- The document contains examples of calculating head loss and pressure differences in pipes due to changes in diameter or flow rate.
- In example 1, the slope of a pipe needed to be calculated to maintain equilibrium based on a given flow rate, diameter, and friction coefficient.
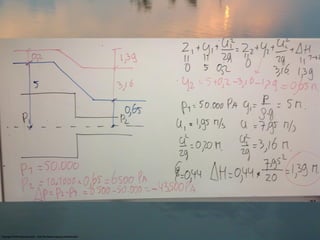
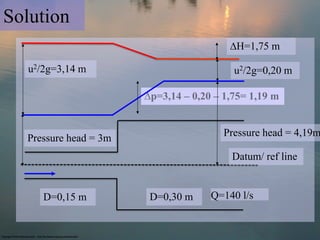
- Example 2 involves calculating the head loss and pressure difference across a sudden enlargement in pipe diameter.
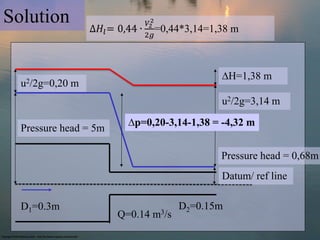
- Example 3 is similar but calculates values for a sudden contraction in pipe diameter.
![Exercise 1 calculation slope pipe
• V = 1 m/s
• D= 1 m , 50% filled
• λ = 0,022 [1]
• Equilibrium
• Calculate the bed slope of the pipe](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cu06997lecture6exercises-130322051352-phpapp02/85/Cu06997-lecture-6_exercises-1-320.jpg)


![2 2
Darcy-Weisbach L u u
ΔΗ f
4 R 2g 2g
Total Head
L
f
Pressure Head
4R
• ΔH = Head loss by friction [m]
• u2/2g = Velocity head [m]
• L = Length [m]
• λ = (lamda) = Friction coëfficiënt[1]
• ξ (ksie) = Loss coëfficiënt [1]
3 • R = hydraulic radius [m]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cu06997lecture6exercises-130322051352-phpapp02/85/Cu06997-lecture-6_exercises-4-320.jpg)

![Solution calculation slope pipe
• V = 1 m/s
• D= 1 m , 50% filled
• λ = 0,022 [1]
• Equilibrium
• Bed slope pipe??
L V2 100 12
ΔΗ w 0,022 0,11m
D 2g 1 20
• In 100 m the pipe has to drop 0,11 m
• Bed slope 0,11/100 = 0,0011 or 1:909](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cu06997lecture6exercises-130322051352-phpapp02/85/Cu06997-lecture-6_exercises-6-320.jpg)




![Head loss Sudden Pipe Contraction
4
2
𝑉2
∆𝐻 𝑙 = 0,44 ∙
2𝑔
∆𝐻 𝑙 = Head Loss due to sudden pipe contraction [m]
𝑉2 = Mean Fluid Velocity after sudden pipe contraction [m/s]
𝑔 = earths gravity [m/s2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cu06997lecture6exercises-130322051352-phpapp02/85/Cu06997-lecture-6_exercises-12-320.jpg)