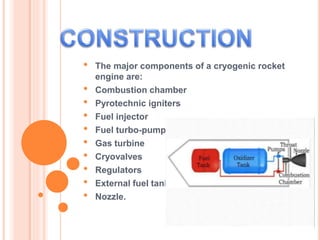
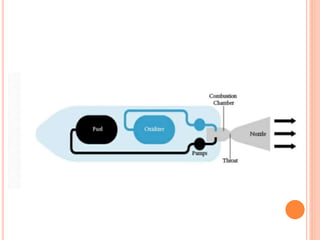
The document describes a cryogenic rocket engine. Cryogenic engines use liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen propellants, which must be stored at extremely low temperatures below -183°C and -253°C, respectively. The engine works on the principle of Newton's third law of motion - burning the cryogenic fuels in the combustion chamber and expanding the gases through a nozzle to generate thrust. Major components include the combustion chamber, injectors, turbo-pumps, and external fuel tanks. Cryogenic engines offer high energy efficiency due to the high energy density of liquid oxygen and hydrogen fuels.