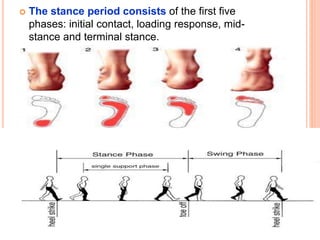
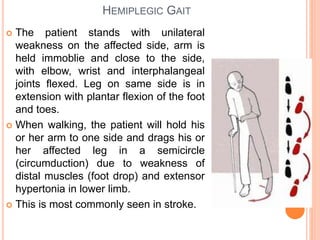
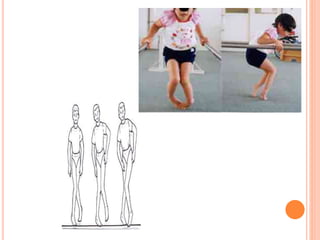
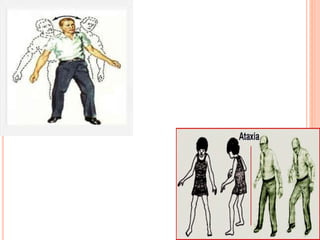
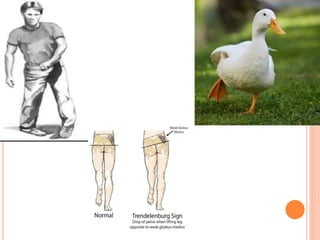
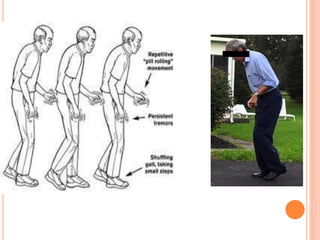
Gait refers to the manner of walking or moving on foot. There are four essential criteria for normal gait: equilibrium, locomotion, musculoskeletal integrity, and neurological control. The gait cycle describes the sequence of foot movements from initial heel contact to the next contact of the same heel. Abnormal gaits can be caused by pain, weakness, tightness, loss of balance, or range of motion issues. Specific abnormal gaits include hemiplegic, diplegic, neuropathic, sensory, myopathic, choreiform, parkinsonian, and age-related gaits. Doctors evaluate gait through physical exam, performance tests, and imaging to diagnose underlying causes and prognosis depends on the medical condition.