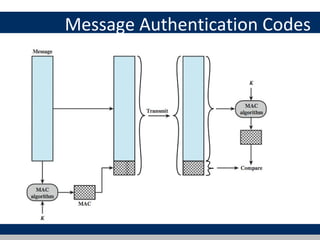
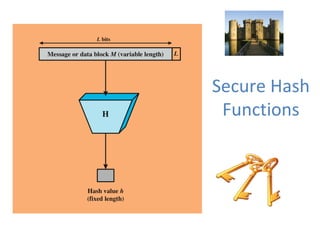
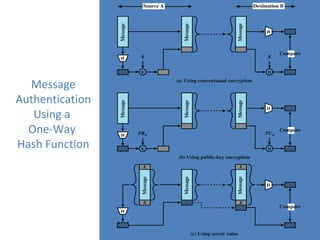
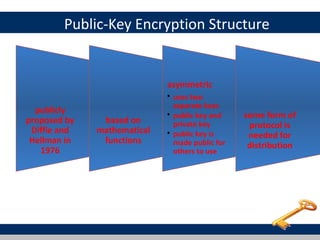
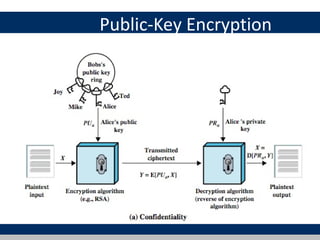
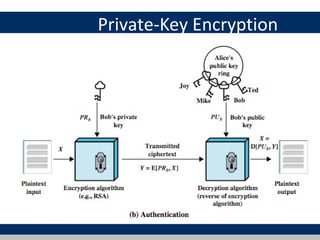
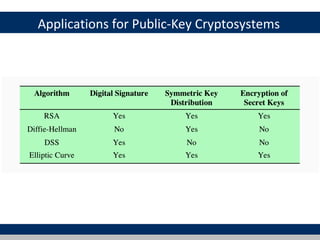
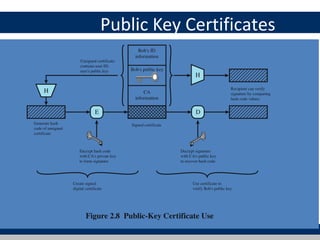
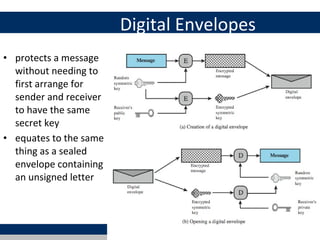
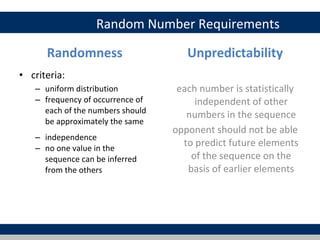
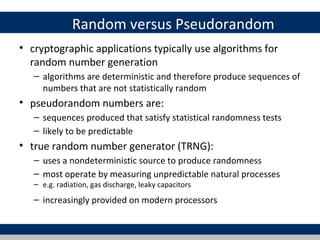
Cryptographic tools discussed include symmetric encryption using secret keys, public-key encryption using key pairs, hash functions for message authentication and digital signatures, and random numbers. Symmetric encryption is the most commonly used prior to public-key encryption due to efficiency. Hash functions are used to create digital signatures by encrypting a hash with a private key. Digital envelopes allow message protection without pre-arranged keys. Random numbers must be unpredictable and independent to be cryptographically secure.