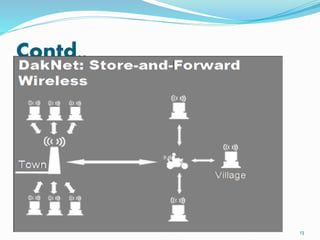
DakNet is a wireless network that provides internet access to remote villages in India and Cambodia using a store-and-forward technique. It transmits data between kiosks and mobile access points (MAPs) mounted on vehicles. MAPs come within range of kiosks or internet hubs to transfer messages and videos. DakNet leverages low-cost wireless and digital storage to provide affordable connectivity without real-time requirements. It has been successfully deployed to provide education, healthcare, government services, and commerce to rural communities in a scalable way.