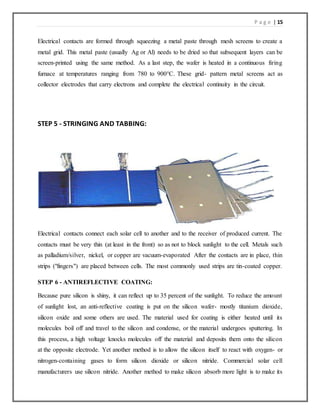
This document is a seminar report submitted by Pappu Jaiswal to fulfill requirements for a Bachelor of Technology degree in Electrical Engineering at Madan Mohan Malaviya University of Technology. The report is about solar trees and includes chapters on the working principle of solar cells, the manufacturing process of solar cells, and applications, advantages, and disadvantages of solar trees. It was supervised by Mr. Kishan Bhushan Sahay of the Electrical Engineering department.