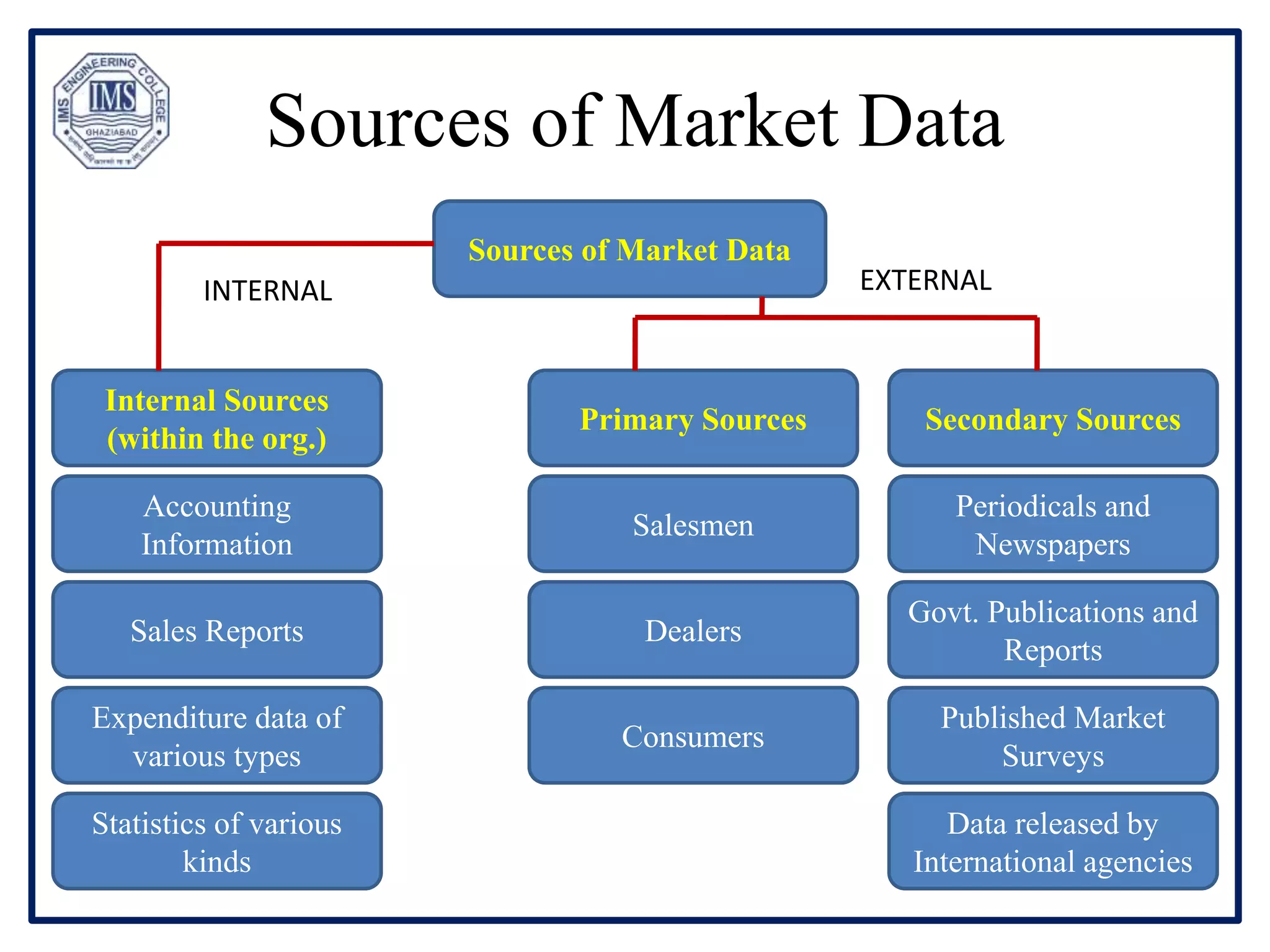
The document provides an overview of marketing analytics, emphasizing its importance in measuring, analyzing data, and making informed marketing decisions to maximize ROI. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of marketing analytics, highlighting the need for accurate data interpretation and target market identification. Additionally, it outlines market sizing methods, namely top-down and bottom-up approaches, to assess market potential effectively.