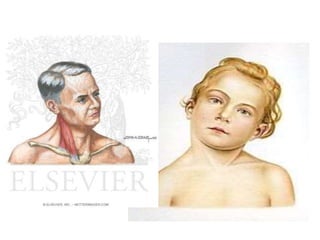
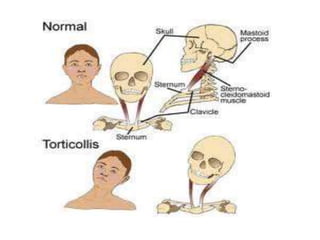
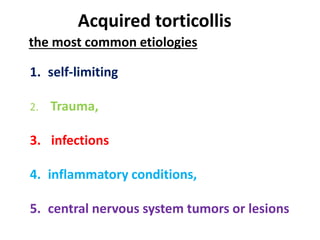
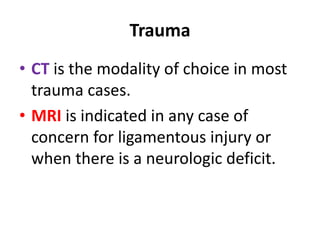
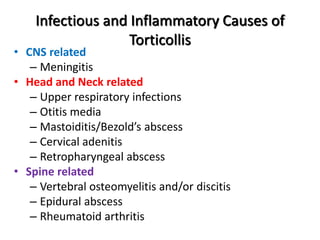
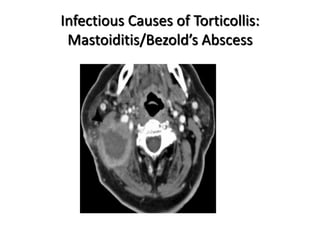
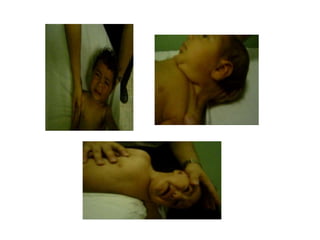
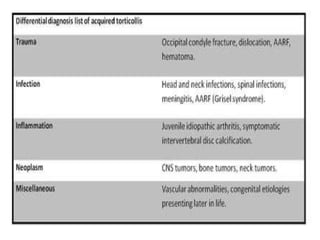
Torticollis is a twisting of the neck that can have many causes. In newborns, it is often due to issues during birth or position in the uterus. Older children may experience torticollis after neck injuries or infections. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include stretching, medication, bracing, or surgery. Imaging like ultrasound, CT, or MRI can help identify conditions like muscle issues, infections, fractures, or tumors that are causing the neck twisting.