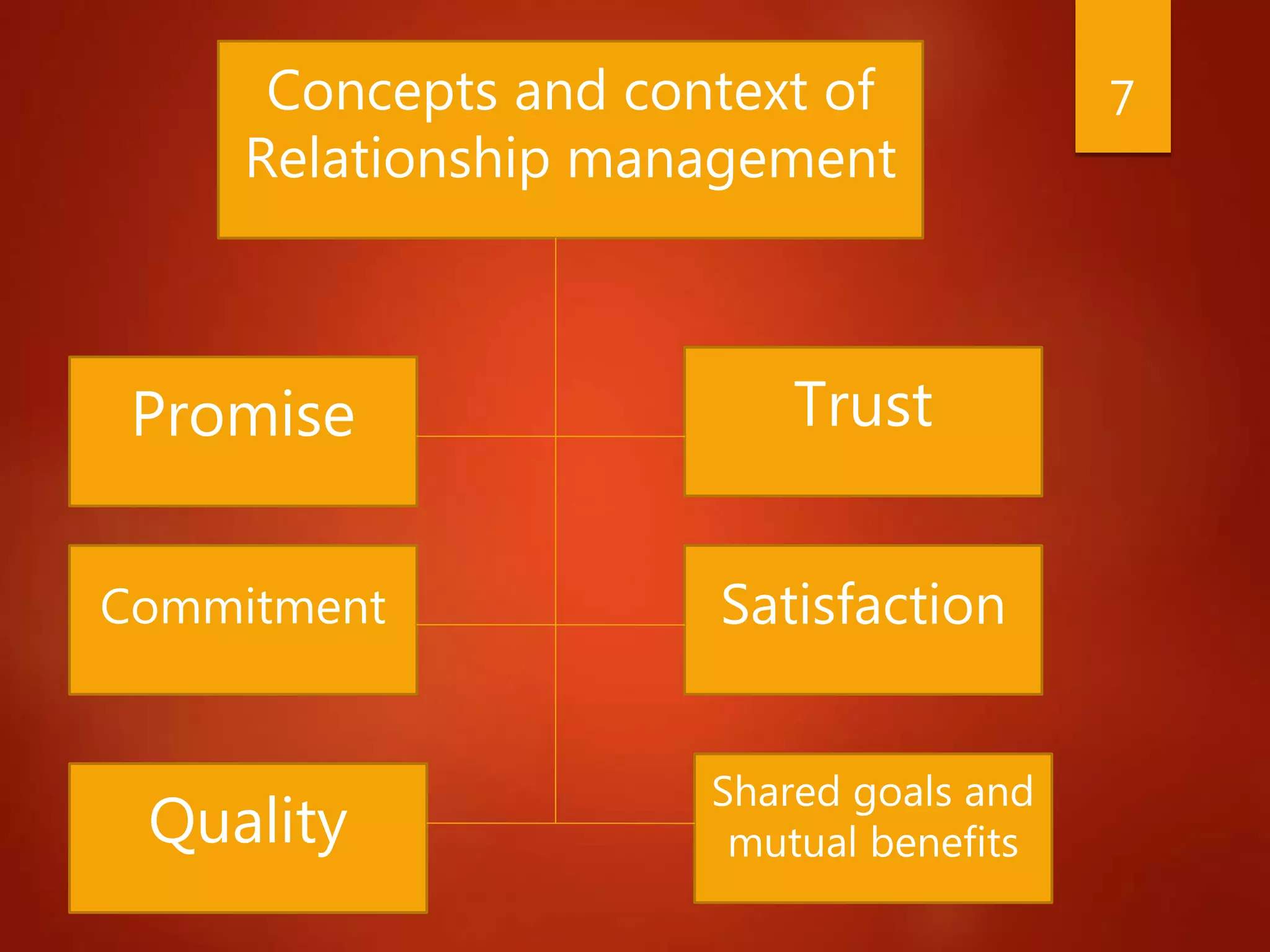
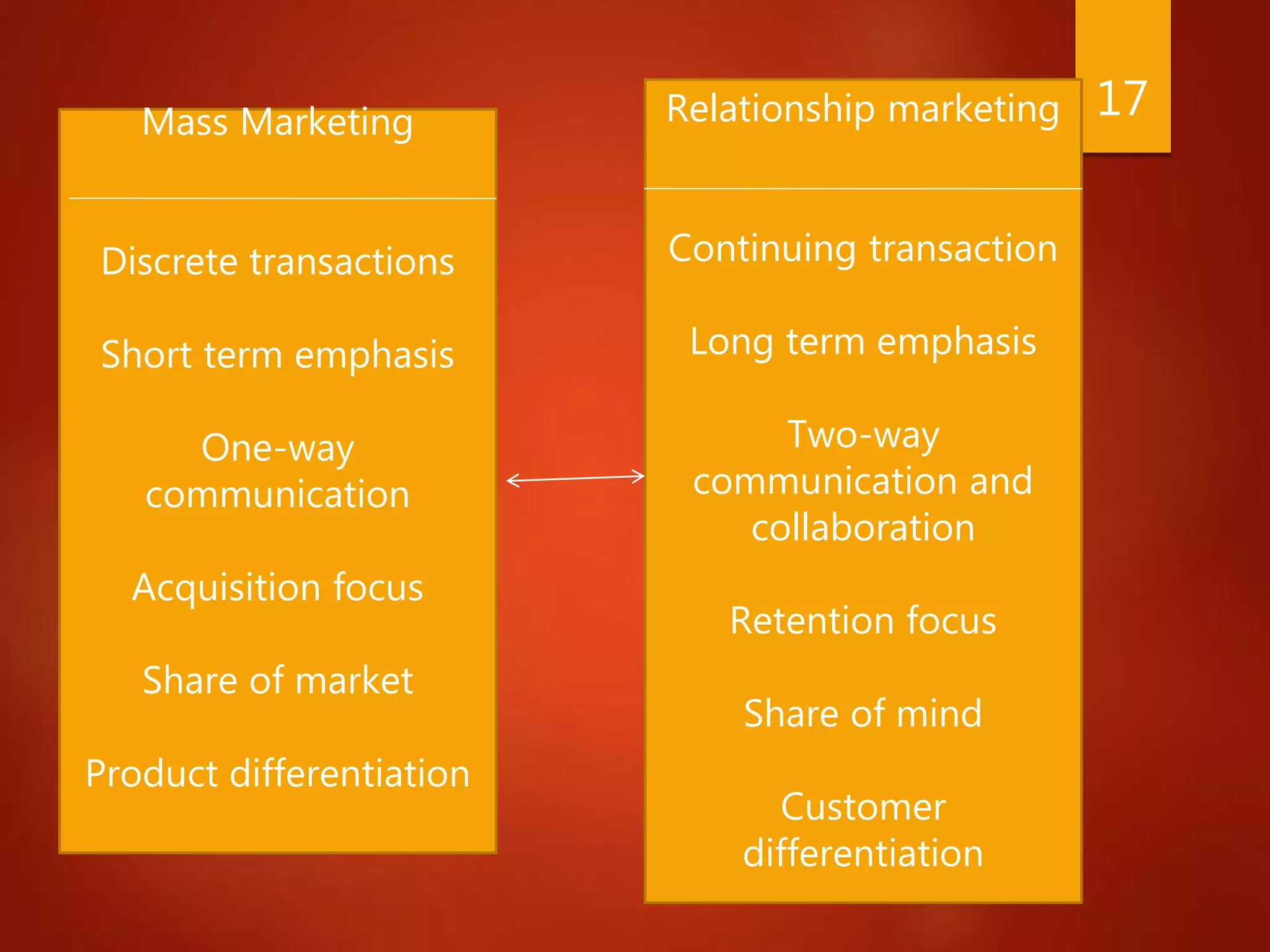
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Customer Relationship Management (CRM), defining it as a business strategy focused on building loyalty with profitable customers. It outlines the evolution of CRM from functional approaches to strategic ones, discusses various types of CRM, and emphasizes the importance of relationship marketing over transactional marketing. Additionally, it highlights the significance of CRM for stakeholders and its potential benefits, limitations, and misconceptions.