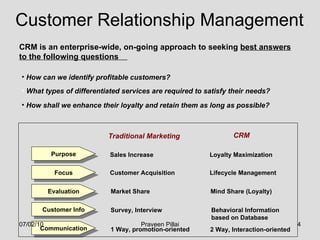
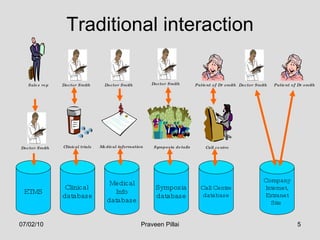
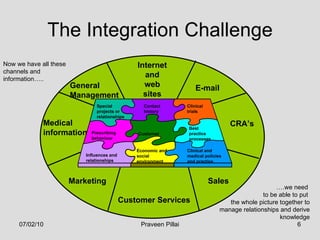
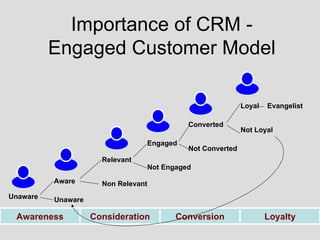
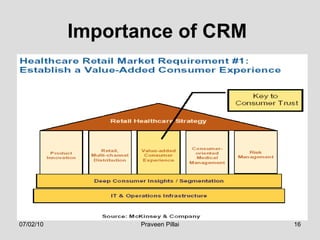
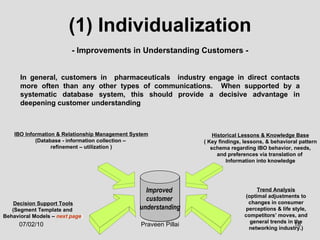
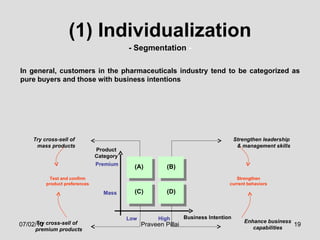
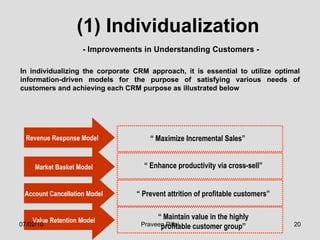
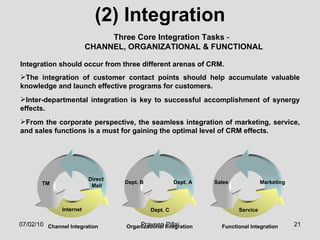
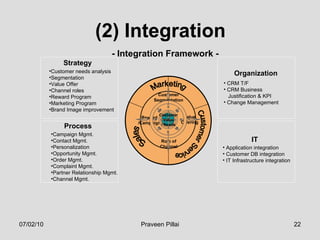
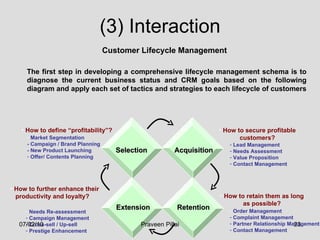
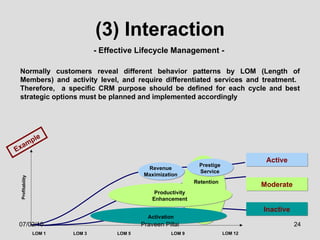
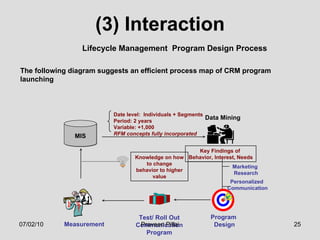
The document discusses customer relationship management (CRM) in the pharmaceutical industry. It defines CRM and explains its importance. It discusses key aspects of CRM including identifying customer needs, developing long-term relationships through trust and value, integrating customer data and channels, and the roles of salespeople in relationship building and management. The document also outlines factors driving the need for CRM and strategies to individualize CRM through customer segmentation, understanding, and integration across departments.