM 'user‘@'localhost';
Example: GRANT [write] ON [company_details].[employee] TO ‘[sandeep]’@'localhost’;
•Revoke
•Syntax: REVOKE [permission ]ON database.table FROM 'user‘@'localhost';
Example: REVOKE [write] ON Company_details.Employee FROM ‘Sandeep'@'localhost';
MJS-15 Introduction 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dbmspresentaion-150511052104-lva1-app6892/85/Dbms-presentaion-17-320.jpg)

