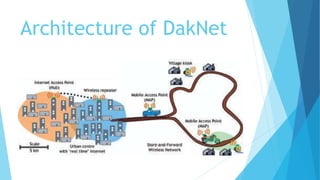
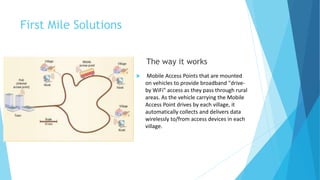
DakNet is a wireless network developed at MIT to provide connectivity to rural areas in developing nations using a hub, kiosks, and Mobile Access Points (MAPs) that deliver data between kiosks and portable storage devices called MAPs, addressing the need for affordable connectivity in remote villages where access to phones and internet requires long travel. The architecture uses short-range wireless links between low-cost components to seamlessly scale affordable broadband connectivity, applications, and information services to unequipped rural communities.