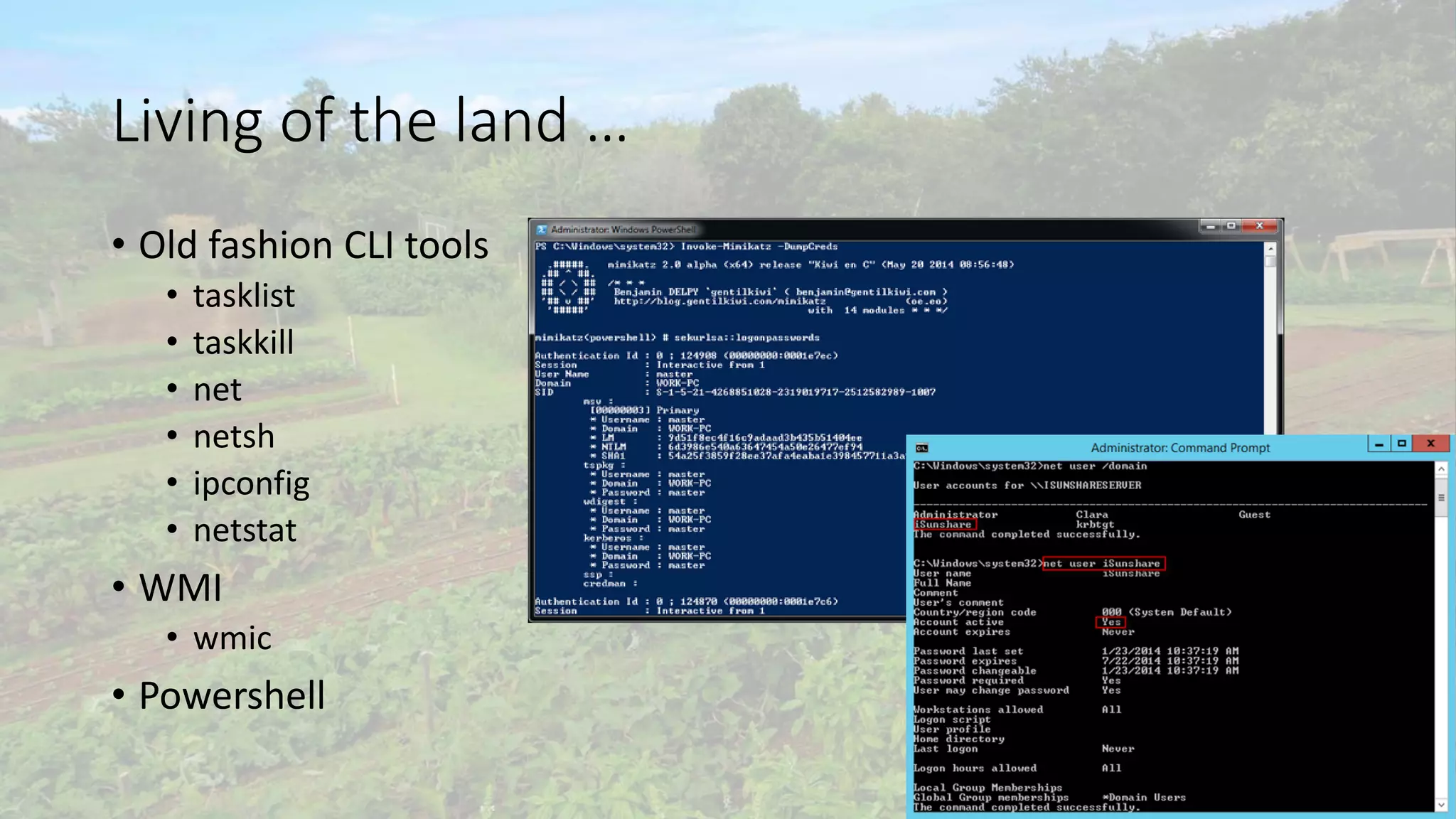
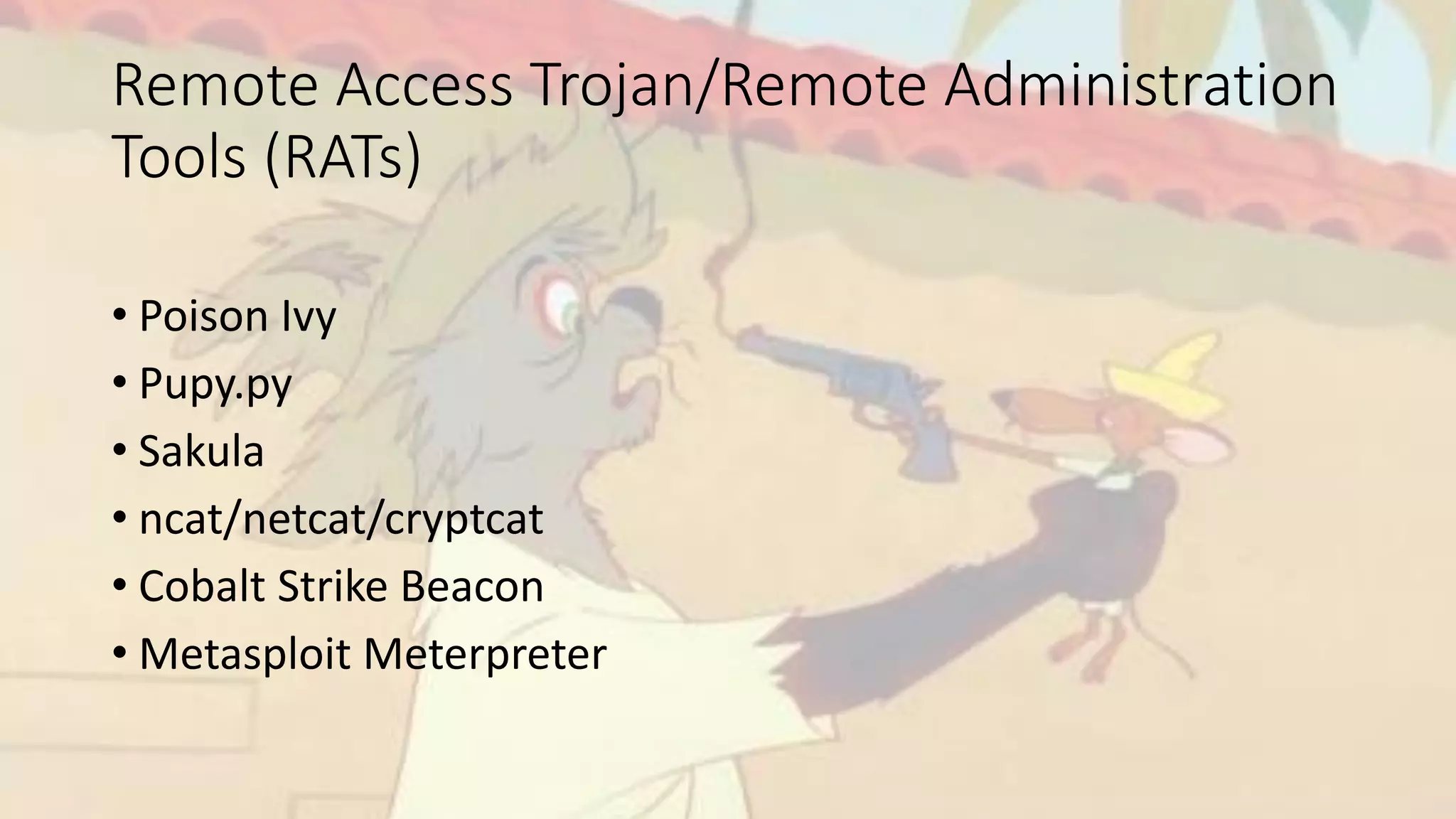
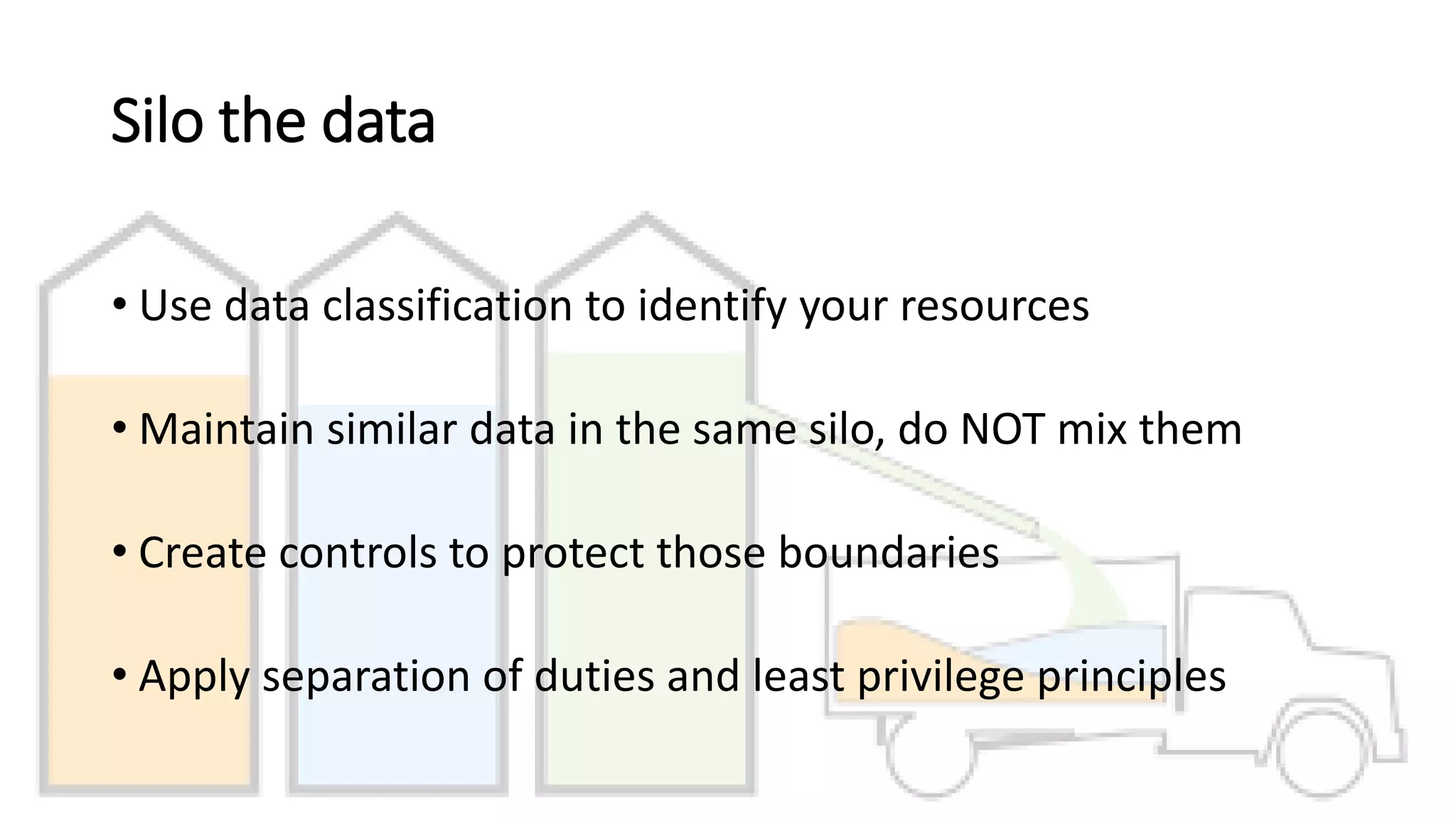
The document outlines a comprehensive incident handling process for managing adverse events in information systems and networks, covering stages such as preparation, identification, containment, eradication, recovery, and lessons learned. It emphasizes the importance of policies, situational awareness, and technical controls against hacking and penetration tactics, detailing tools and techniques for vulnerability scanning, exploitation, and post-exploitation activities. Additionally, it highlights the necessity of continuous detection and response, as security breaches are inevitable.