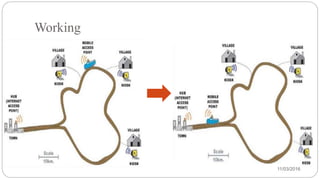
Daknet is an ad hoc wireless network designed to provide low-cost digital connectivity in remote areas, leveraging existing transportation and communication systems. It enables asynchronous digital communication and has been successfully implemented in villages in India and Cambodia, making broadband access affordable. While it offers benefits like cost-effectiveness and wireless technology, it faces challenges such as high power consumption and limited range.