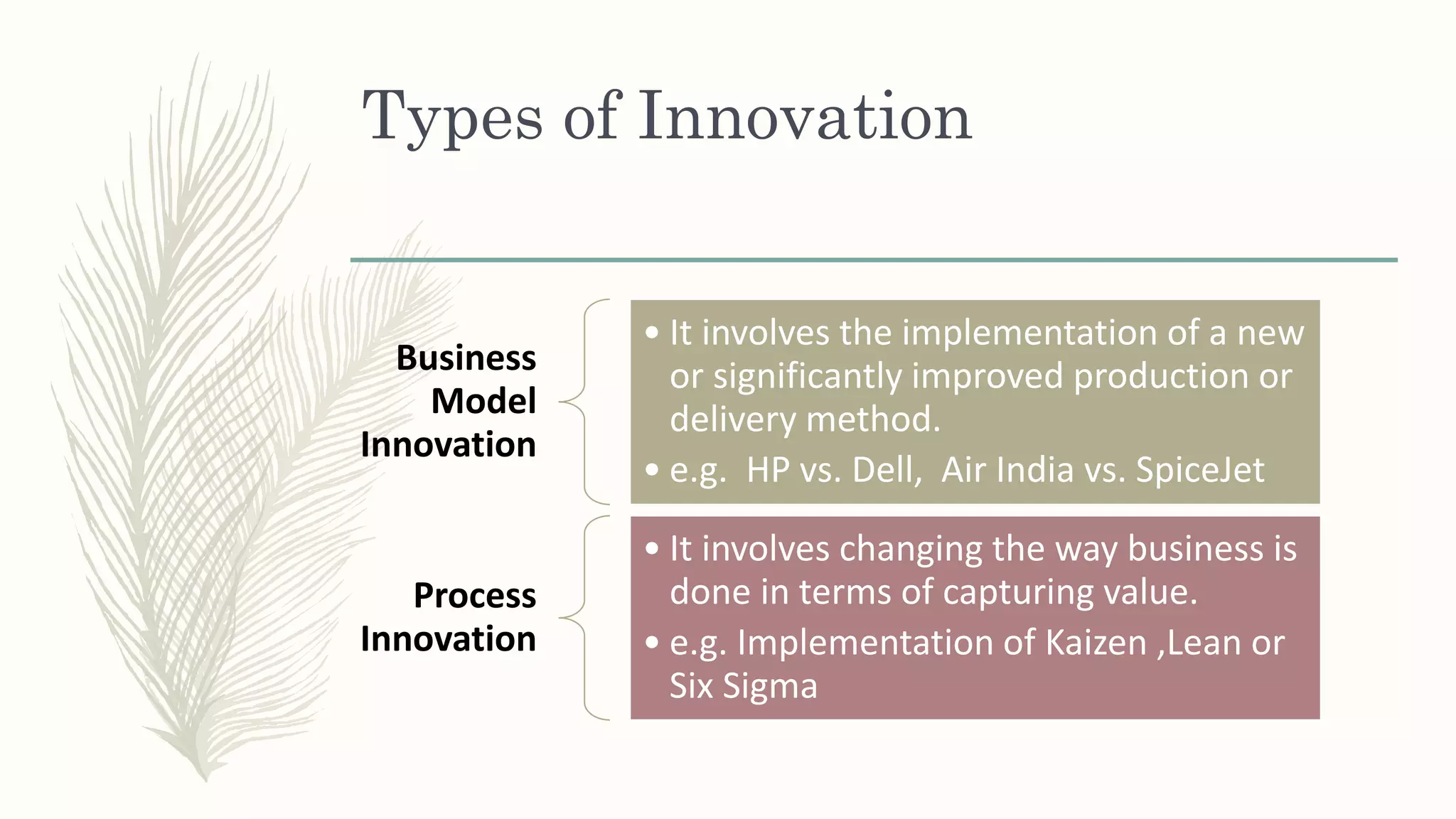
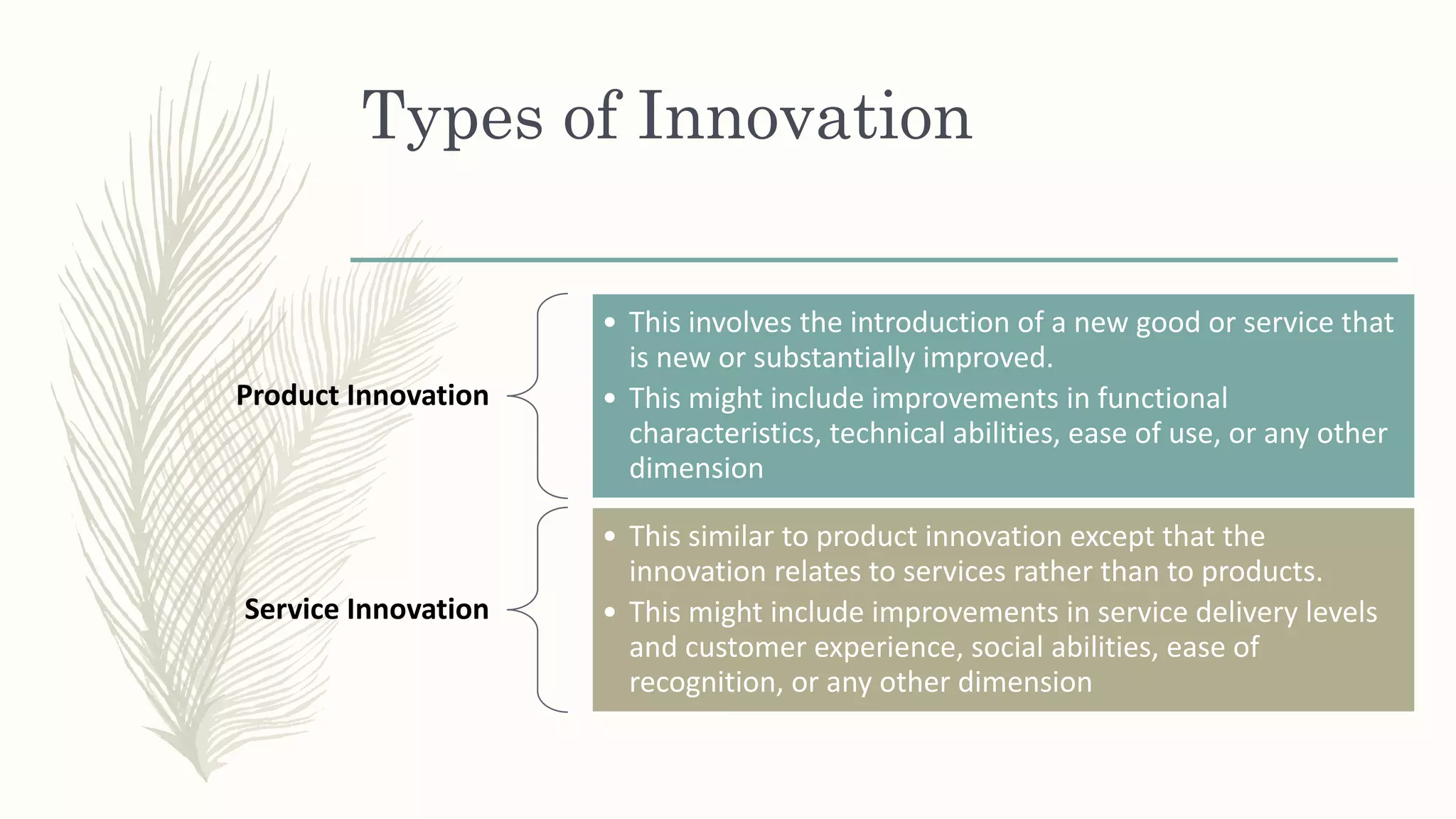
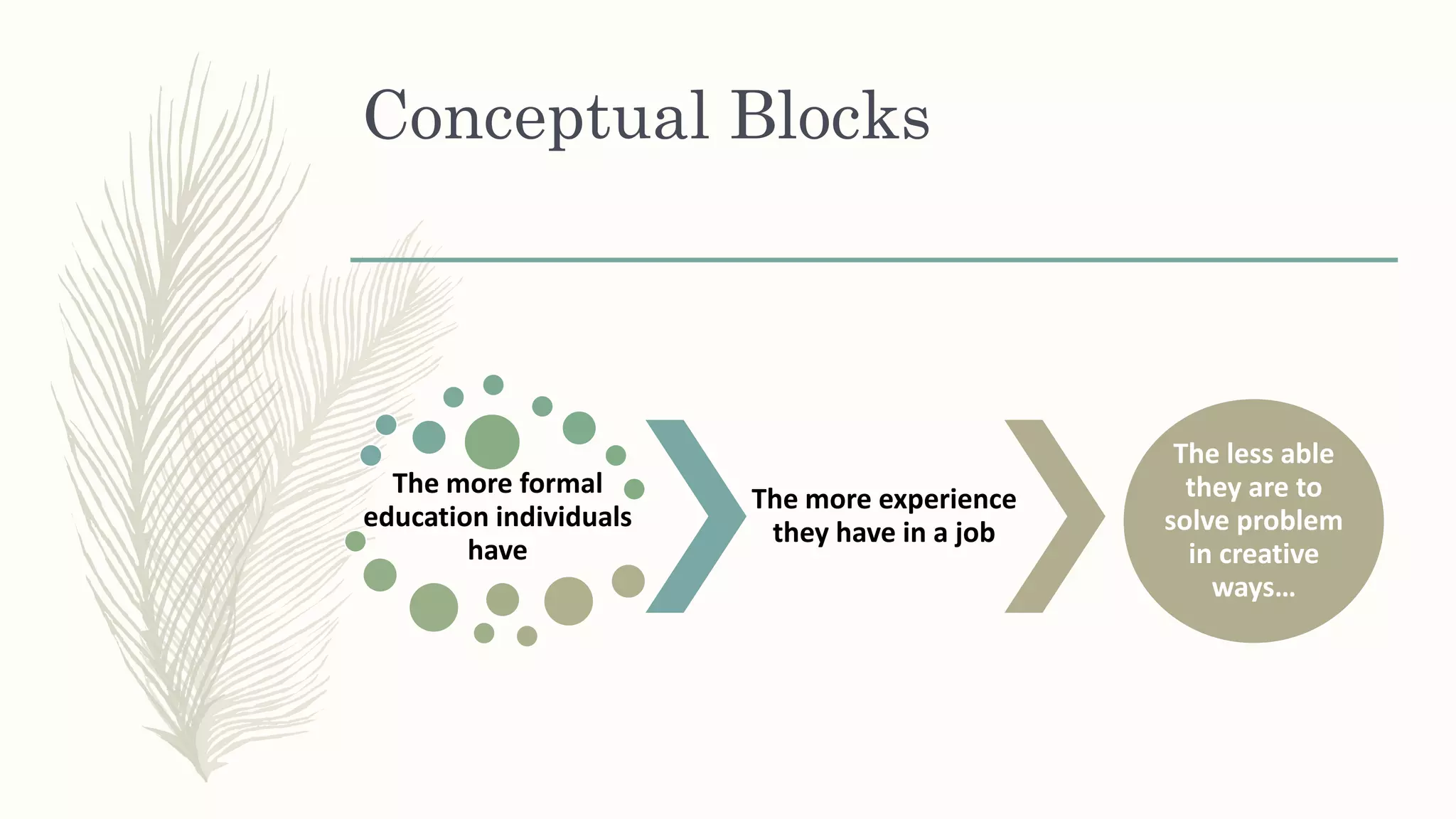
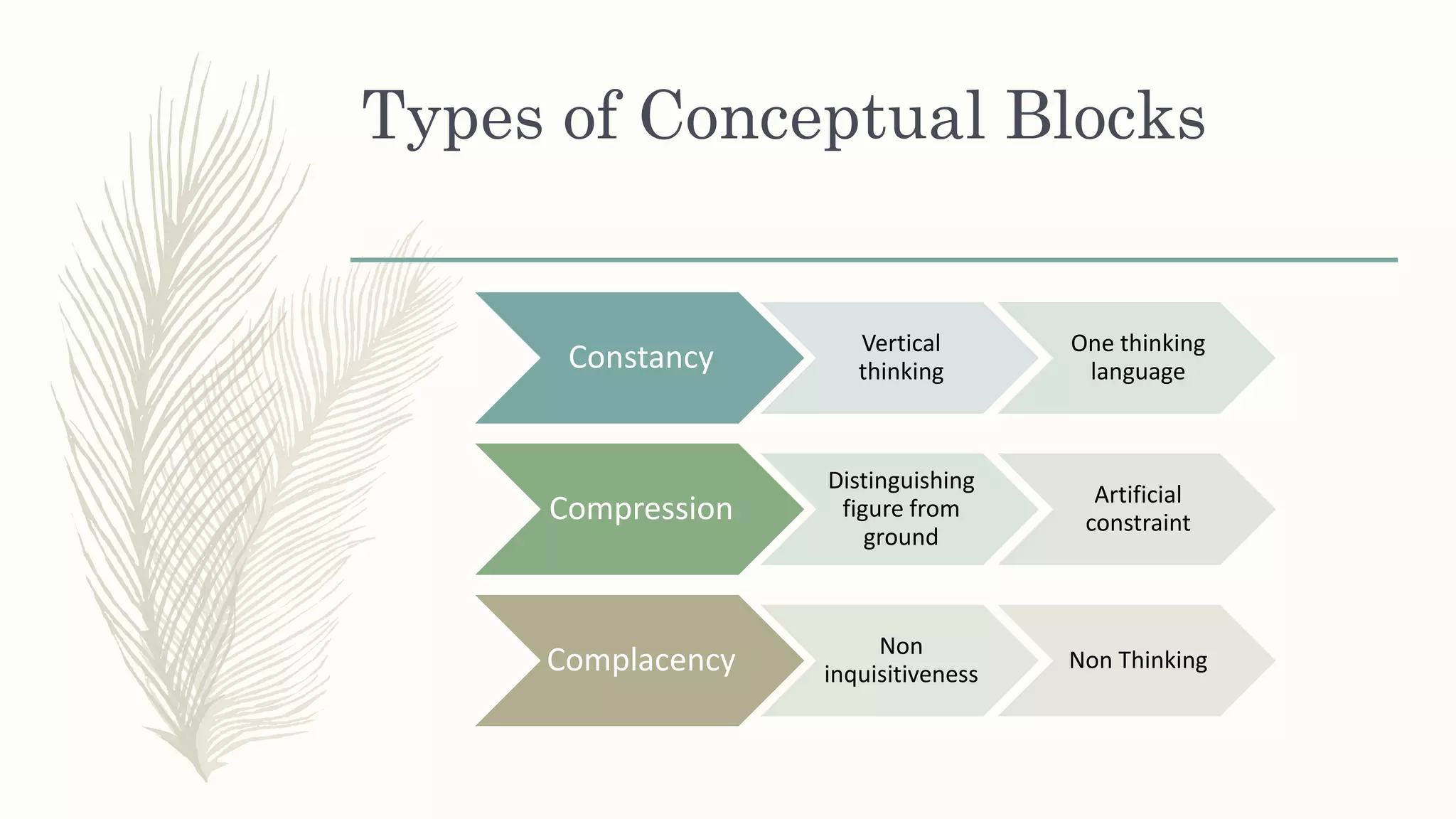
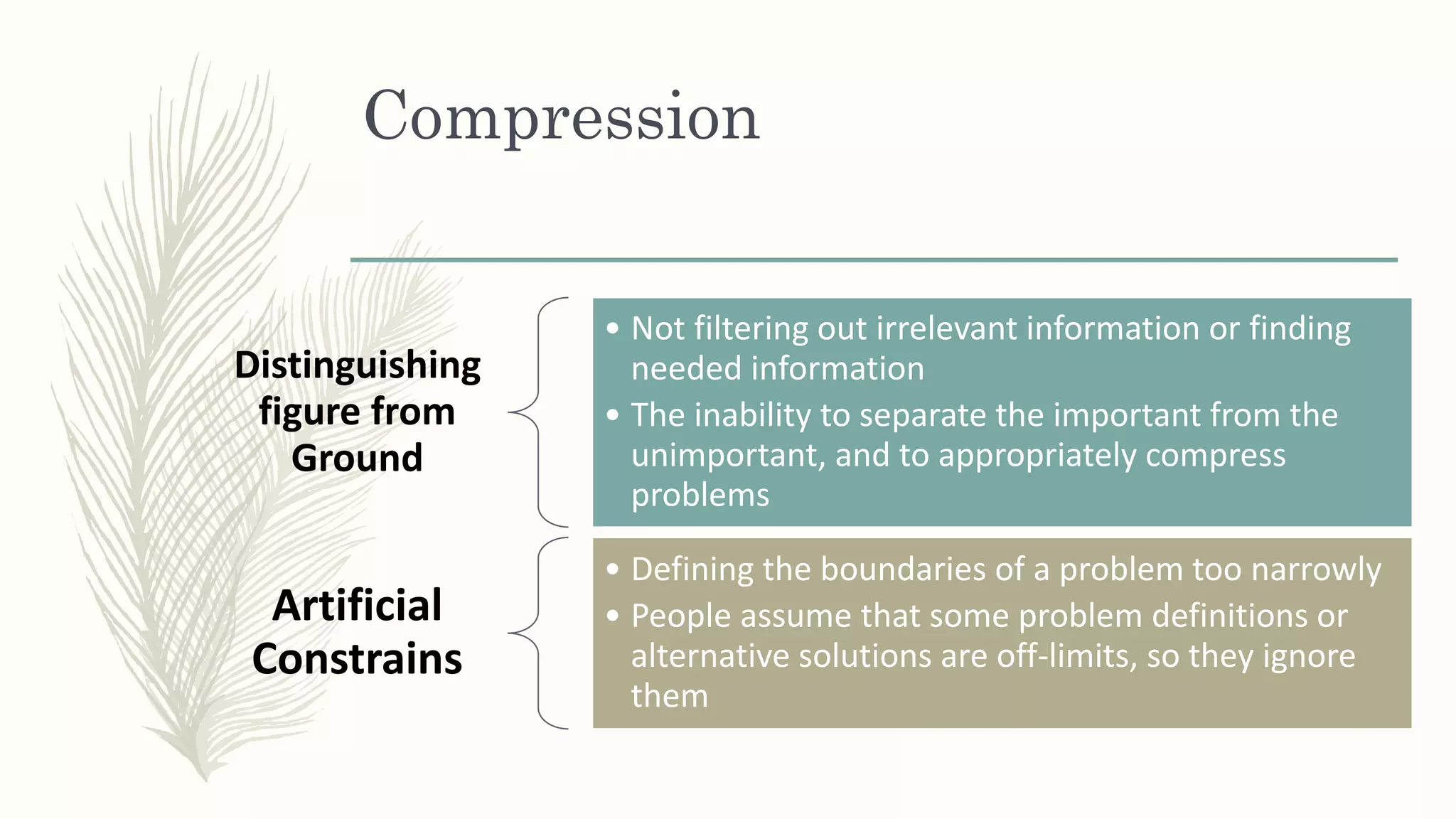
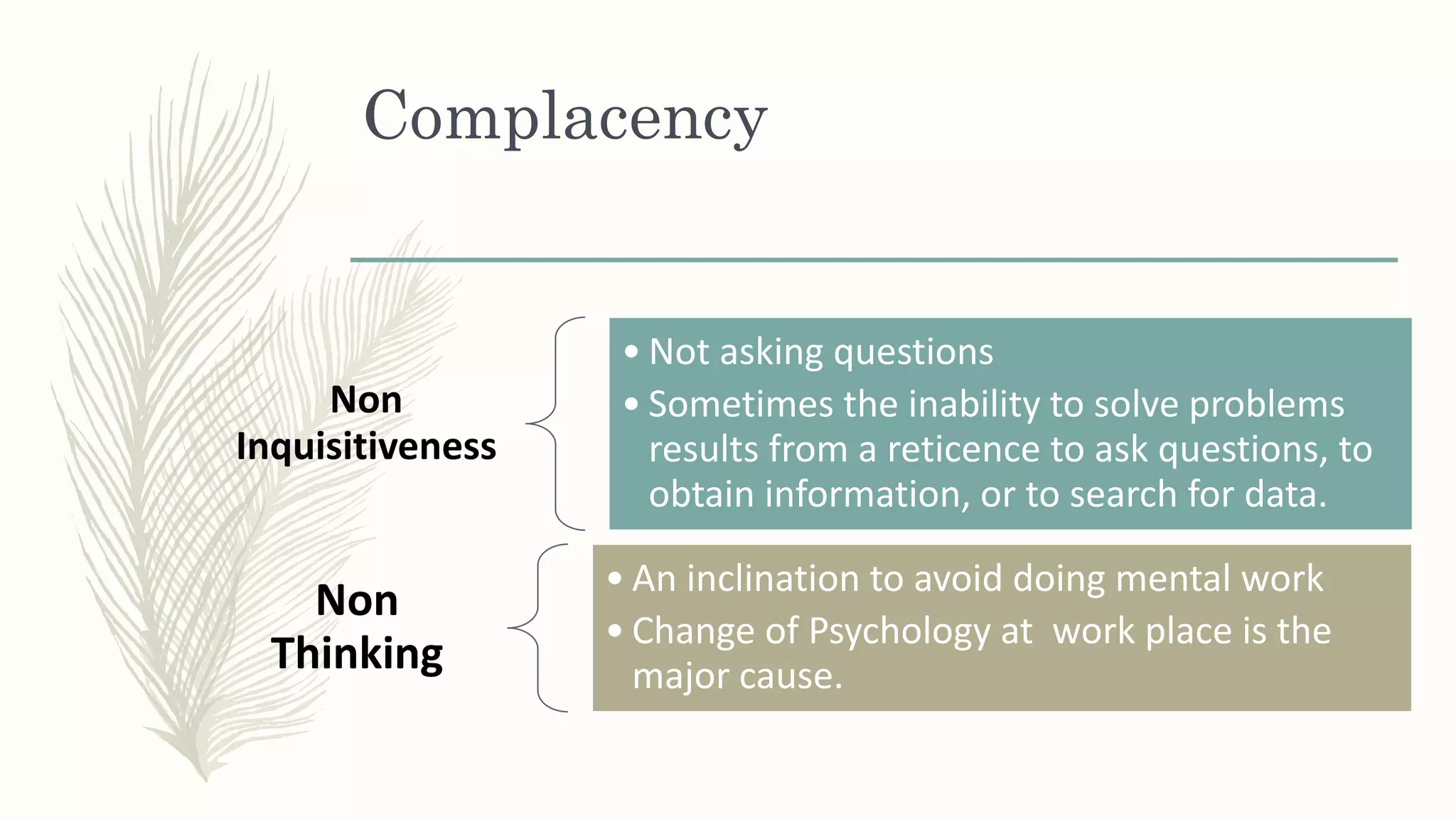
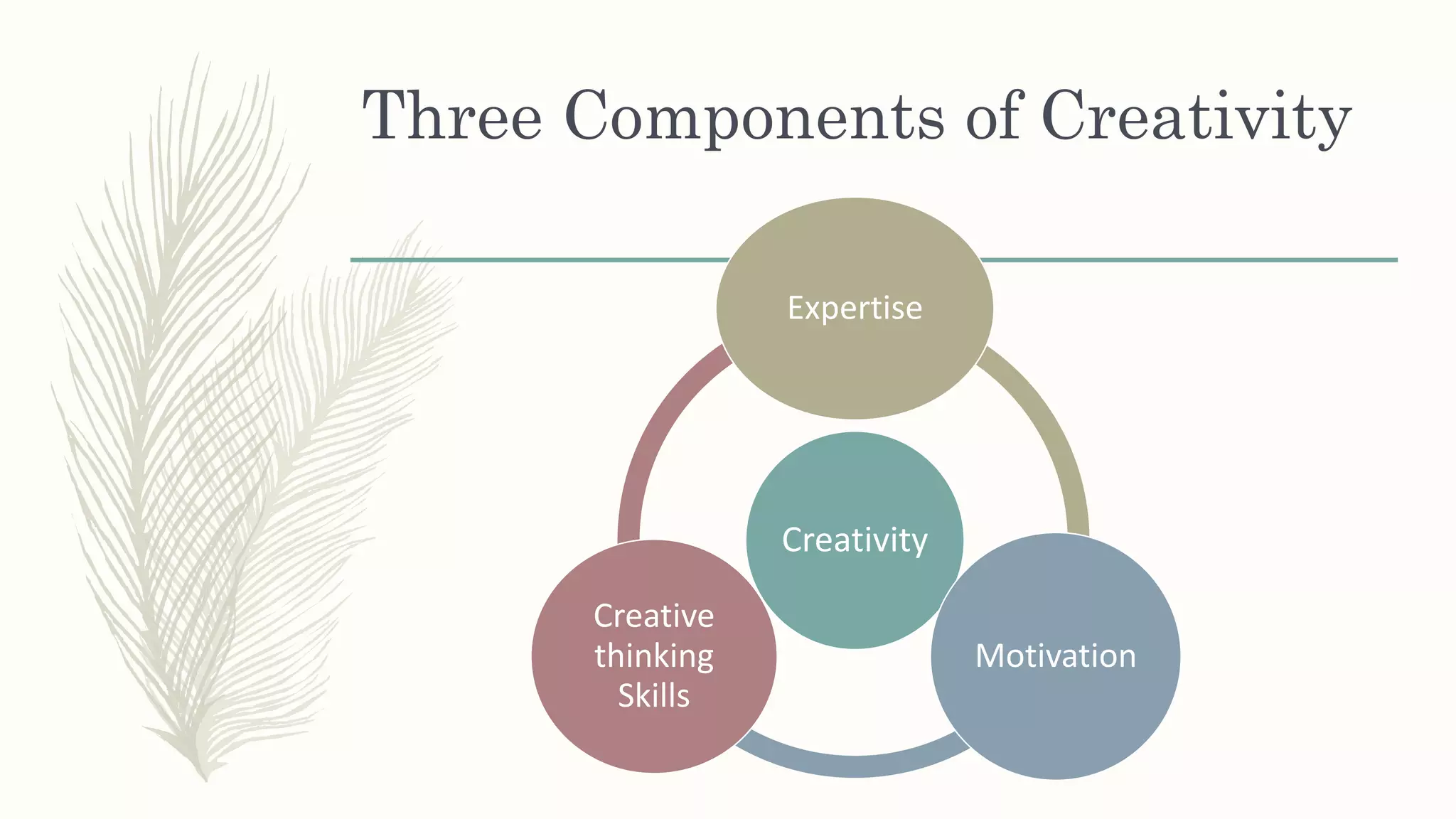
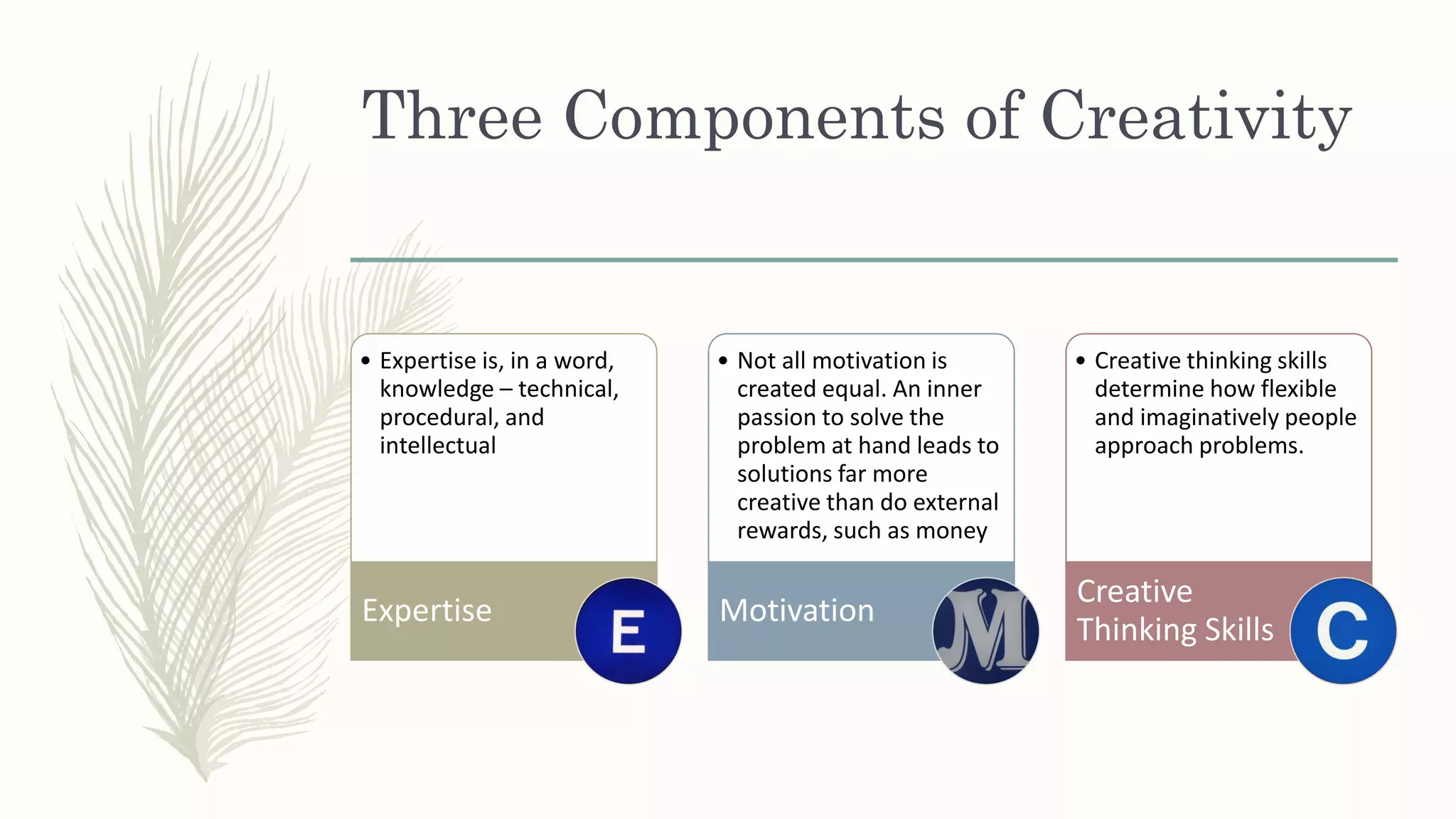
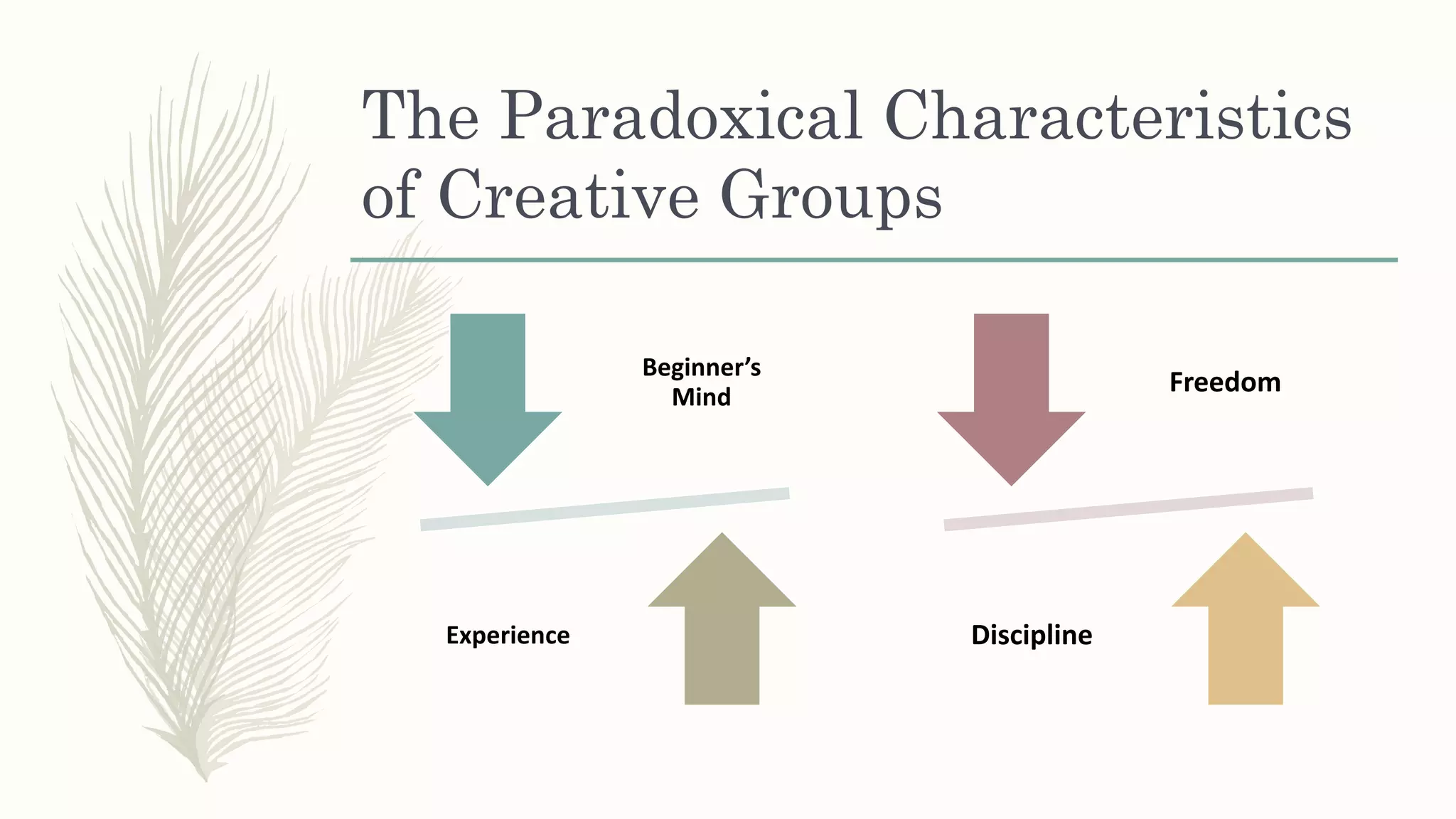
This document summarizes a workshop on creative and innovative thinking skills. It discusses what creativity and innovation are, types of innovation including product, process, business model, and service innovation. It covers conceptual blocks to creativity like constancy, compression, and complacency. The three components of creativity are discussed as expertise, motivation, and creative thinking skills. Tools for defining problems like the Kipling method and creating new ideas like brainstorming and attribute listing are presented. Finally, the document discusses creating a creative climate in the workplace with elements like risk-taking, access to knowledge, rewarding innovators, and openness to new ideas.