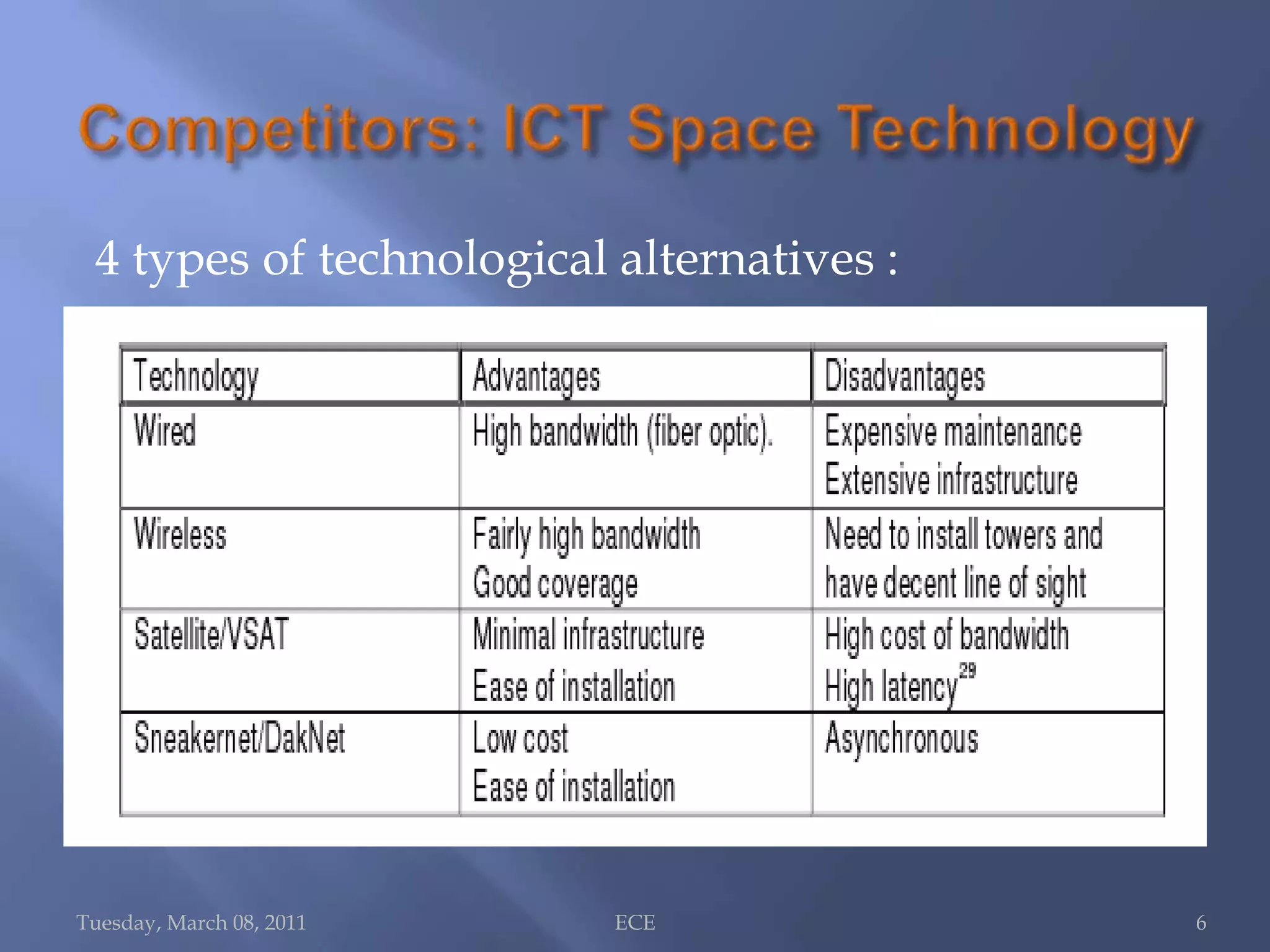
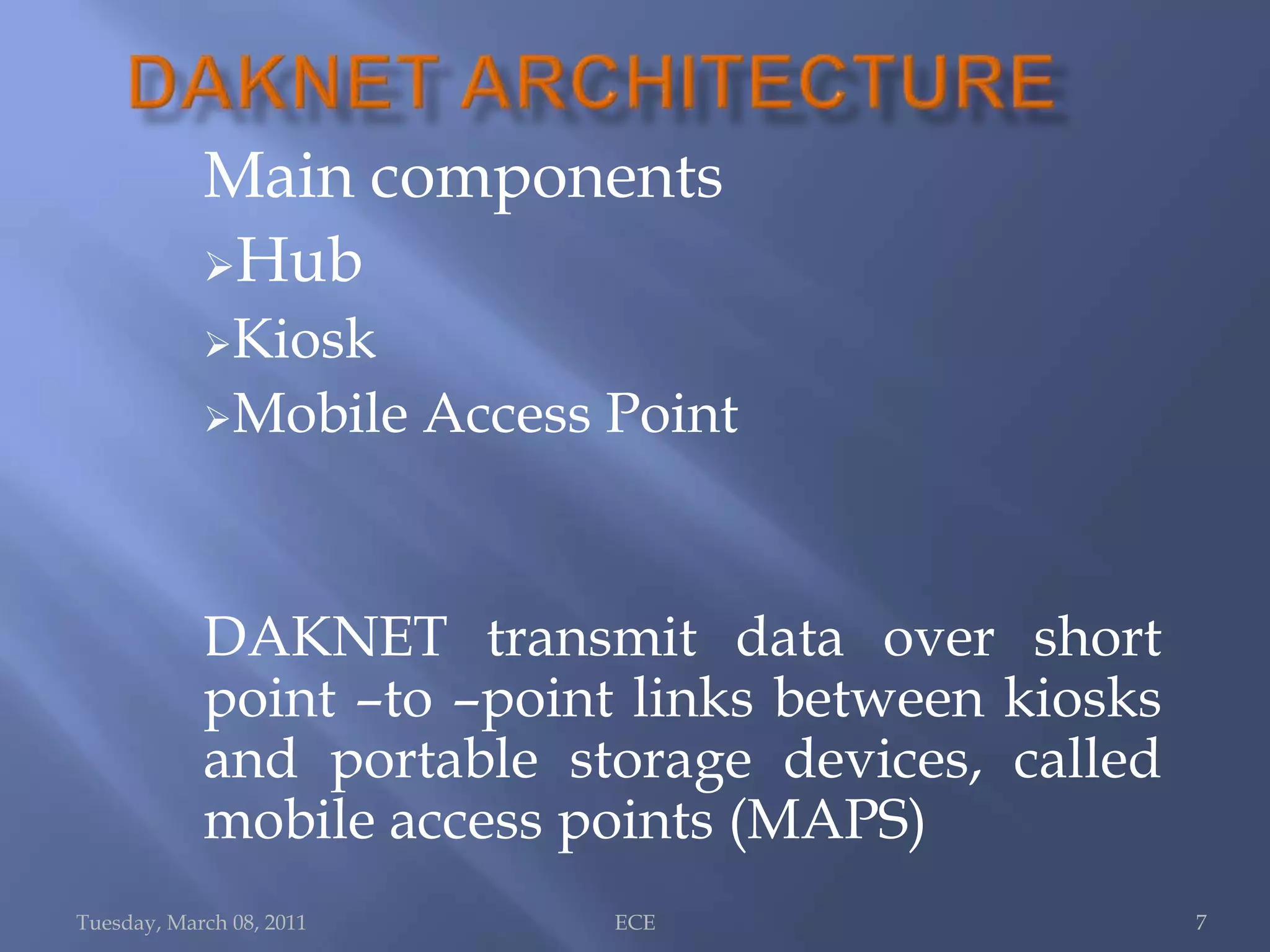
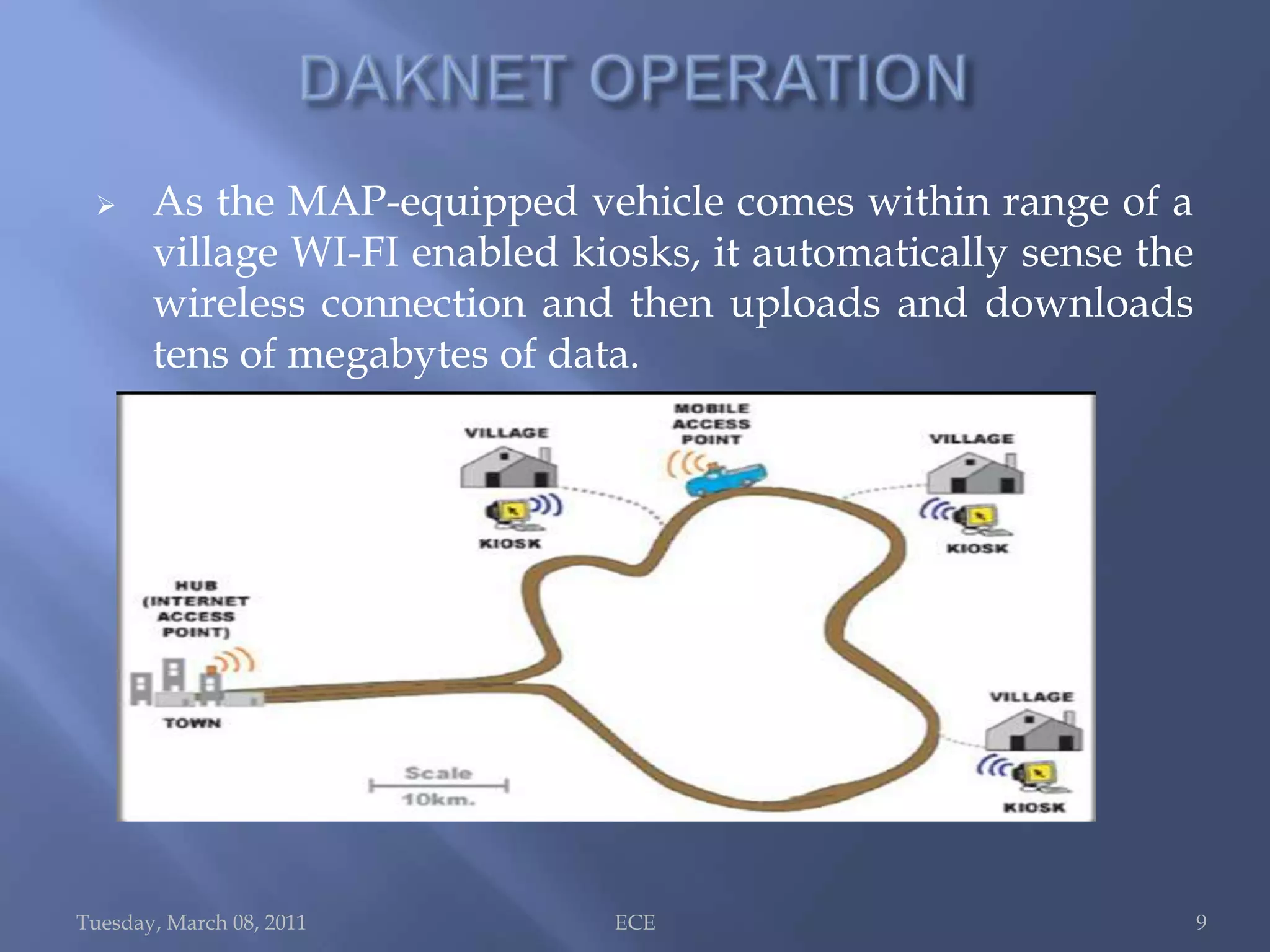
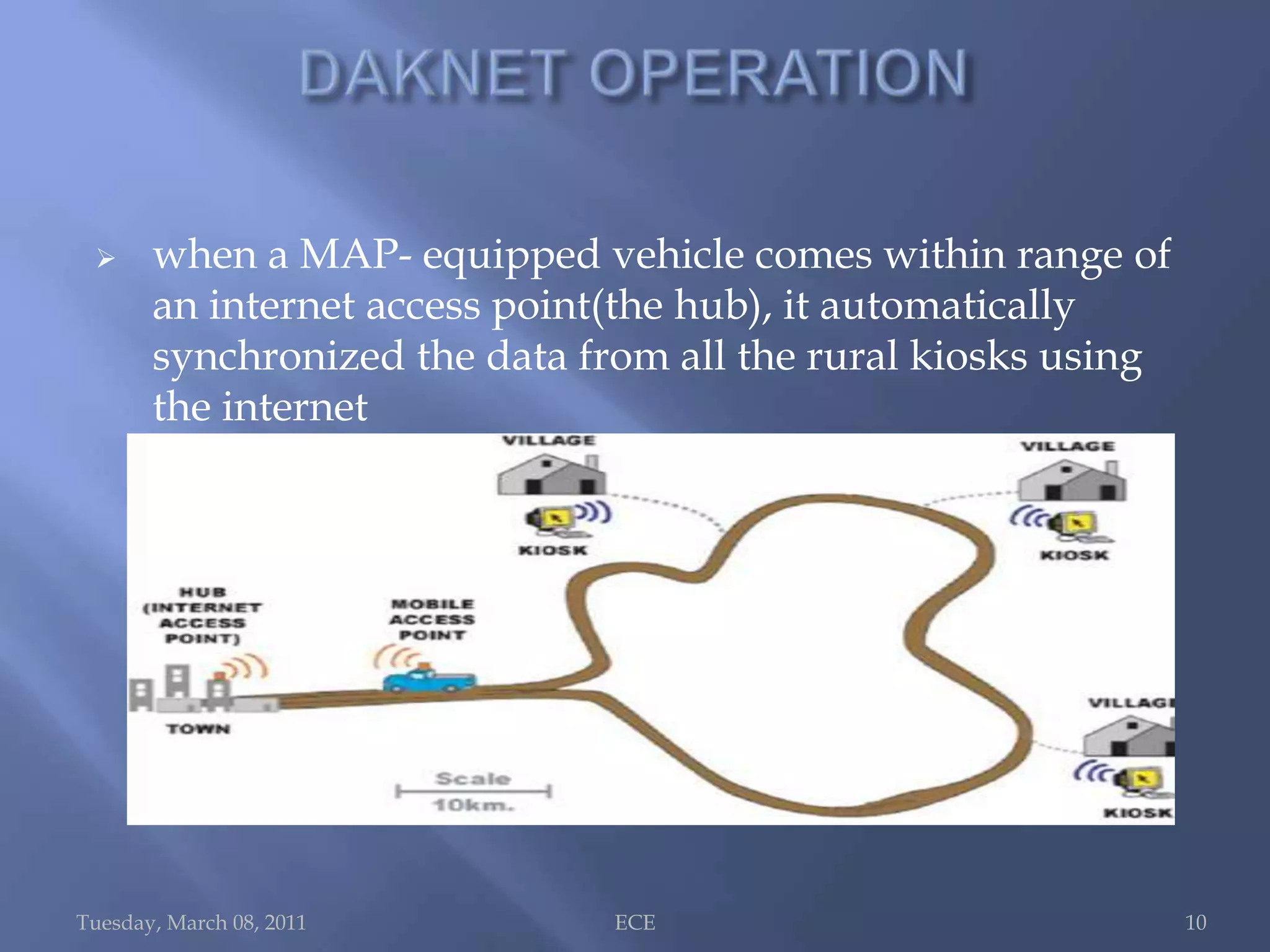
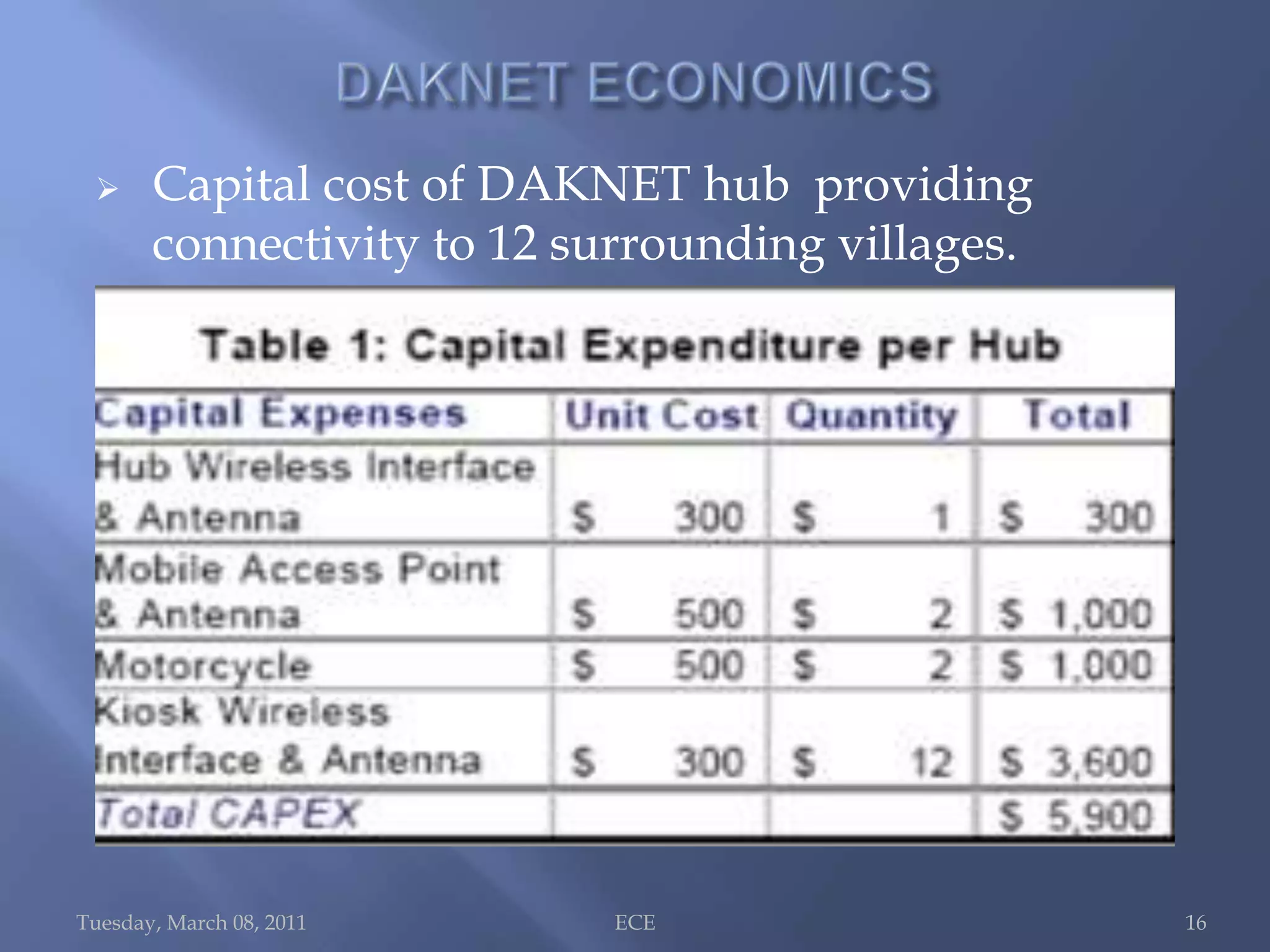
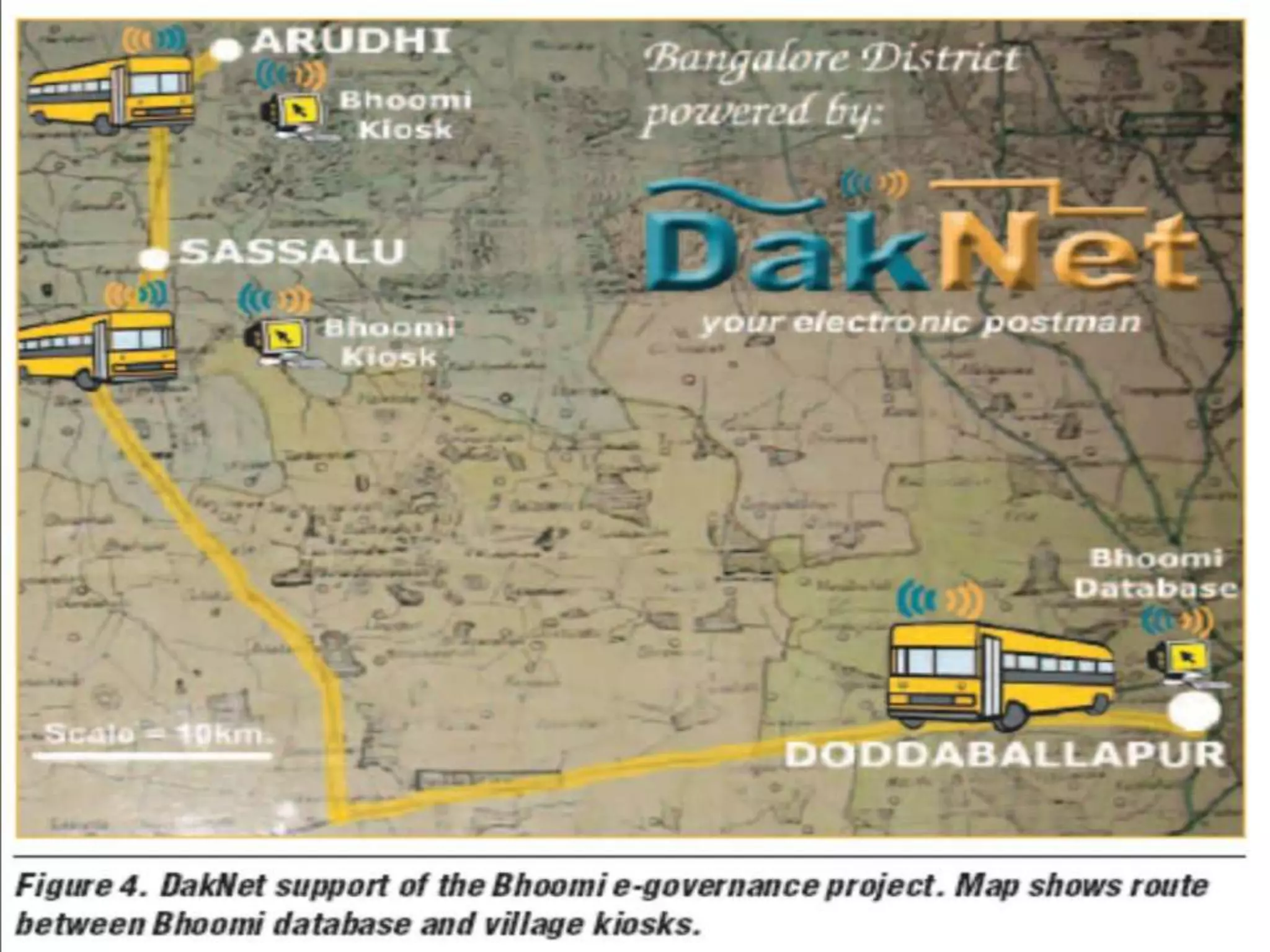
The document summarizes Daknet, an ad hoc wireless network developed by MIT researchers to provide digital connectivity to remote villages in India and Cambodia. Daknet uses portable storage devices called mobile access points (MAPs) that are transported between villages by vehicles and allow for asynchronous data transfer. When a MAP comes within range of a village kiosk or internet hub, it automatically uploads and downloads data. This provides a low-cost solution for digital connectivity without requiring real-time connectivity. Daknet has been used for applications like e-mail, information distribution, and supporting e-governance projects in India.