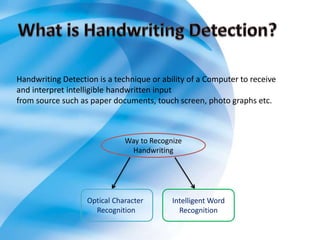
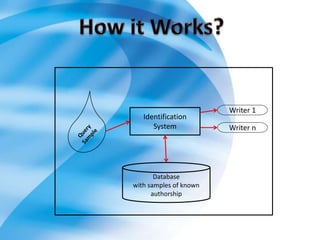
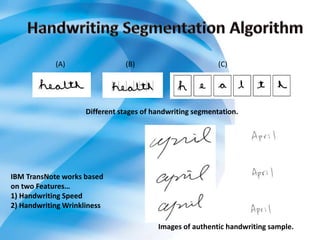
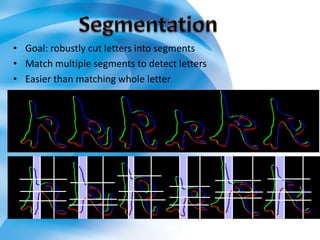
On-line handwriting recognition involves converting handwriting as it is written on a digitizer to digital text, while off-line recognition converts static images of handwriting. Both techniques face challenges from variability in handwriting styles. Current methods use feature extraction and neural networks, but do not match human-level recognition abilities. Handwriting recognition remains an important but difficult area of research.