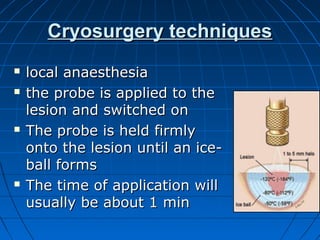
Cryosurgery is a procedure that uses freezing temperatures, typically from liquid nitrogen or nitrous oxide, to destroy tissue. A temperature of -15°C is needed to cause intracellular ice formation while -50°C is used to destroy malignant tumors. Cryoprobes, which have cold tips determined by the boiling point of the refrigerant liquid, are used to apply precisely targeted freezing. Cryosurgery is commonly used in oral surgery to ablate warts, tumors and haemangiomas with minimal scarring and bleeding. It can also treat conditions like trigeminal neuralgia or block nerves and reduce recurrence of lesions in bone.