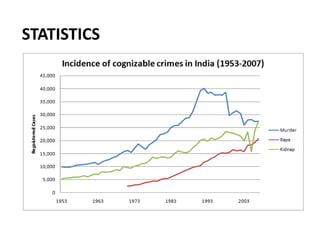
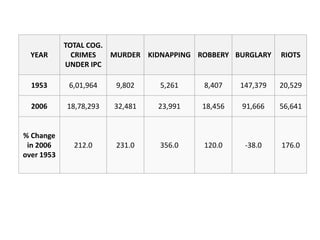
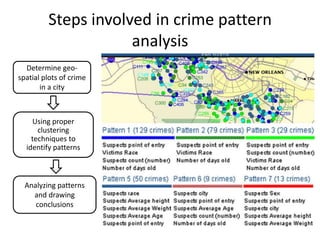
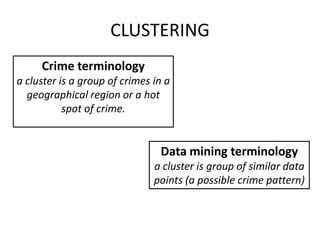
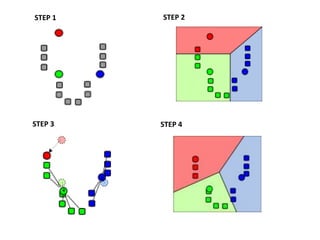
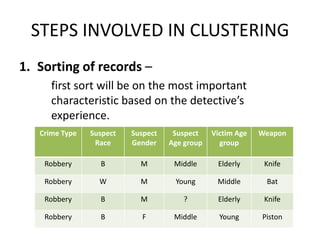
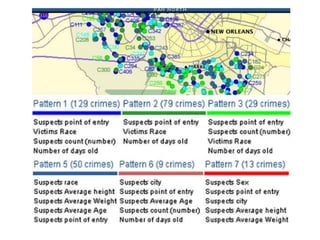
Crime pattern detection uses data mining techniques like clustering to analyze crime data and identify patterns. This involves plotting past crimes geographically, clustering similar crimes to detect sprees, and analyzing the results to draw conclusions. It helps improve crime solving by learning from history and preempting future crimes. The method augments detectives' work but has limitations like relying on data quality. Overall, crime pattern detection aids operational efficiency and enhancing resolution rates by optimizing resource deployment based on observed crime trends.