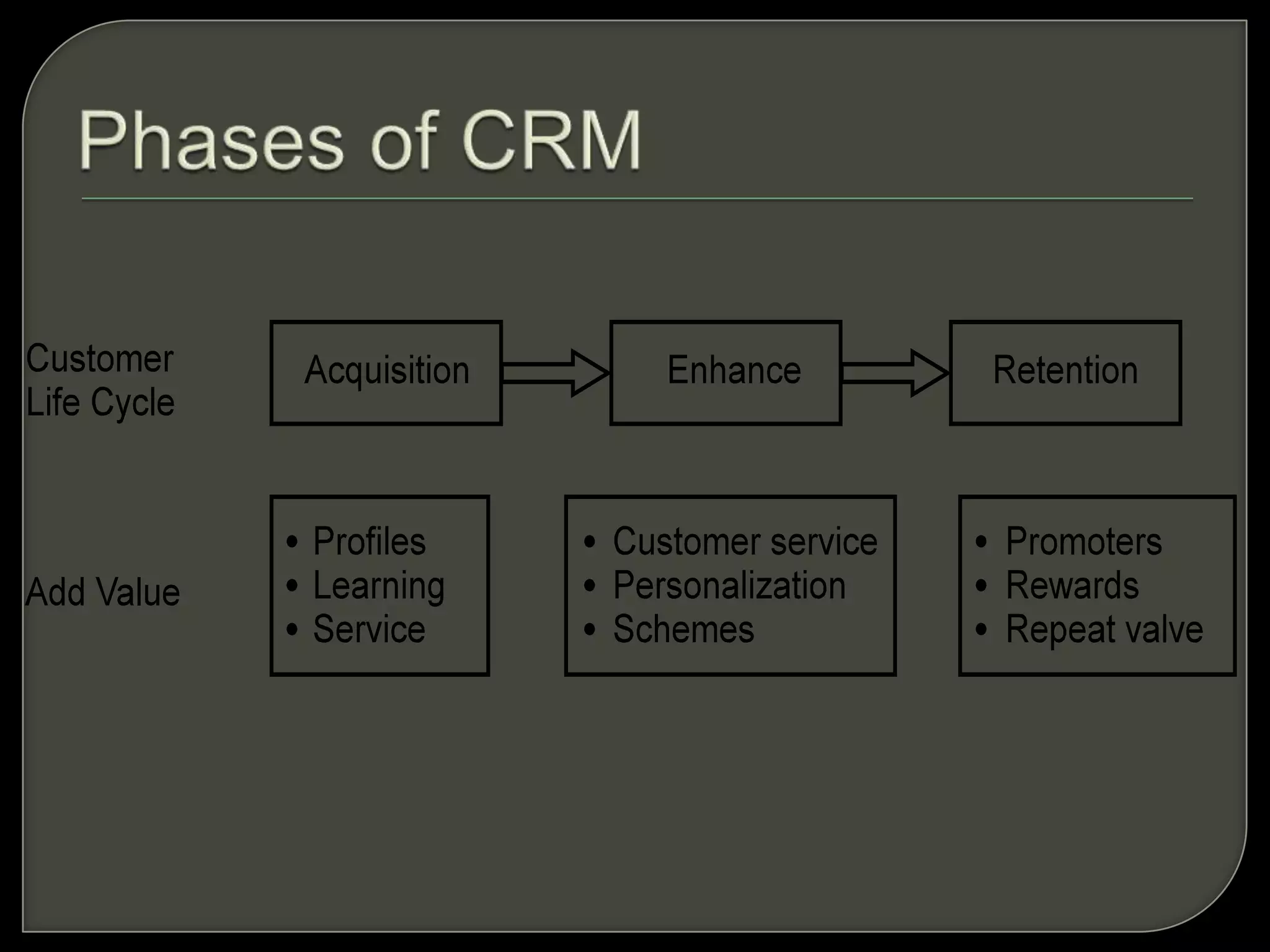
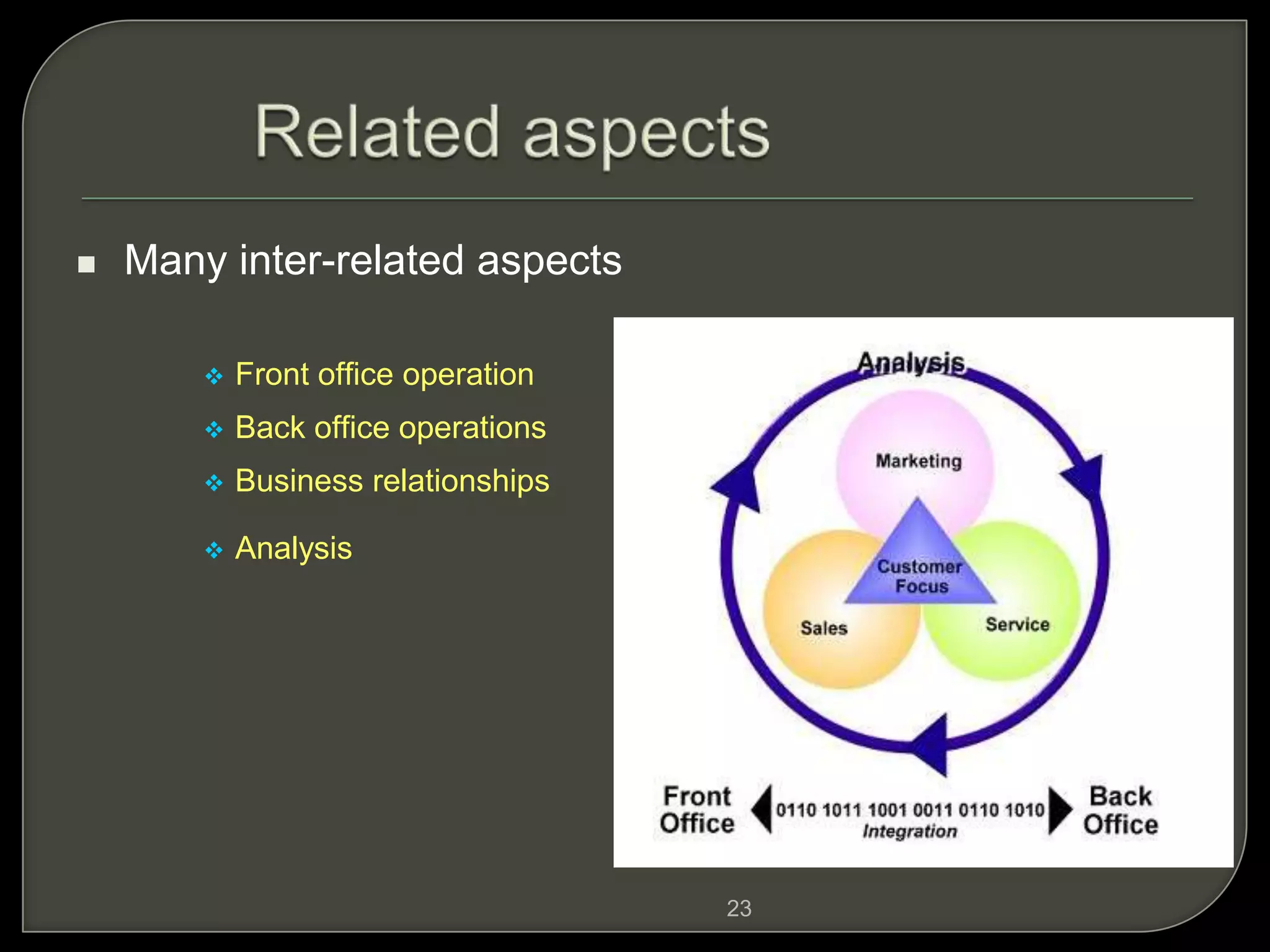
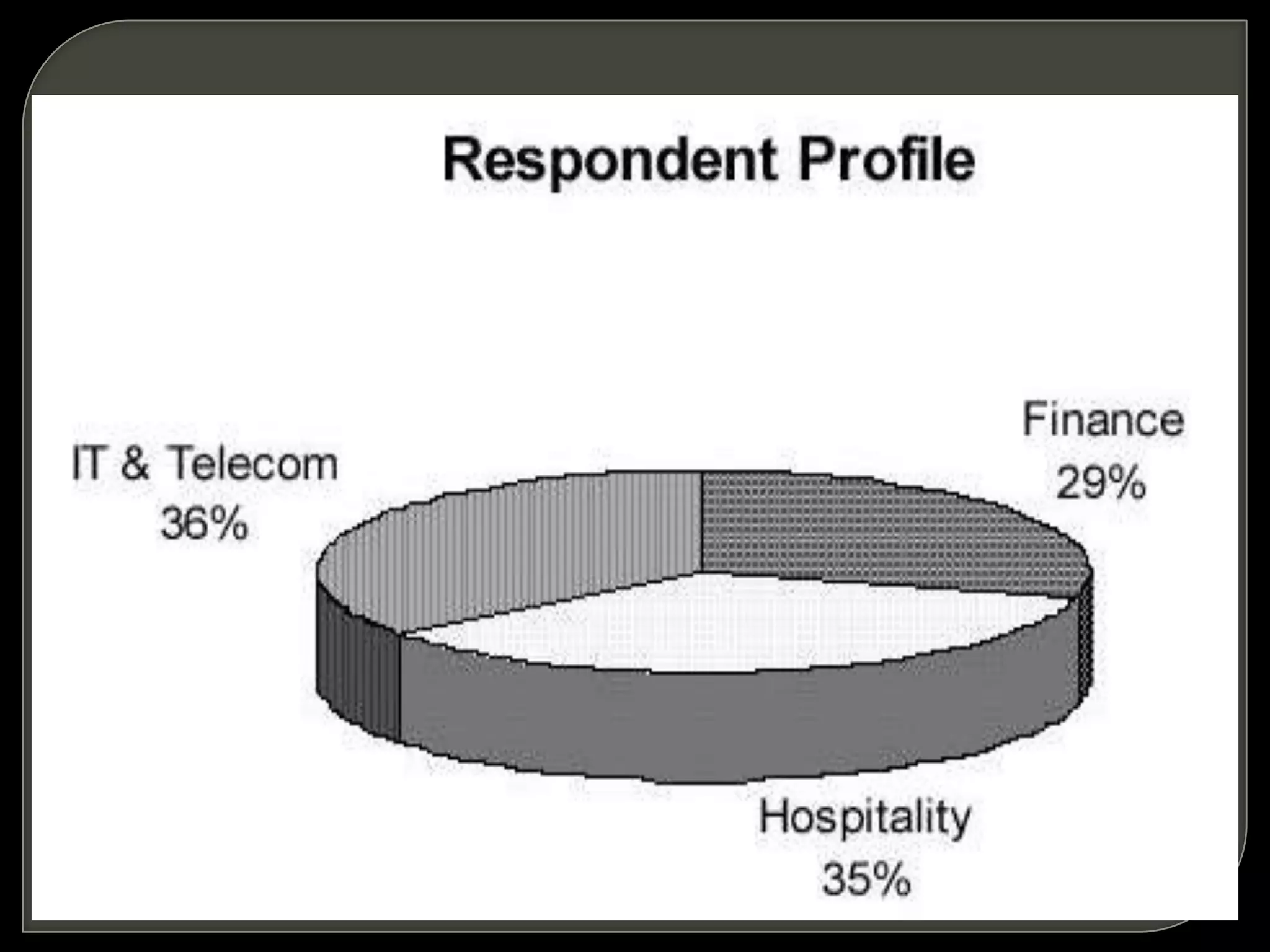
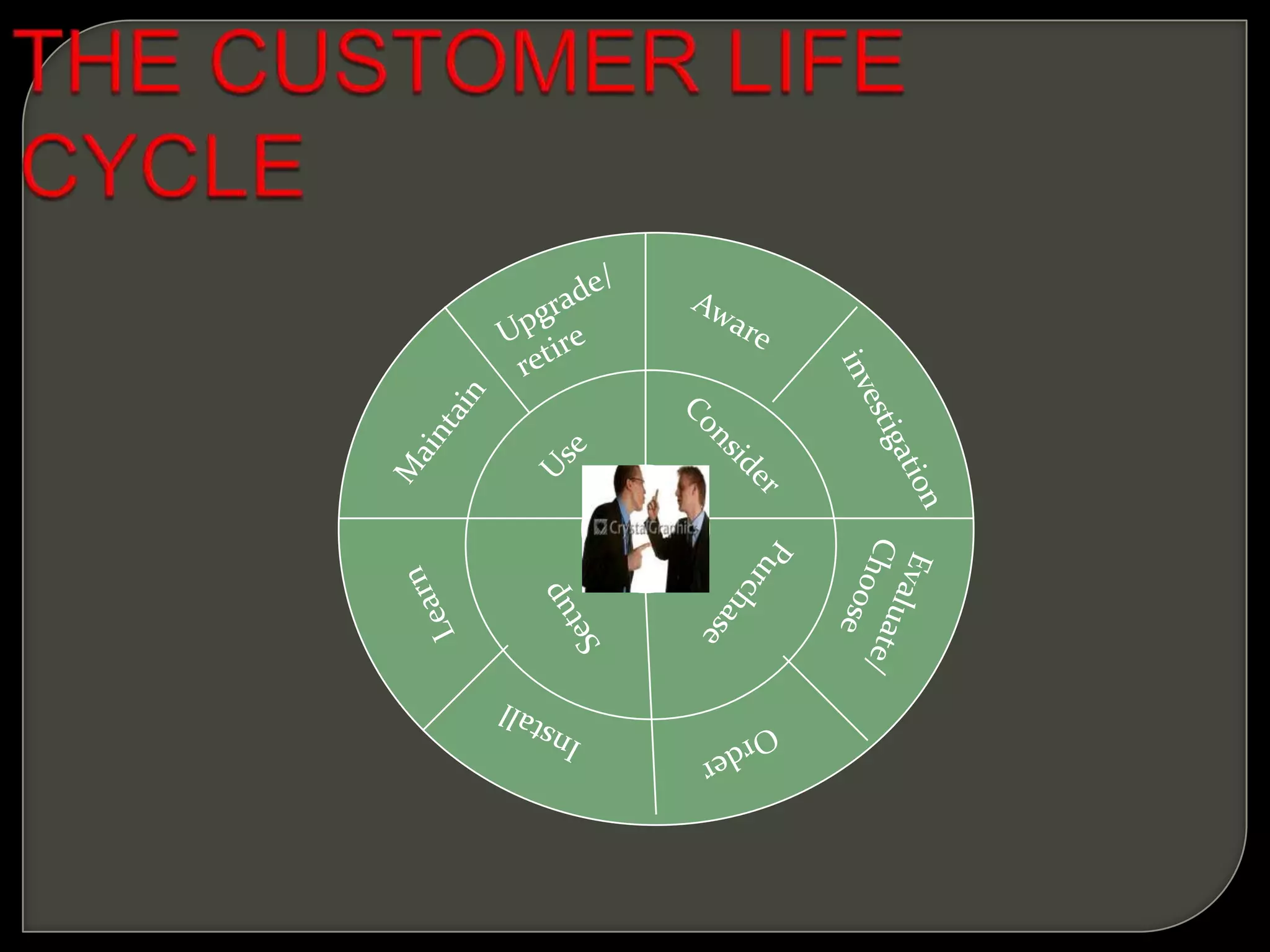
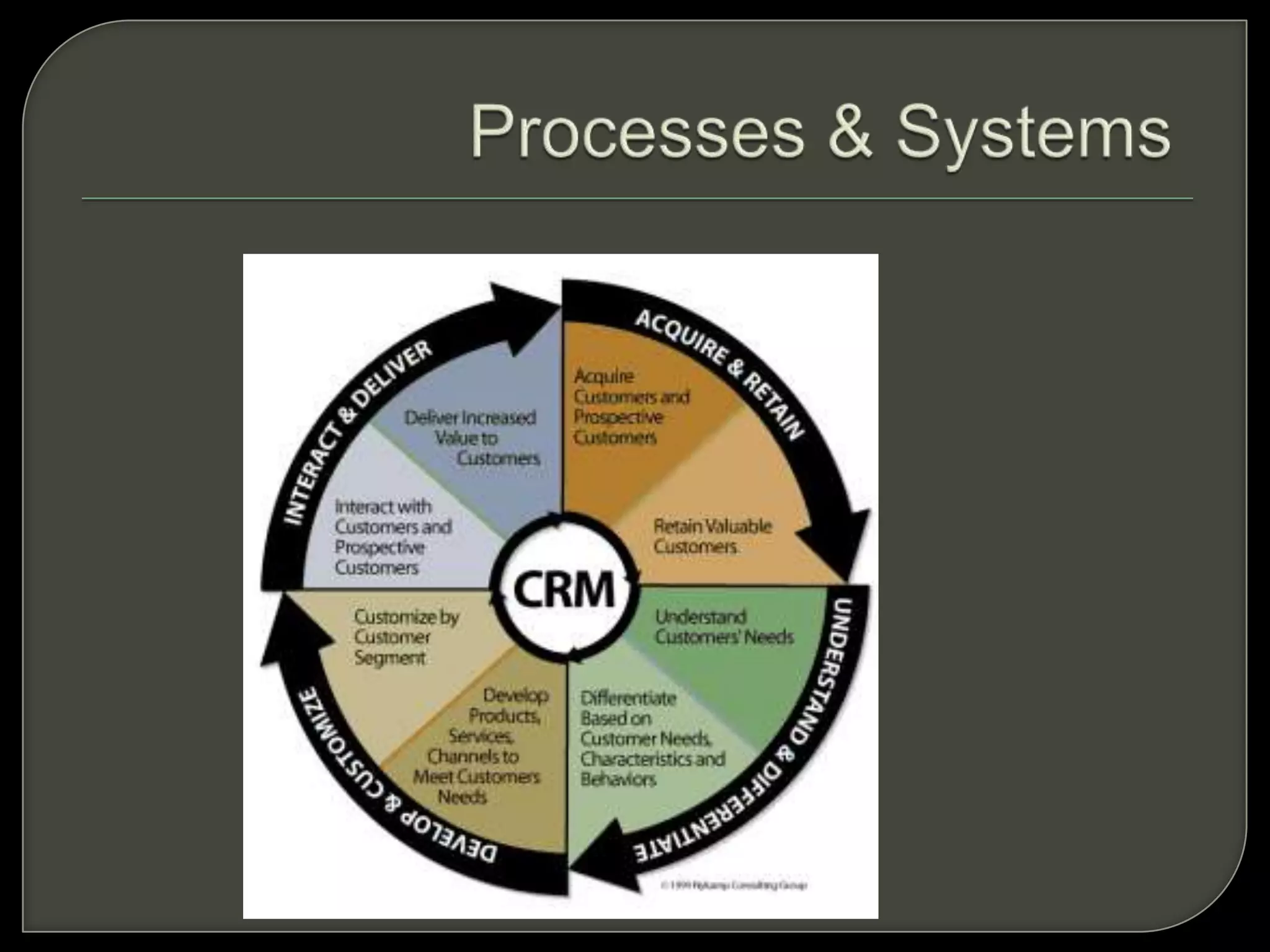
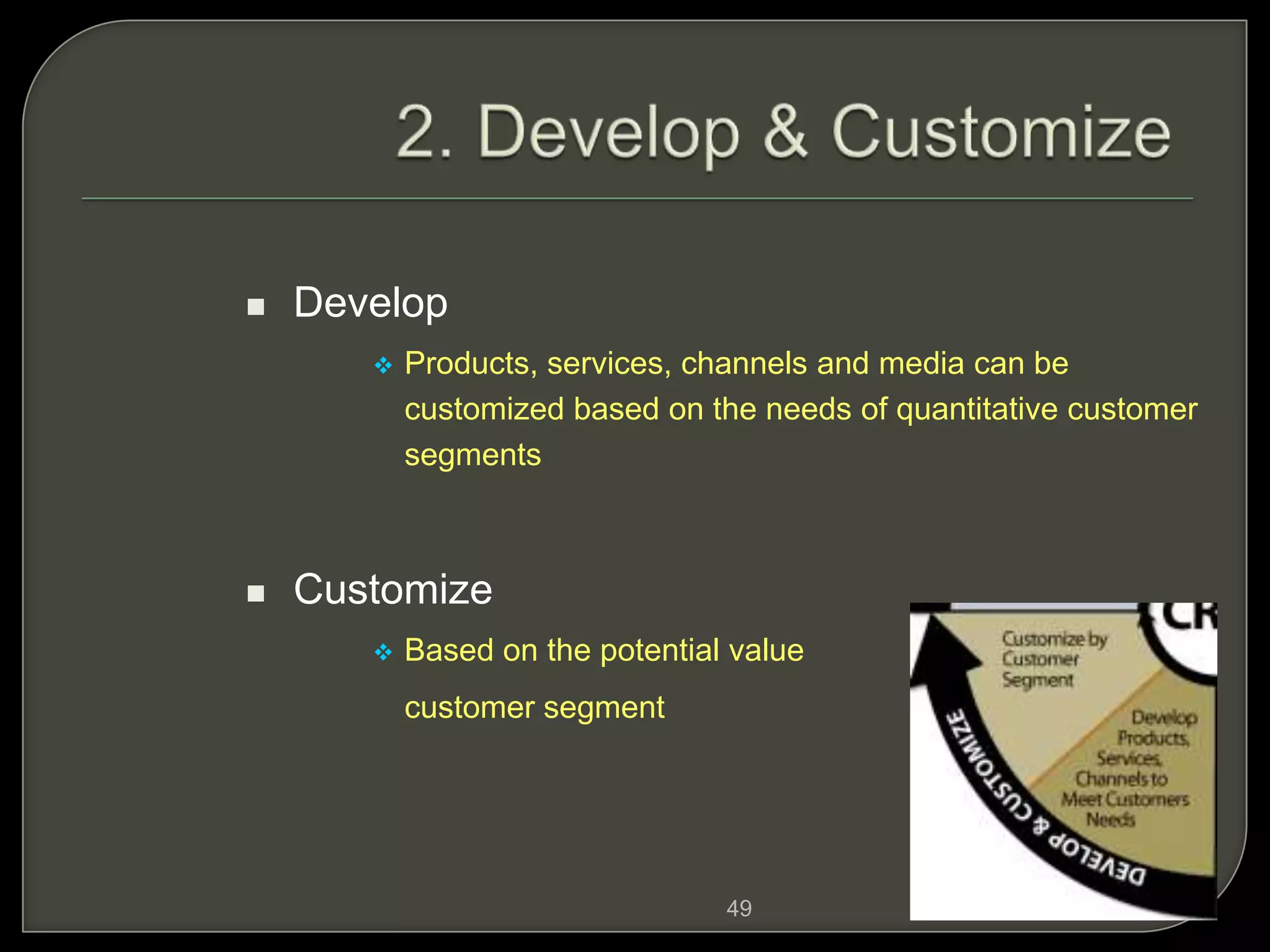
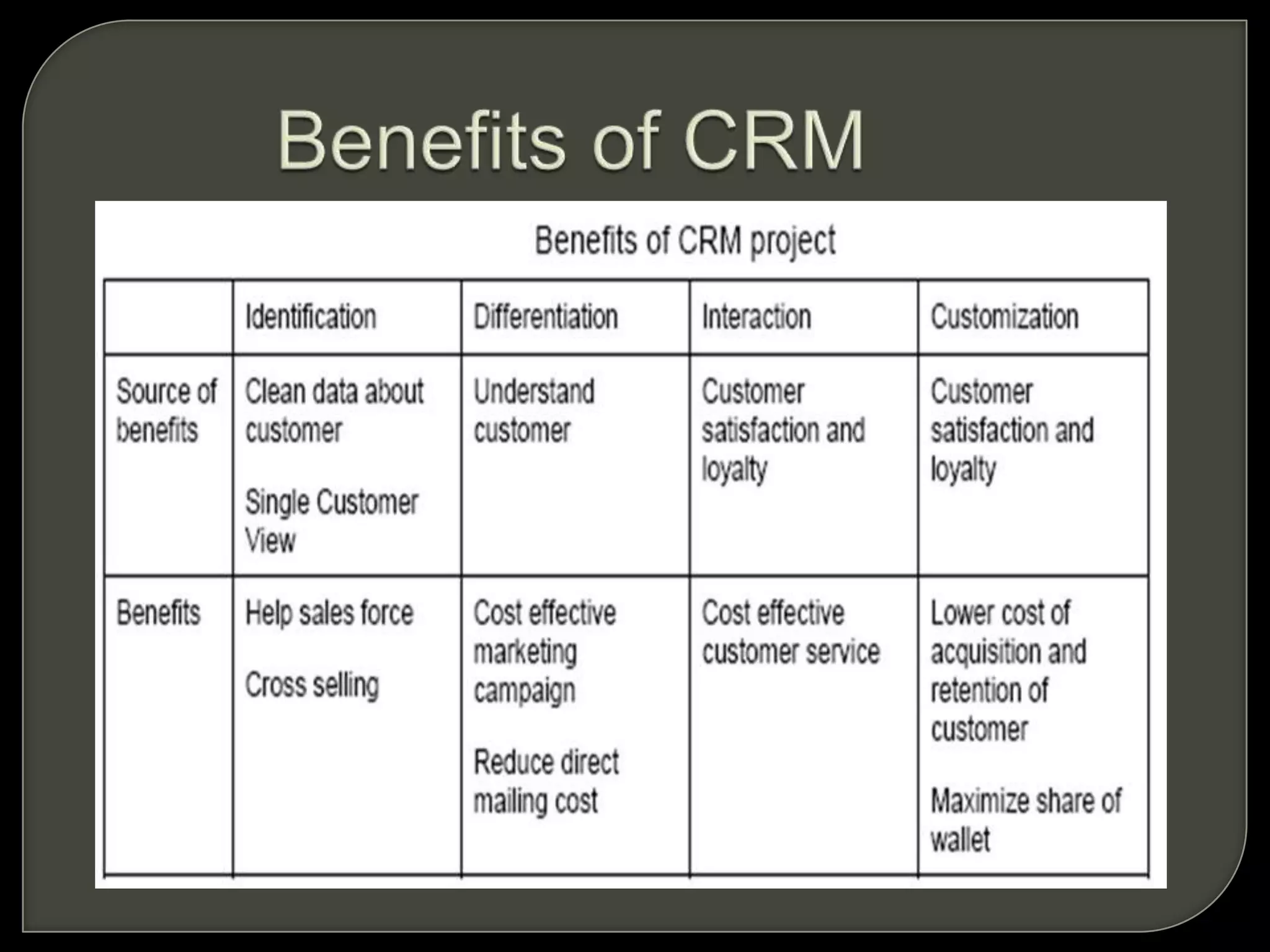
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) involves processes and software to manage interactions with customers, aiming to enhance relationships and retention. It encompasses various methodologies, including operational, analytical, and collaborative CRM, to analyze customer data and improve services. The ultimate goal is to optimize customer satisfaction, loyalty, and profitability across the customer lifecycle while addressing privacy concerns.