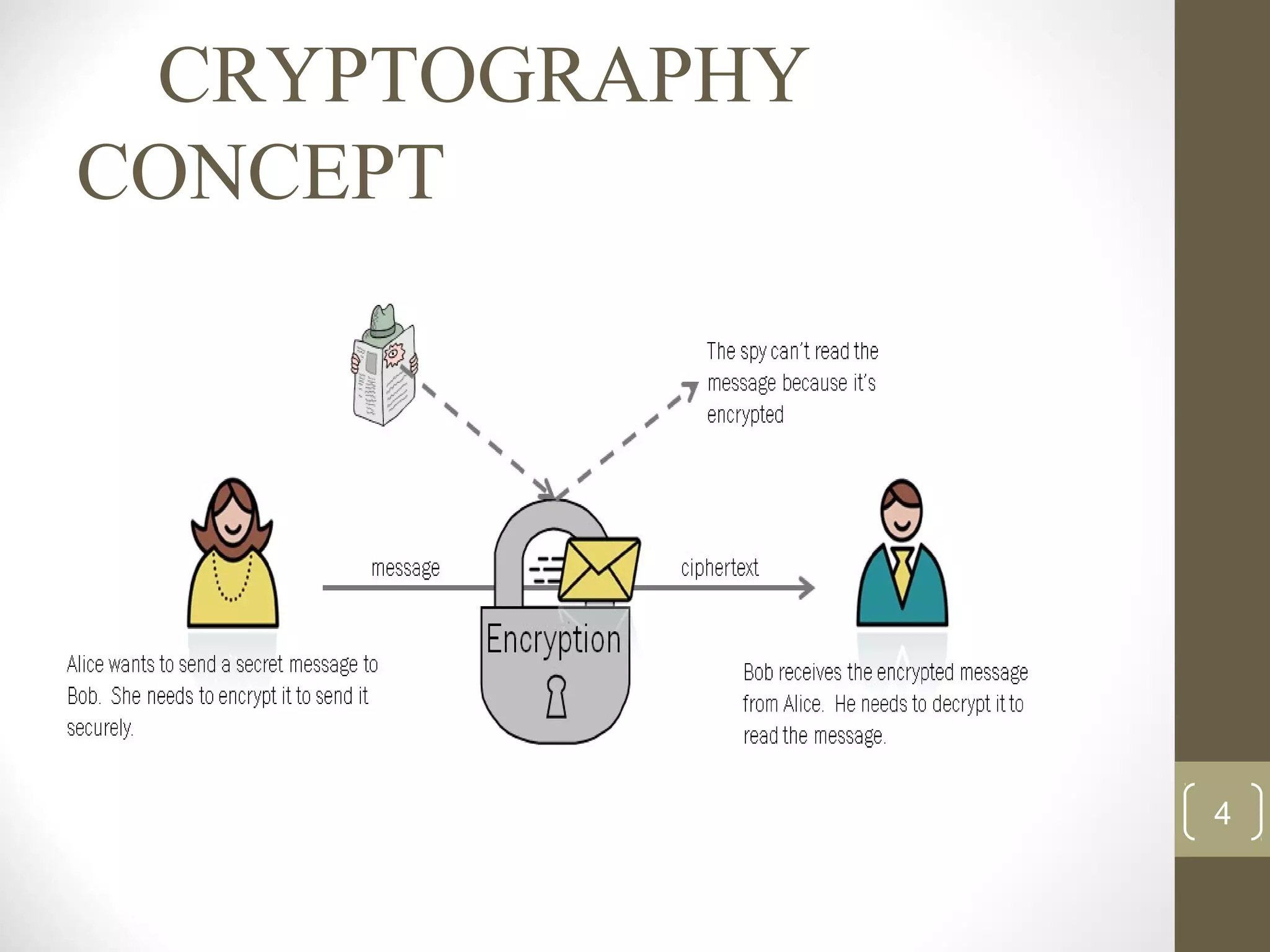
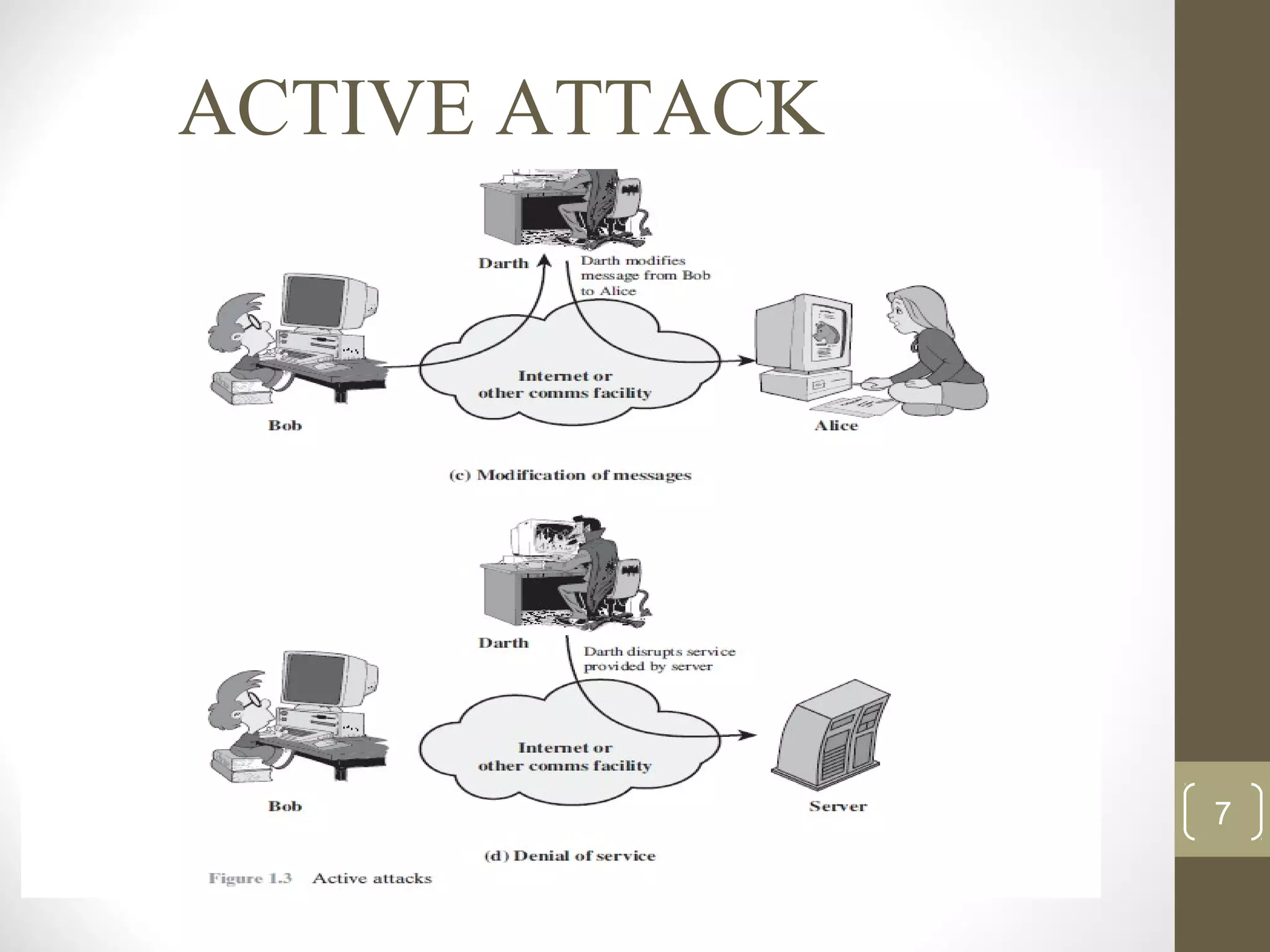
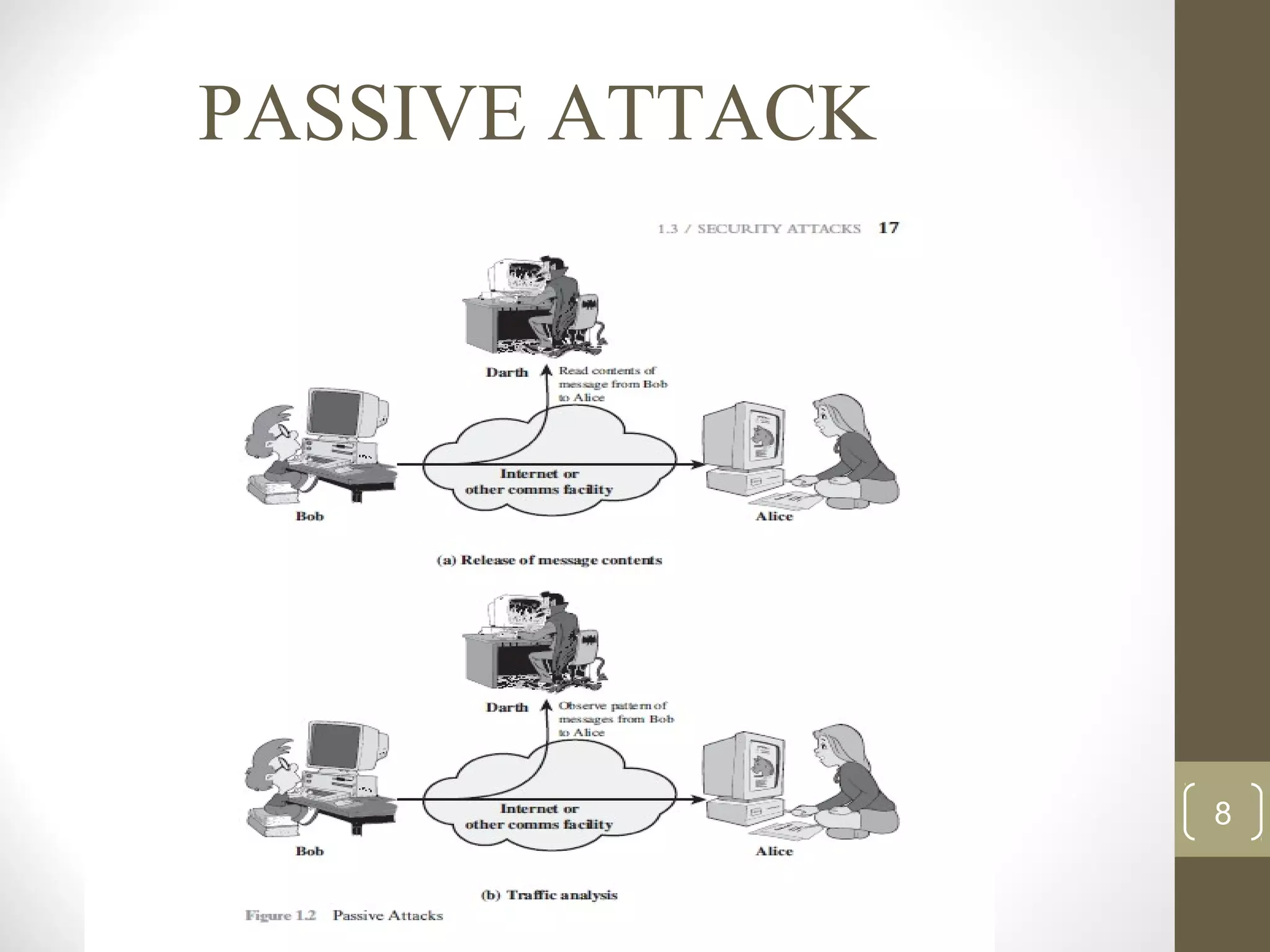
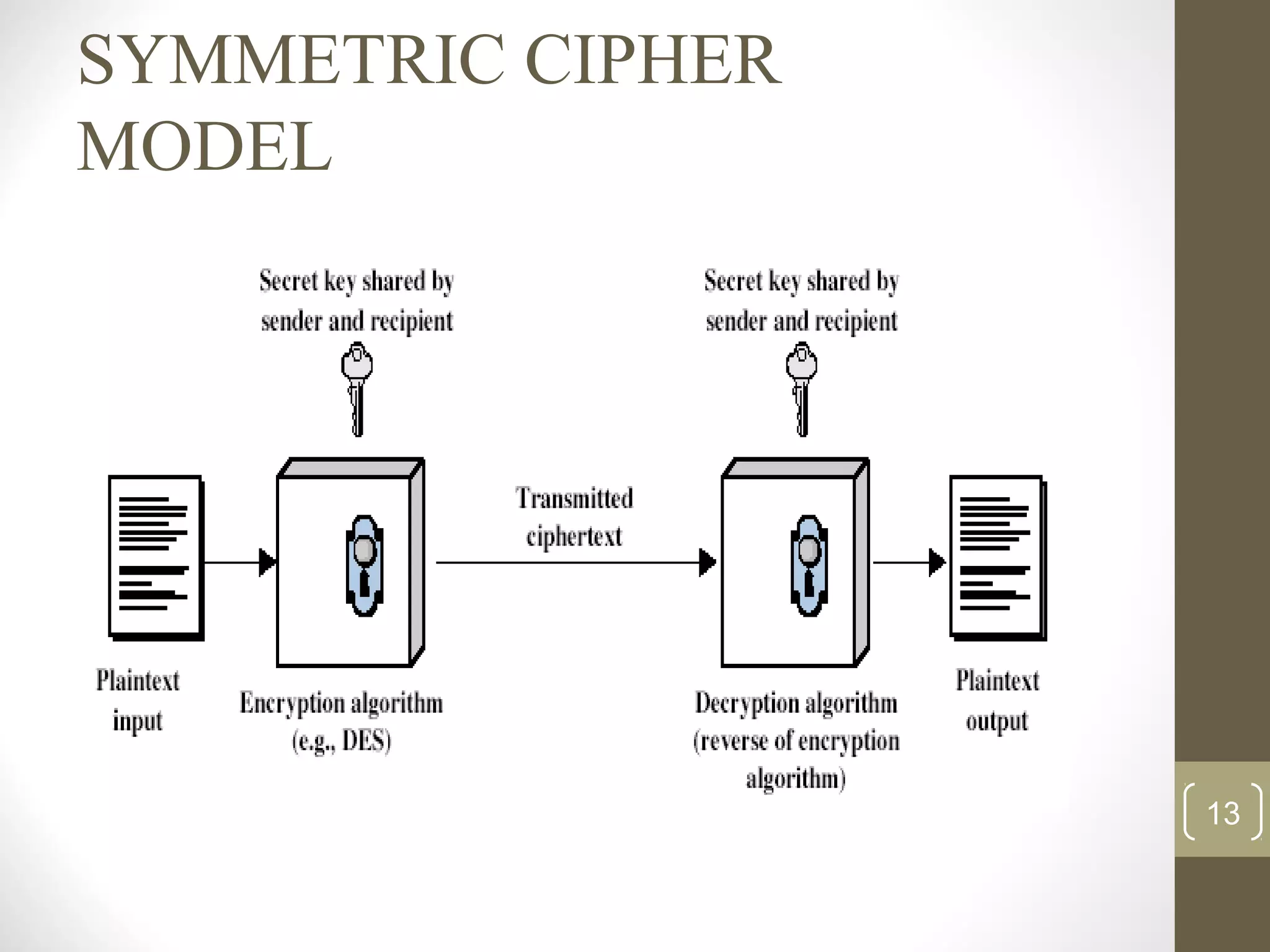
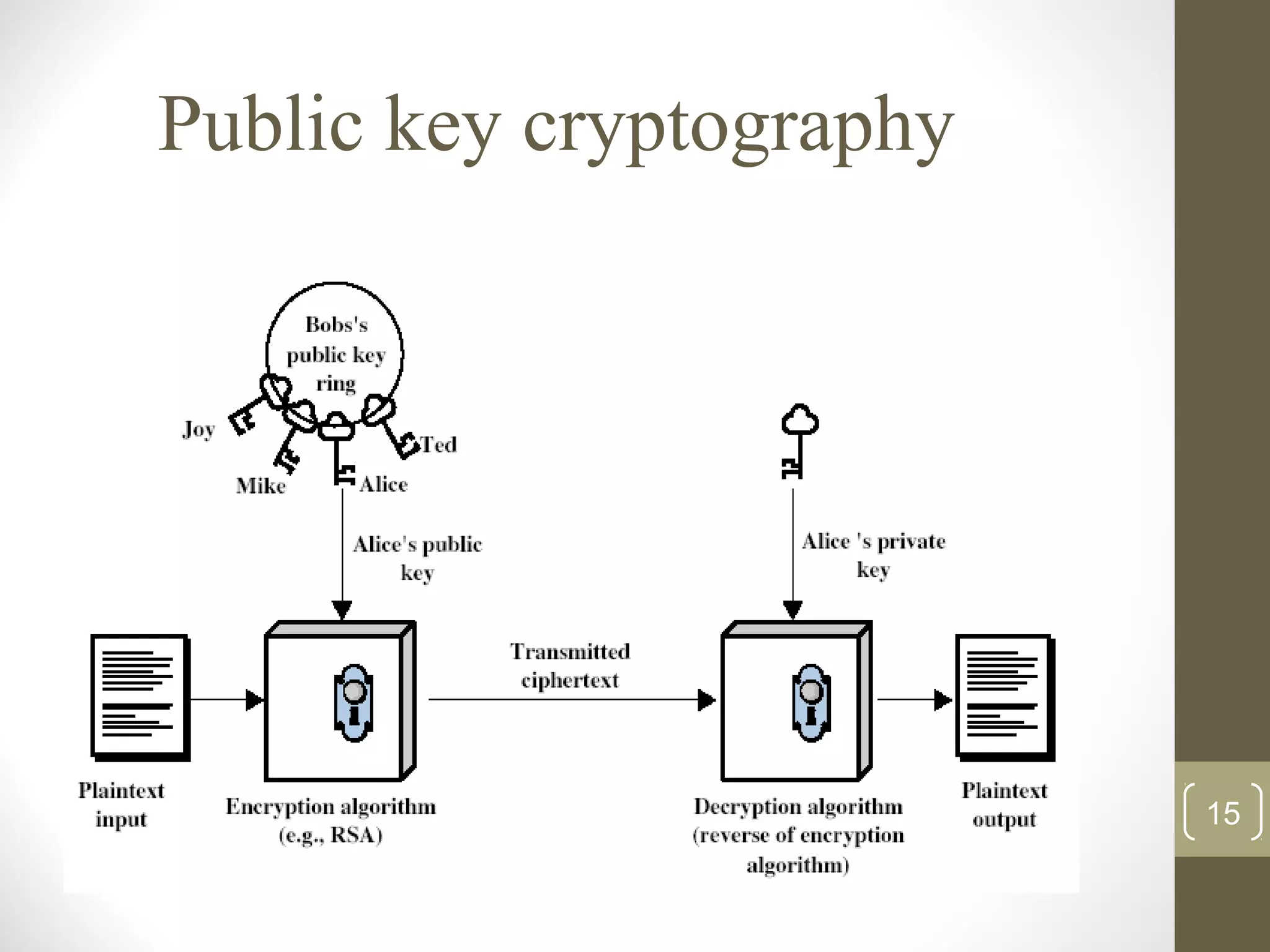
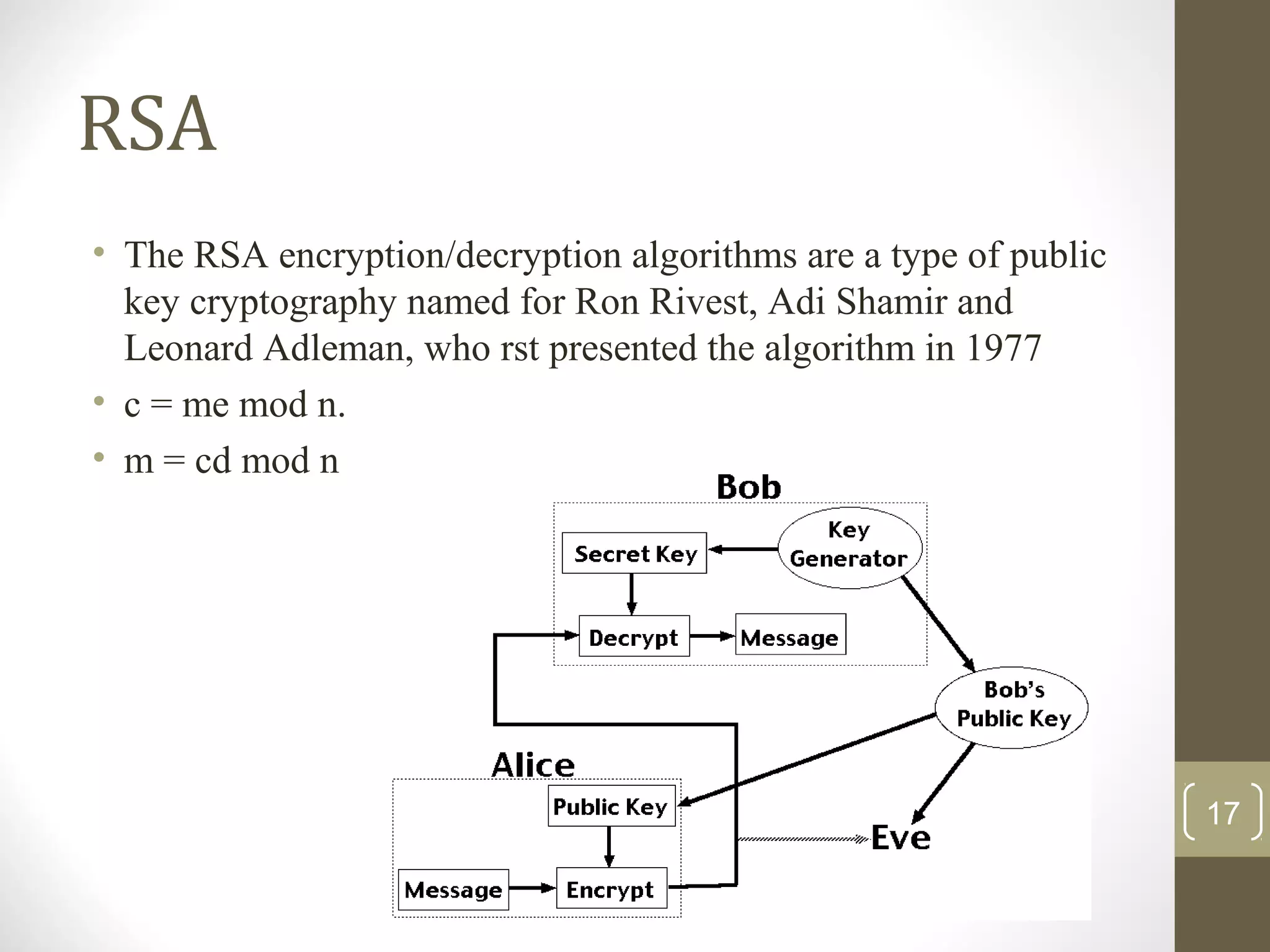
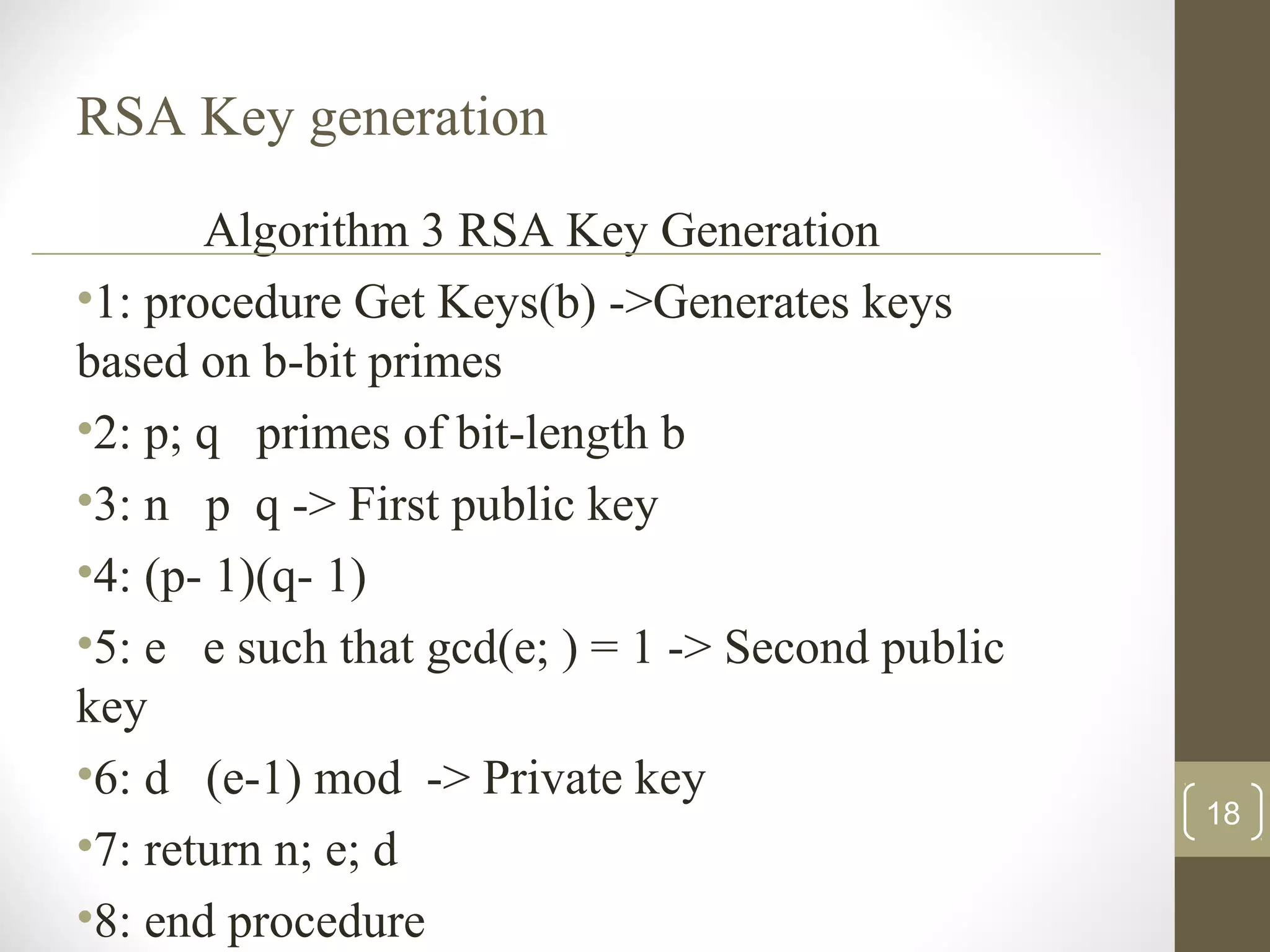
This document surveys cryptographic algorithms including DES (block cipher), RC4 (stream cipher), SHA-1 (hash), and RSA (public-key cryptography). It discusses how cryptography encrypts messages from sender to receiver using cipher text to hide messages from hackers. Symmetric algorithms like DES use the same key for encryption and decryption while asymmetric algorithms like RSA use public and private key pairs. The document also examines the RSA encryption algorithm and how it generates keys based on prime numbers.