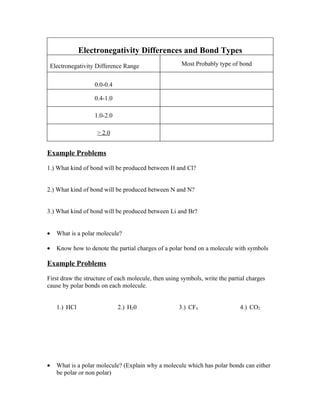
This document provides a study guide for a chapter 8 test on covalent bonding. It includes definitions and characteristics of ionic compounds and covalent compounds. It outlines steps to draw Lewis electron dot structures and provides example questions to practice this. It also covers drawing resonance structures, defining polar bonds and molecules, denoting partial charges on polar molecules, and ranking intermolecular forces. The review sheet is intended to guarantee covering all topics that will be on the 12-15 question test, with an option to use the sheet during the test with a maximum grade of 90%.