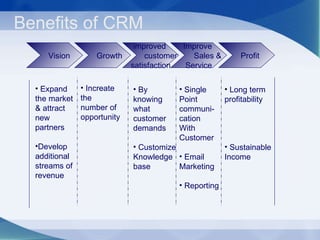
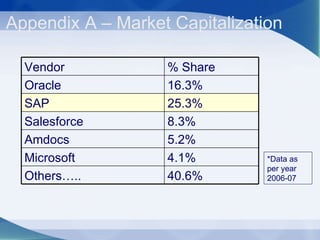
The document discusses customer relationship management (CRM). It defines CRM and explains why companies need it. It describes the main goals of CRM as gaining insights into customer behavior and values to improve customer service, marketing/sales processes, and increase customer revenue. It also outlines different types of CRM, such as operational, analytical, consumer, and collaborative CRM. Finally, it covers CRM implementation options, benefits, costs, and provides definitions of CRM from industry experts.