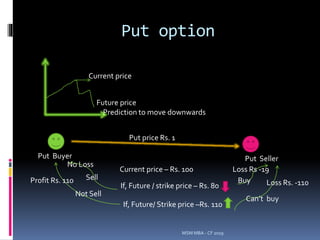
This document discusses corporate financing decisions and cash flow issues for firms. It covers topics like cash insolvency, cash inadequacy, determining debt capacity, and using simulation and option pricing models to evaluate financing choices. Key factors that influence the valuation of call options are discussed, including the current stock price, exercise price, risk-free rate, time to expiration, and price volatility. The Black-Scholes option pricing model is also introduced as a way to calculate the theoretical value of an option.





























![d1 = Ln [S0/E] + [ r+0.5(σ2 )] × t
σ √t
d2 = d1 - σ √t
Here “σ ” – Measure ofVolatility (standard
deviation)
V(p) =V(c) + [E e- rt] ] – So
MSM MBA - CF 2019](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfunit4financingdecision-190822140856/85/Corporate-Finance-unit-4-Financing-decision-32-320.jpg)



![Step 1: Determine d1
d1 = Ln [S0/E] + [ r+0.5(σ2 )] × t
σ √t
d2 = d1 - σ √t
= Ln [415/400] + [0.05+(0.5 * (0.22)2 )] 0.25
0.22 * √0.25
= 0.03922* 1.04 + 0.01855 /0.11
= 0.5252
= 0.53
MSM MBA - CF 2019](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfunit4financingdecision-190822140856/85/Corporate-Finance-unit-4-Financing-decision-37-320.jpg)




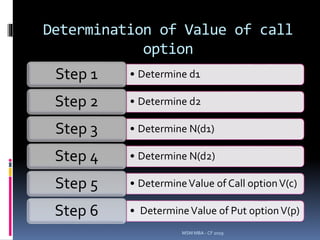
![Step 6: Determination of Value
of call option
Using call – put parity theory, value of put
option is,
V(p) =V(c) + [E e- rt] ] – So
= 28.81 + (400 * 0.9905) – 415
V(p) = 9.83
MSM MBA - CF 2019](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfunit4financingdecision-190822140856/85/Corporate-Finance-unit-4-Financing-decision-42-320.jpg)



![ PV of option value = 7/1.05 = Rs.6.67
Value of option = Cu P + Cd (1-P)
R
Where,
Cu = Call option Up
Cd = Call option down
P = Probability
R = Rate of return
Calculation of Probability
P = [R-d]/[U-d] = p(U)
MSM MBA - CF 2019](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfunit4financingdecision-190822140856/85/Corporate-Finance-unit-4-Financing-decision-47-320.jpg)
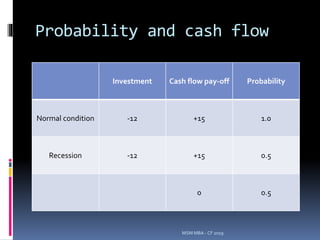
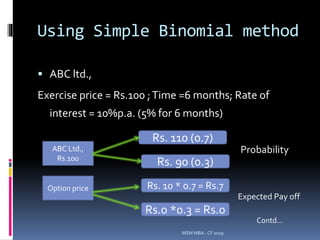
![Example problem
Exercise price = Rs.100 ;Time = 6 months; So Current
price = Rs.100 ; U=10% ; d= 10%; R=10% p.a. (6
months =0.5)
Step 1: (Probability of up and down)
P(u) = [1.05-0.90]-[1.10-0.90] = 0.75
P(d) = 1 – P(u) = 1 – 0.75 = 0.25
Value of option = Cu P + Cd (1-P)
R
= (10 * 0.75)+(0*0.25)/1.05 = 7.5/1.05 = Rs.7.14
MSM MBA - CF 2019](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfunit4financingdecision-190822140856/85/Corporate-Finance-unit-4-Financing-decision-48-320.jpg)





