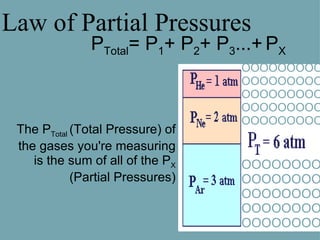
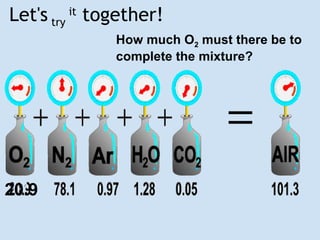
John Dalton was an English chemist, physicist and meteorologist born in 1776. He formulated the Law of Partial Pressures in 1801, which states that the total pressure of a mixture of gases in a container is equal to the sum of the pressures of each gas if they occupied the container alone at the same temperature. Dalton's law is useful for calculating the pressure of individual gases in a mixture based on their partial pressures and the total pressure. It can be applied, for example, to find the air pressure inside a bottle by subtracting the pressure of water vapor from the total pressure.