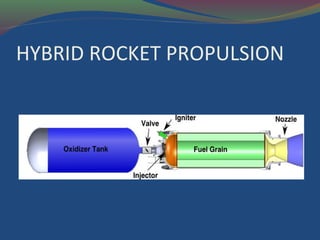
Hybrid rockets use a liquid oxidizer and solid fuel. They are mechanically simpler than other rocket types and can provide denser fuels. A hybrid rocket consists of a pressure vessel containing liquid oxygen and a combustion chamber housing solid fuel. When thrust is desired, the liquid oxidizer flows into the combustion chamber where it reacts with the solid fuel surface in a boundary layer flame. Hybrid rockets offer higher safety during fabrication and operation compared to solid rockets, and allow for throttling capability not available with other rocket types. While hybrid rockets currently have some performance disadvantages, their safety features make them promising for future propulsion applications.