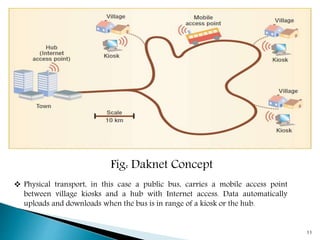
DakNet is an ad hoc wireless network introduced by First Mile Solutions in 2002 to provide digital connectivity in rural India, utilizing a store-and-forward concept. The architecture consists of mobile access points, hubs, and kiosks, with data transmitted automatically as the mobile access points, often mounted on vehicles, move between these kiosks and the internet hub. This initiative aims to enhance access to services like education and e-government while being cost-effective and easy to deploy.























![ [1] Pentland, A et al. "Daknet: rethiniking connectivity in developing nations". Mobile
communication conference. 2004.
[2] Jun Liu And Fukuda, K. "Towards a taxonomy of darknet traffic". Wireless
communication and mobile computing conference (IWCMC), 2014 international conforence
[3] Roos,s. And Strufe, T. "A contribution to analyzing and enhancing Darknet routing". IEEE
Conference on Computer Communications 2013.
[4] Qian Wang et al. "Daknet-based Inference of Internet Worm Temporal Characteristics"
information forensics and security, IEEE transation.
[5] McManamon and Mtenzi, F. "The development and deployment of daknet." Internet
technology and secured transactions (ICITST), 2010 international conference.
[6] Mizoguchi,S. et al. "Daknet Monitoring on real-operated Networks. Broadband, wireless
computing, communication and application (BWCCA), 2010 international conference.
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-170422083530/85/Daknet-ppt-prepared-by-me-for-seminar-in-my-college-25-320.jpg)
