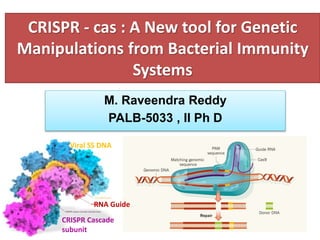
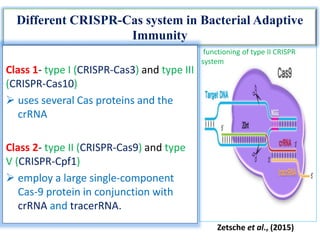
The document discusses CRISPR-Cas systems, which provide bacteria and archaea with adaptive immunity against viruses. It describes the key components and functions of various CRISPR-Cas systems, including Cas9 from type II systems. CRISPR-Cas9 has been engineered into a powerful tool for genome editing in mammalian cells by creating a single-guide RNA to direct Cas9 to cleave specific DNA sequences. The document also compares CRISPR-Cas9 to previous genome editing tools like zinc finger nucleases and TALENs, noting that CRISPR-Cas9 requires only changing the guide RNA sequence rather than re-engineering proteins.