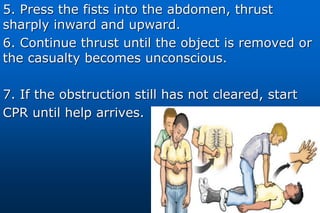
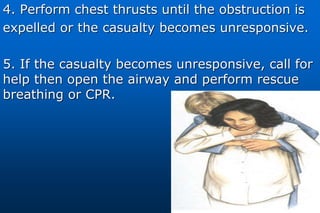
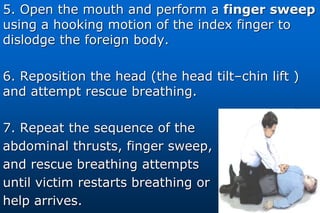
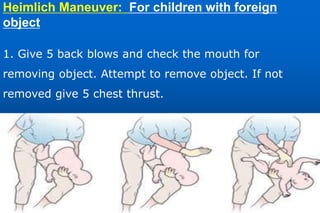
This document provides information on airway obstructions and choking. It discusses causes of partial and complete airway obstructions, signs and symptoms of choking, and treatment procedures. For conscious victims, it describes performing abdominal thrusts (Heimlich maneuver) by standing behind the person and thrusting fists into their abdomen. For unconscious people, it outlines opening the airway, delivering abdominal thrusts, performing a finger sweep, and providing rescue breaths. Procedures are also provided for choking in children and for self-administered choking relief.