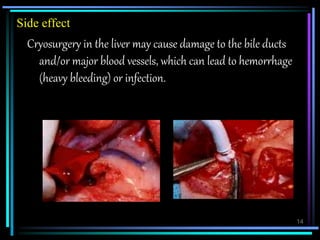
Cryosurgery uses extreme cold produced by liquid nitrogen or argon gas to destroy abnormal tissue. It can be used to treat some cancers and precancerous conditions of the skin, breast, prostate, liver, and cervix. Potential side effects include scarring, loss of sensation or pigmentation, and injury to surrounding tissues. Cryosurgery provides minimally invasive treatment with short recovery times and low risk of infection or complications.