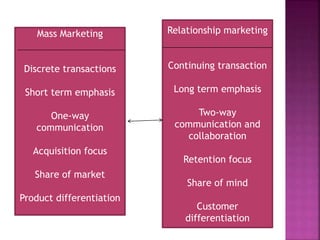
The document discusses customer relationship management (CRM). It defines CRM as a business strategy focused on identifying and building loyalty with profitable customers. CRM has evolved from functional approaches like sales automation to more strategic approaches. Relationship marketing aims to create long-term partnerships rather than isolated transactions. CRM provides benefits like increased revenue, customer retention, and knowledge. It requires organizational support and changes business processes to focus on customer needs.