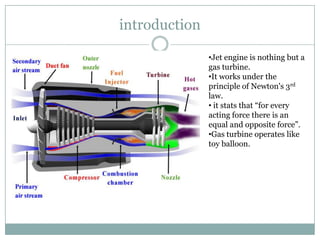
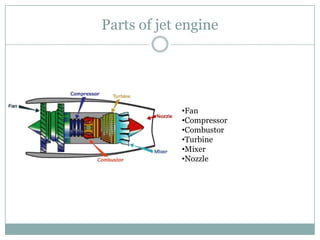
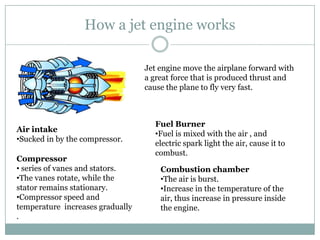
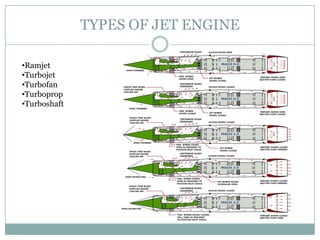
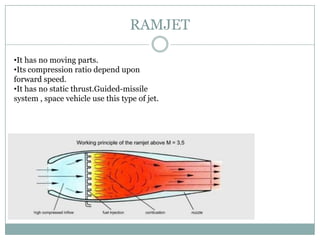
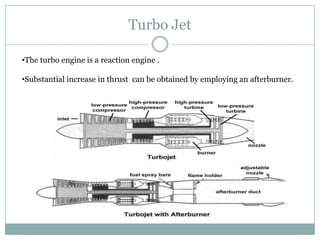
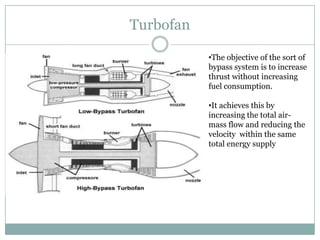
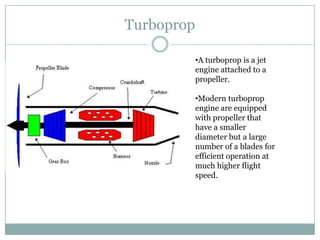
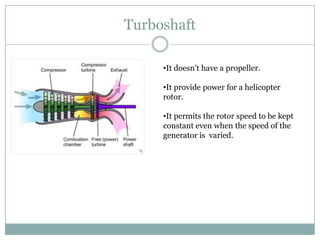
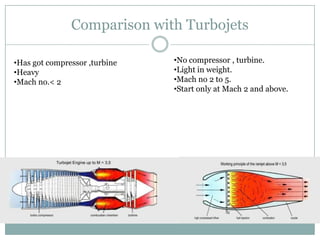
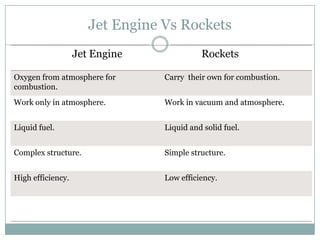
The document presents an overview of jet engines, including their history, components, types, and functionality. It compares jet engines with rockets, discusses their advantages and disadvantages, and highlights their uses in various industries, especially transportation and military applications. The conclusion emphasizes the prevalence of conventional jet engines for domestic purposes and the specialized use of ram and scramjet engines in defense.