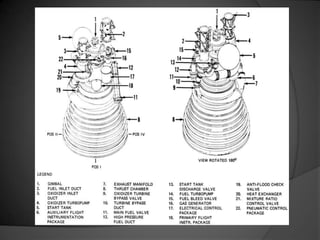
Cryogenic rocket engines use cryogenic fuels such as liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen that are stored at very low temperatures. They provide several advantages including high energy density and producing only water exhaust, but also have challenges like boil off and leakage due to the extreme cold temperatures required. India's first unmanned lunar mission in 2008 failed when the indigenous cryogenic upper stage engine did not ignite as planned. Future rocket technologies being researched include ion engines, nuclear thermal engines, and other alternatives to further space exploration.











![Why didn't the cryogenic engine of India ignite?The GSLV D3, which lifted off well from Sriharikota on Thursday, April 15, 2010 later plunged into the sea as the indigenous cryogenic engine failed to ignite.The vehicle lifted off as planned at 4.27 p.m. and its performance was normal up to the end of its second stage till 293 seconds from the lift-off.An authoritative former ISRO official said: “It is very clear that the cryogenic engine did not ignite when you look at the curve [of the vehicle's trajectory]the vehicle developed problems when the cryogenic upper stage should have ignited 304 seconds after the lift-off, and it fell into the sea](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cryogenicrocketengine-100430083207-phpapp02/85/Cryogenic-rocket-engine-14-320.jpg)


