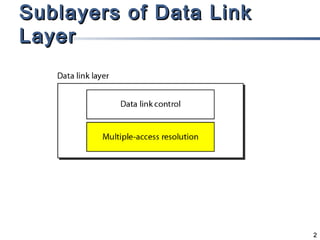
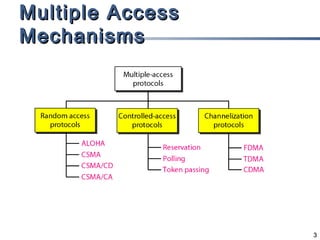
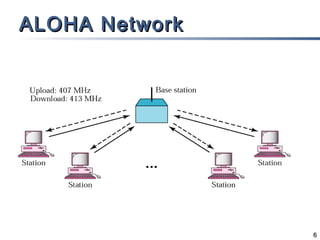
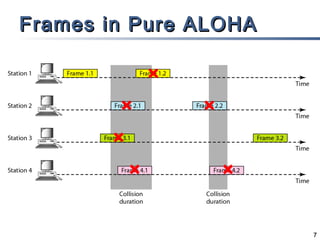
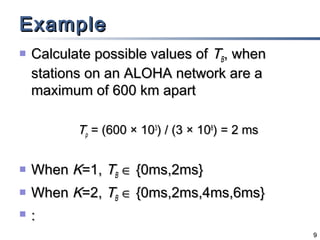
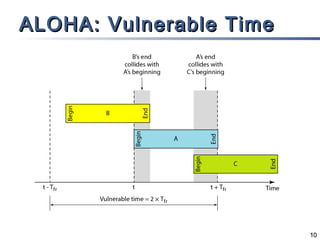
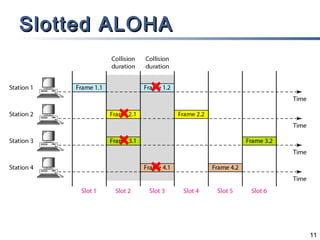
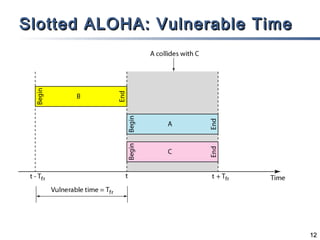
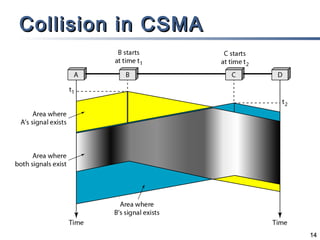
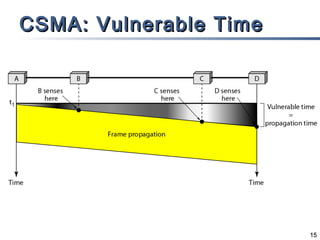
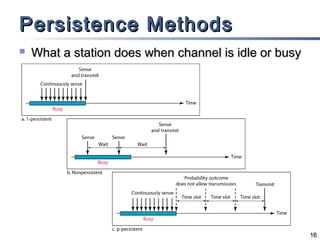
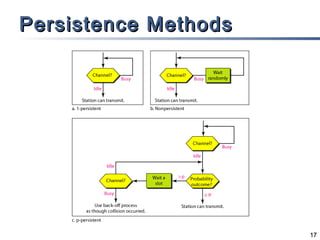
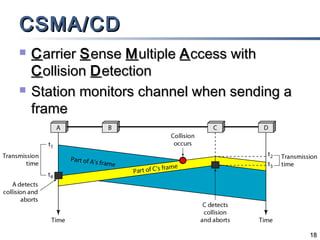
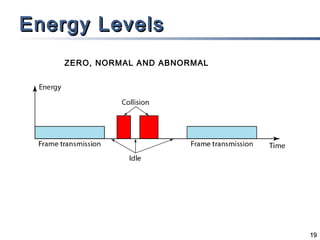
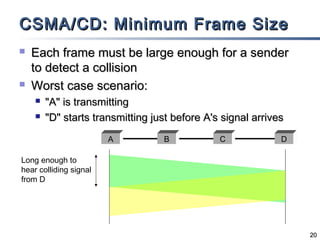
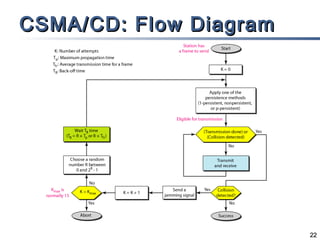
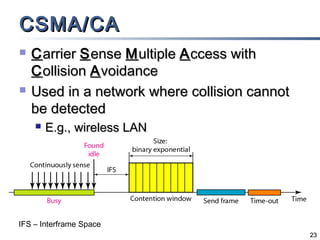
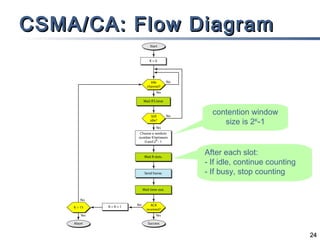
The document outlines different multiple access mechanisms for data link layers, including random access, controlled access, and channelization. It then describes the sublayers of the data link layer and various random access protocols like ALOHA, slotted ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CD, and CSMA/CA. It provides details on how each protocol handles channel access and collisions.