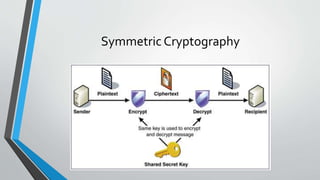
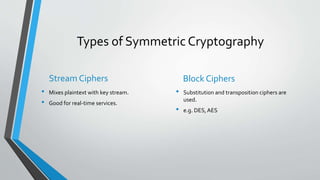
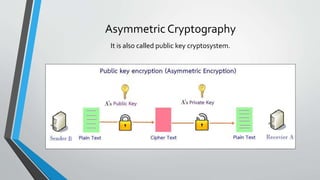
This document provides an overview of cryptography. It defines cryptography as a method of storing and transmitting data in a way that only the transmitter and receiver can access the information. The document then discusses the history of cryptography, including classic ciphers like the Caesar cipher and modern techniques like symmetric and asymmetric cryptography. It describes how symmetric cryptography uses a single key for encryption and decryption while asymmetric cryptography uses public-private key pairs. The document outlines some examples of symmetric and asymmetric algorithms and analyzes the advantages and disadvantages of each approach. Finally, it discusses some applications of cryptography like ATM PINs, encrypted drives, digital signatures, and time stamping.