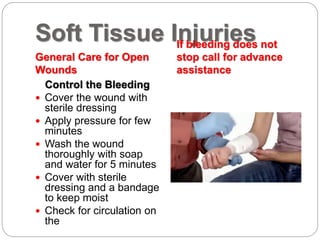
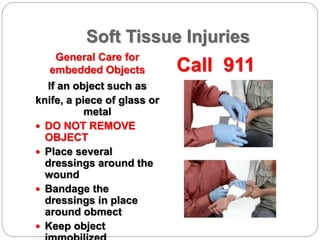
This document discusses the importance of CPR and first aid certification skills. It covers how to recognize various medical emergencies like cardiac issues, breathing problems, strokes, seizures, diabetic emergencies, allergic reactions, and injuries. For each type of emergency, it describes signs and symptoms to look for and basic steps to take, such as calling 911, providing comfort, and not moving the injured body part. The overall message is that first aid training can help bystanders identify emergencies and provide initial care until emergency responders arrive.