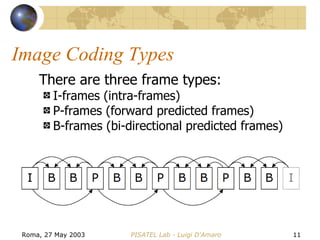
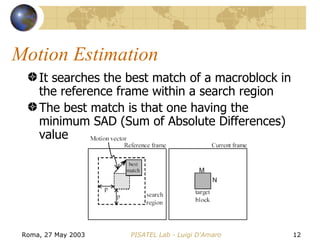
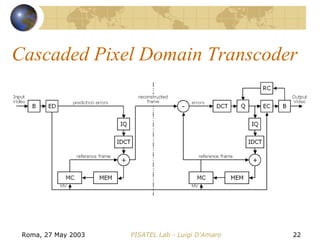
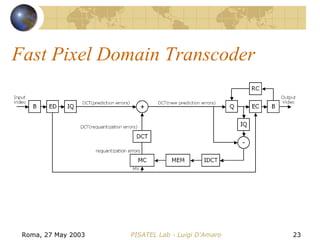
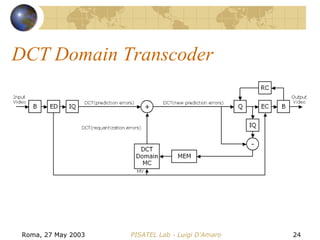
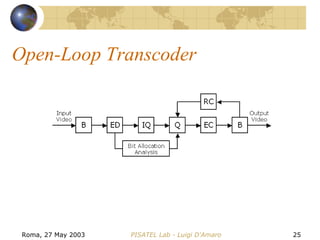
The document discusses video transcoding for mobile telephony. It motivates the need for video transcoding by describing how mobile users may experience bandwidth reductions during calls, requiring the video bitrate to be lowered. It then provides an overview of video coding standards and how transcoding can convert a compressed video stream to a different format, resolution, frame rate or quality level. Future work is proposed to address video transcoding challenges caused by temporary bandwidth reductions during mobile calls.