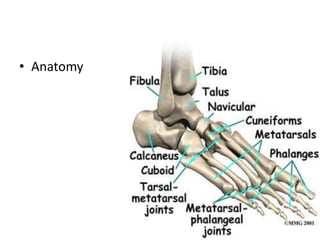
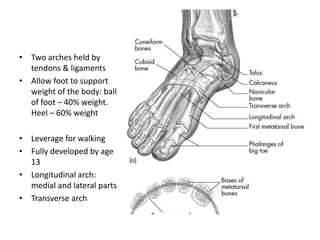
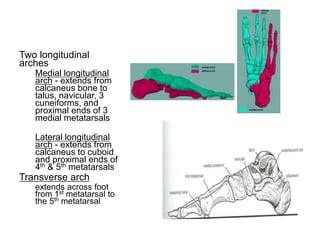
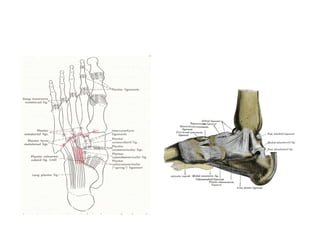
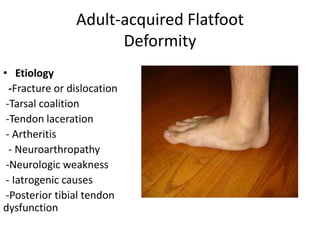
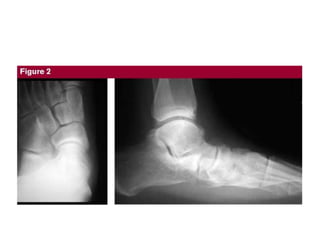
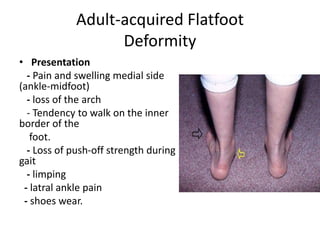
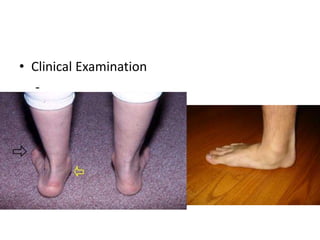
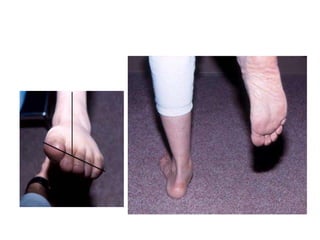
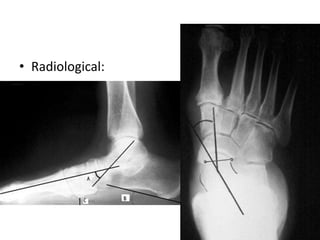
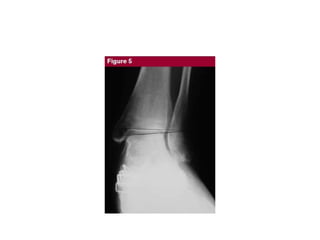
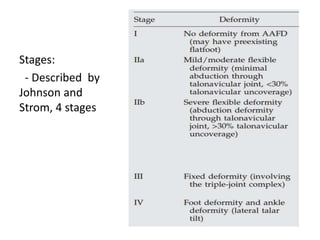
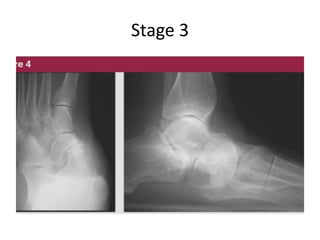
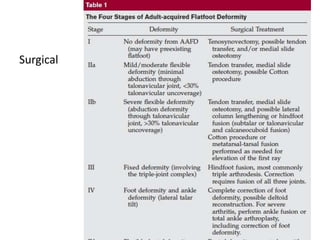
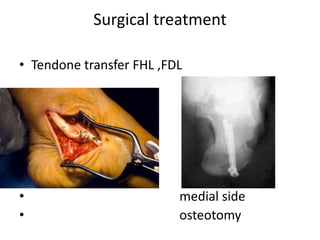
This document discusses adult-acquired flatfoot deformity, including its anatomy, causes, presentation, diagnosis, and treatment options. It notes that the deformity encompasses a wide range of conditions that vary in location and severity. The posterior tibial tendon is a major dynamic stabilizer of the arch, and its dysfunction or failure is a common cause of the deformity. Treatment progresses from nonsurgical options like orthotics to surgical procedures like tendon transfers or osteotomies when symptoms increase or the deformity worsens. The goal of any treatment is to relieve pain while maintaining foot flexibility and proper alignment.