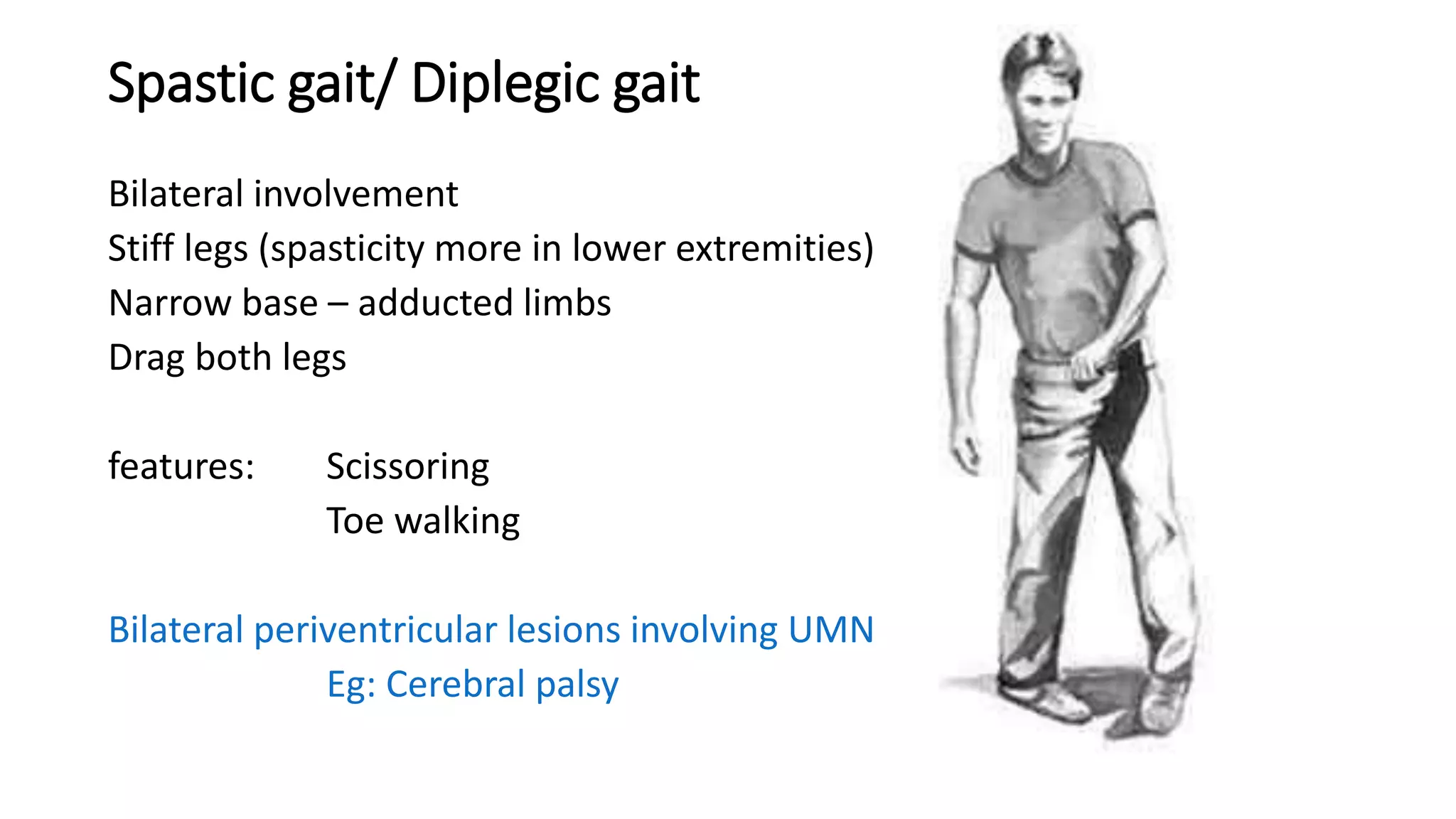
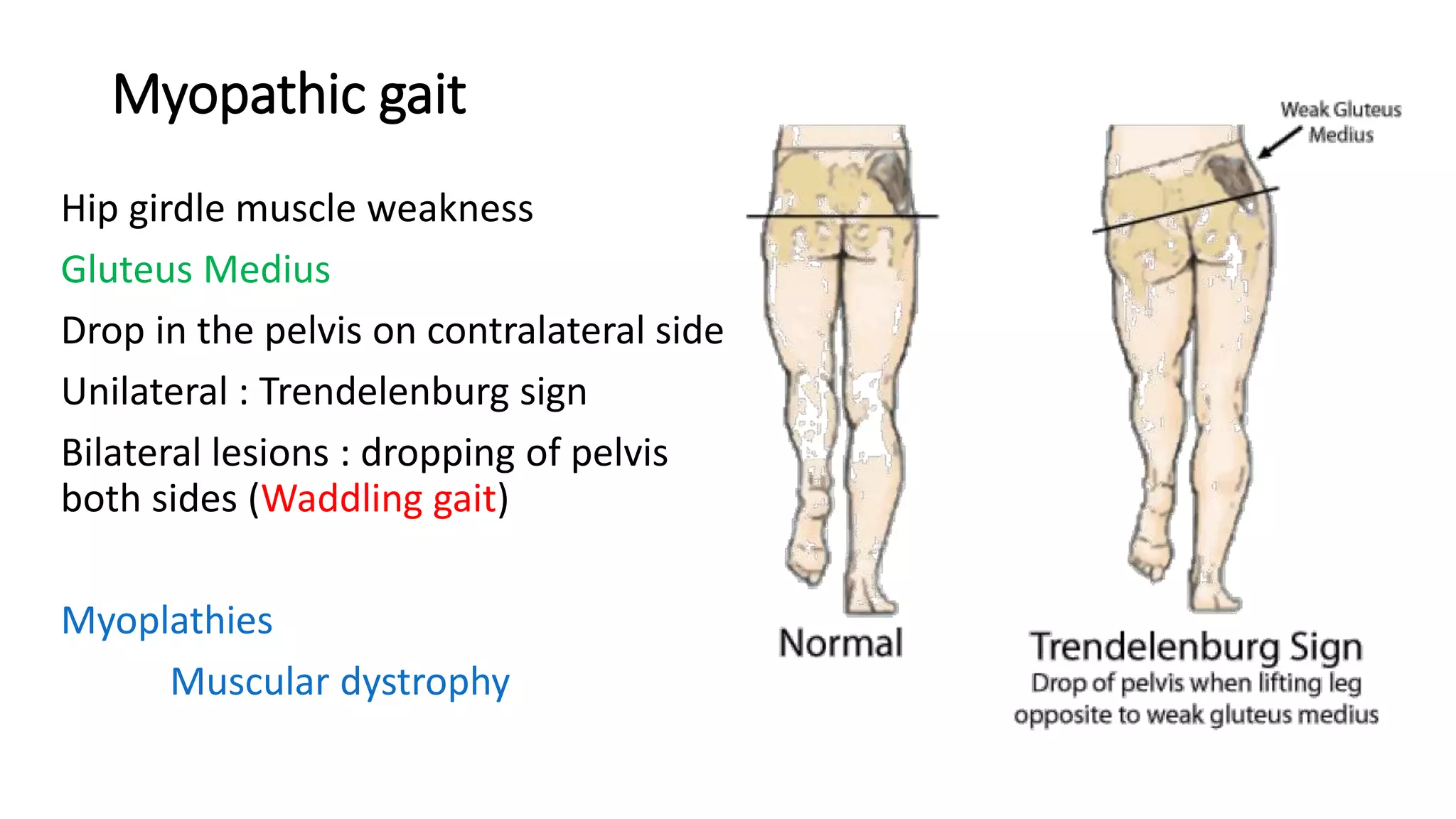
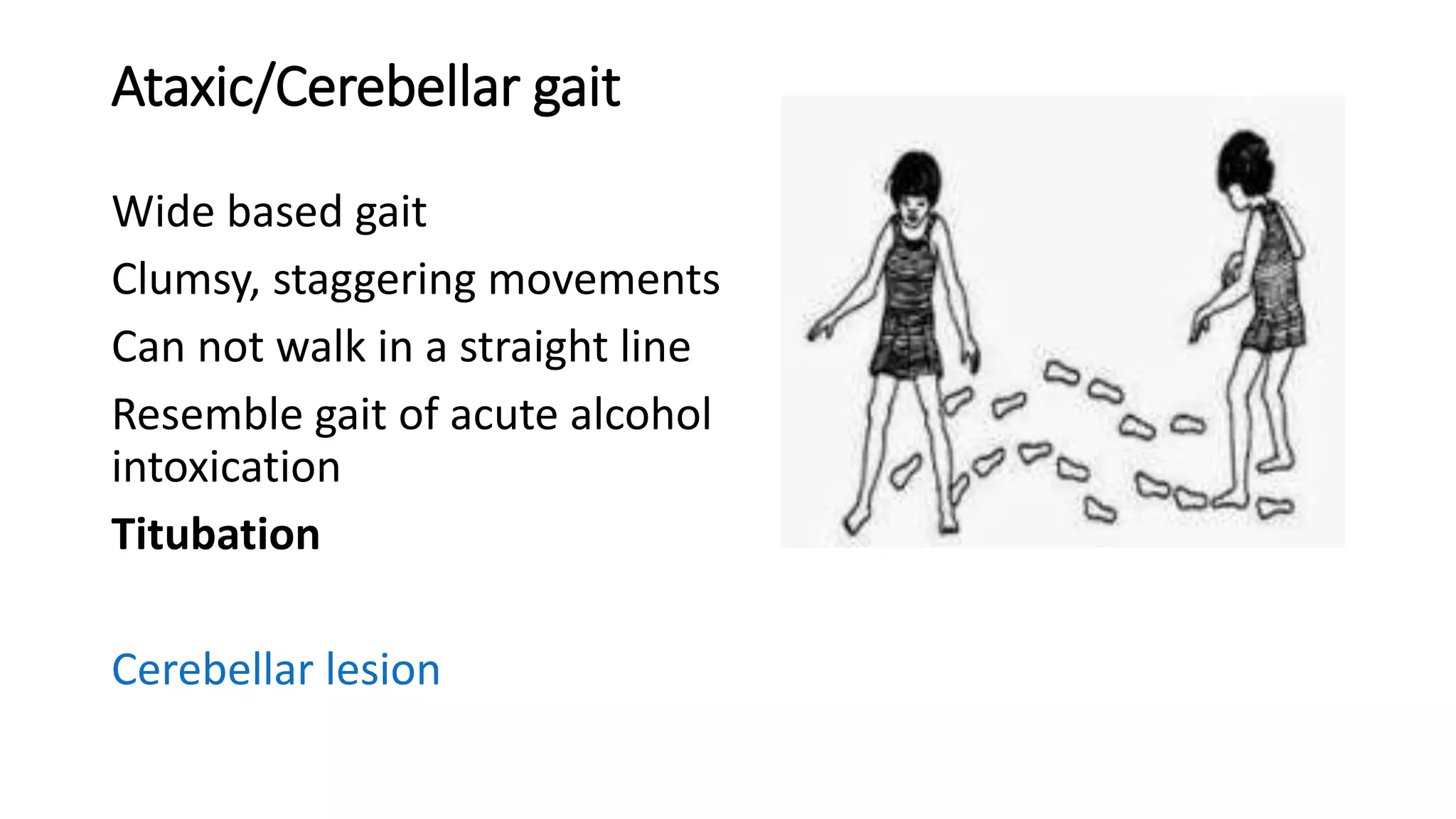
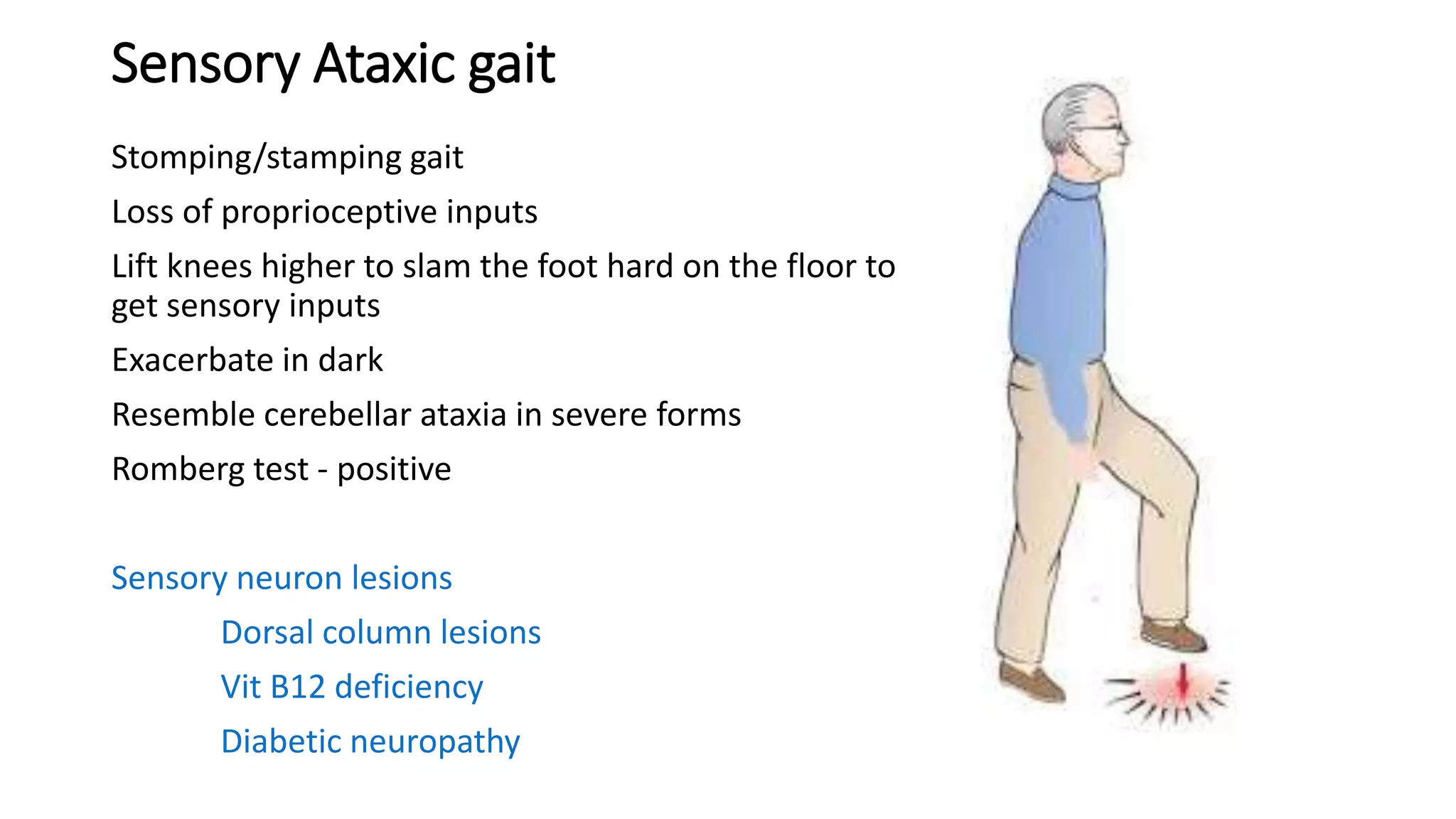
This document describes different types of gait abnormalities and their physiological bases. It outlines eight types of neurological gaits - hemiplegic, spastic, neuropathic, myopathic, ataxic, choreiform, parkinsonian, and sensory ataxic - and discusses their characteristic features and underlying neurological conditions. It also mentions two types of non-neurological gaits: antalgic gait associated with pain and psychogenic gait involving voluntary movements. The document provides details on clinical presentations and pathophysiology for each gait abnormality.