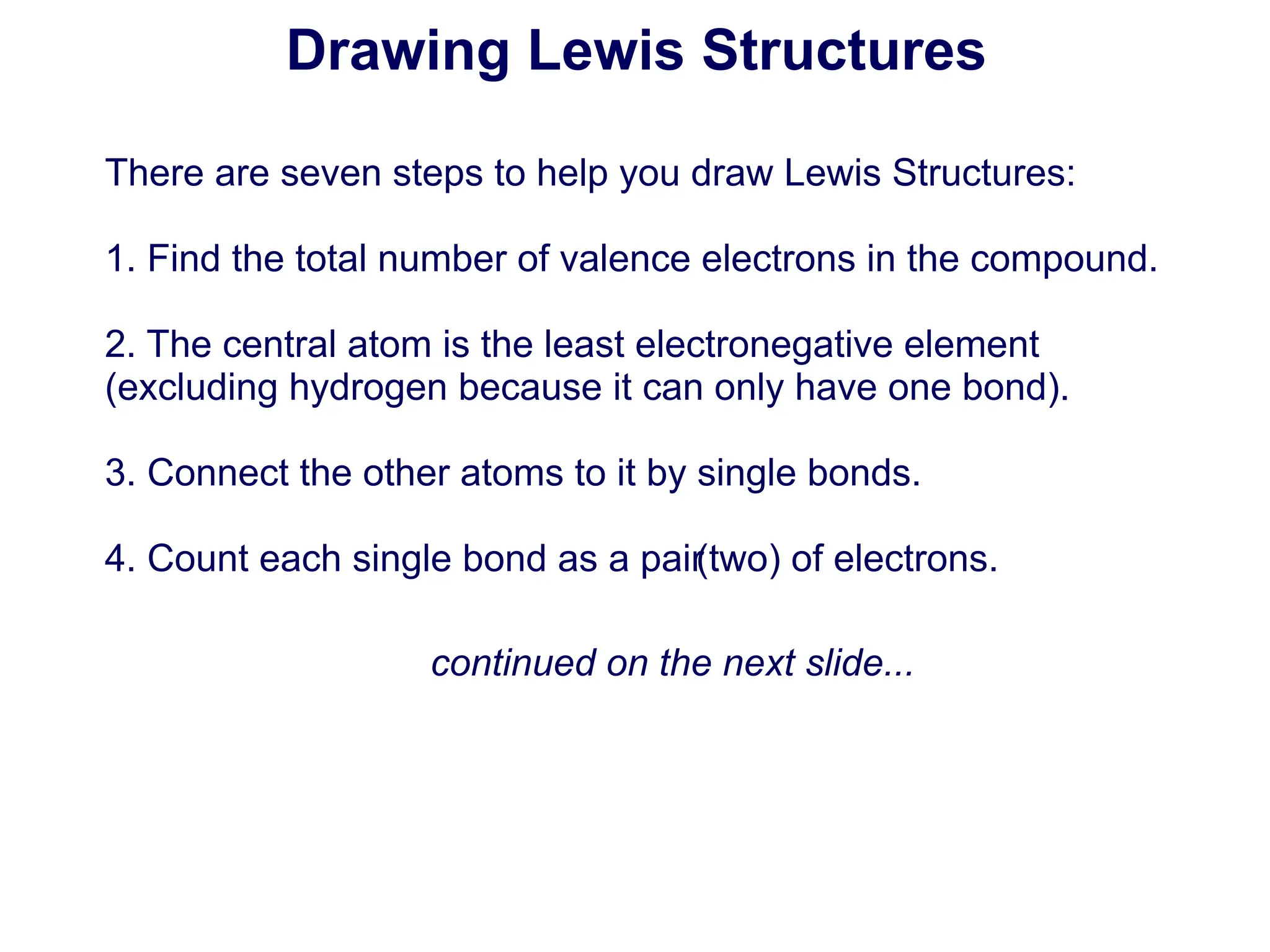
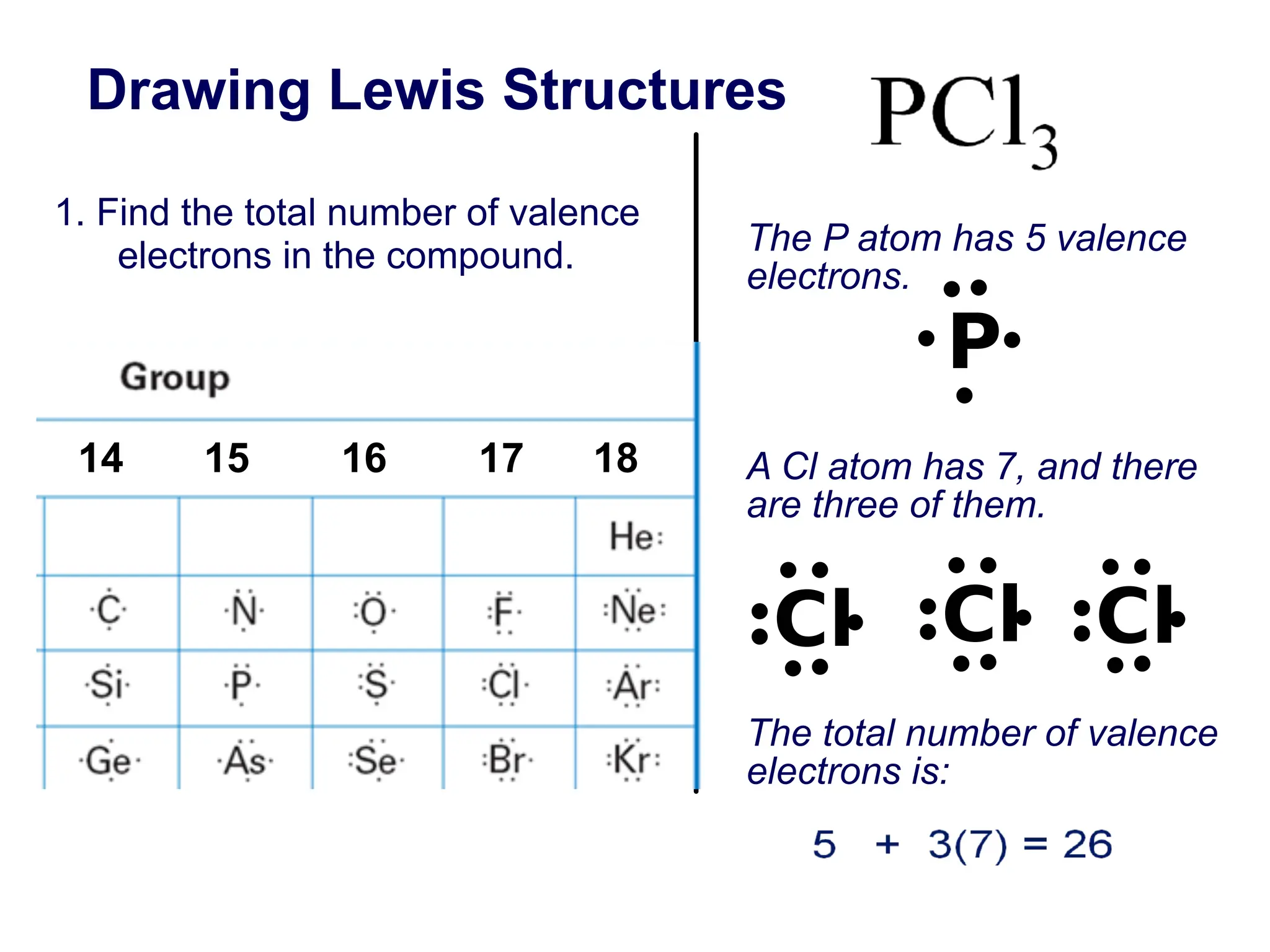
This document provides an overview of covalent bonding and Lewis dot structures. It begins with an introduction to covalent compounds and how covalent bonding occurs through the sharing of valence electrons between nonmetal atoms. Lewis dot structures are introduced as a way to represent covalent bonds using dots to represent valence electrons. The document then covers steps for drawing Lewis dot structures, including finding the total valence electrons, identifying the central atom, adding single bonds, and adding electrons to attain full octets. Examples of drawing Lewis structures for PCl3 and NH3 are shown. The document concludes with sections on exceptions to the octet rule and practice drawing Lewis diagrams.






![Types of Covalent Compounds
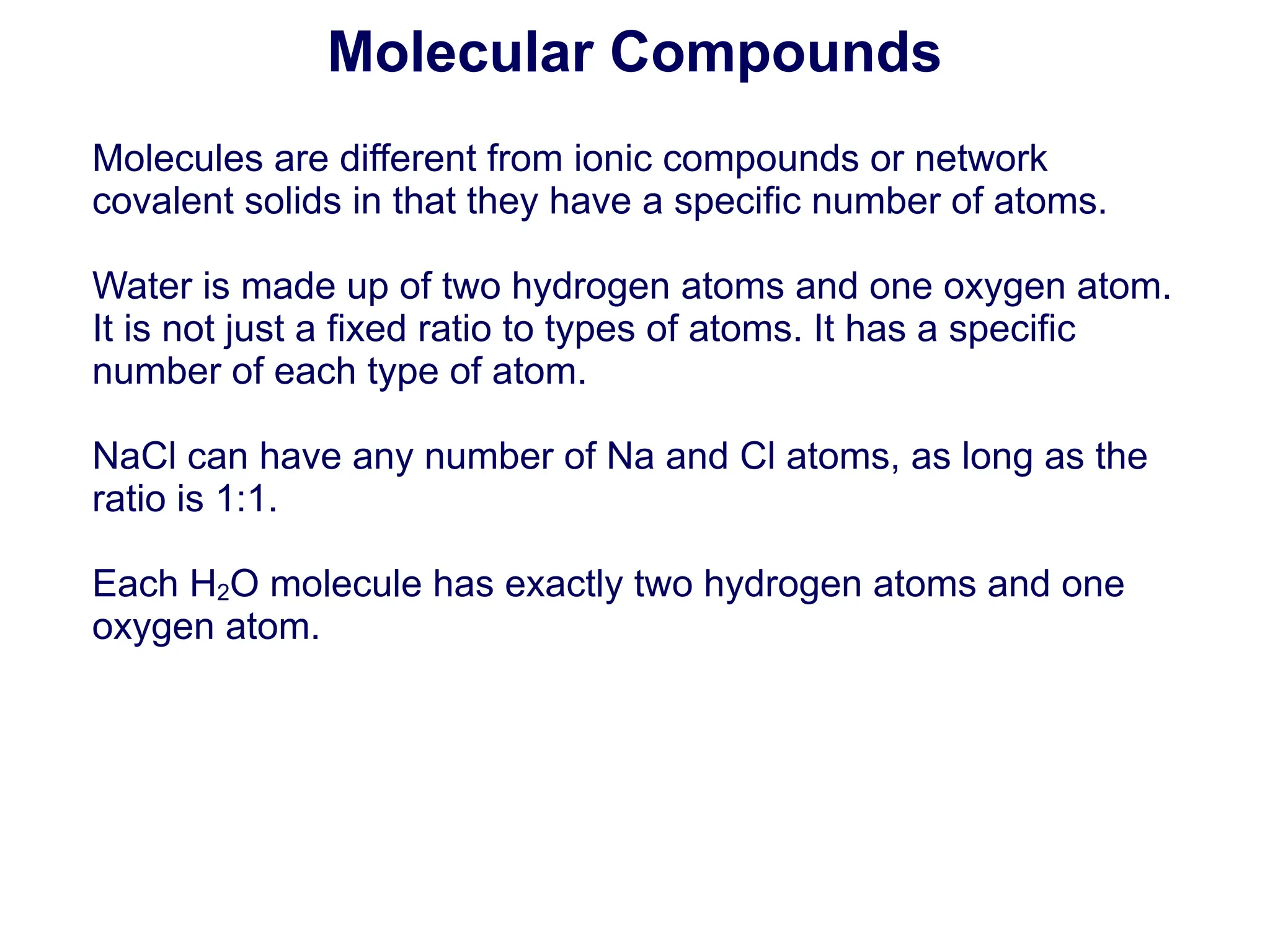
There are two types of compounds created by the covalent
bonding of atoms:
Covalent networks - larger compounds consisting of repeating
elemental or molecular units all covalently bonded together, such
as diamond (Cn) or quartz [(SiO2)n].
Molecules - smaller compounds of one or more elements bonded
together, such as water (H2O) or oxygen gas (O2).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-9-2048.jpg)






![1 Which pair of atoms will form a covalent bond?
A Li and Ne
B K and Br
C C and O
D Na and Cl
E I need
help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
C
https://njctl.org/video/?v=UrJnVvbze04](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-18-2048.jpg)

![A Li and Cl
B Na and Cl
C K and Fl
D H and O
2 Which pair of atoms will form a covalent bond?
E I need
help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
D
https://njctl.org/video/?v=TycvVmV8t-E](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-20-2048.jpg)

![3 The atoms that would form the MOST covalent bond
would be:
A C - H
B O - H
C Cl - H
D F - H
E I need
help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
A
https://njctl.org/video/?v=PF5JKZE_83E](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-22-2048.jpg)
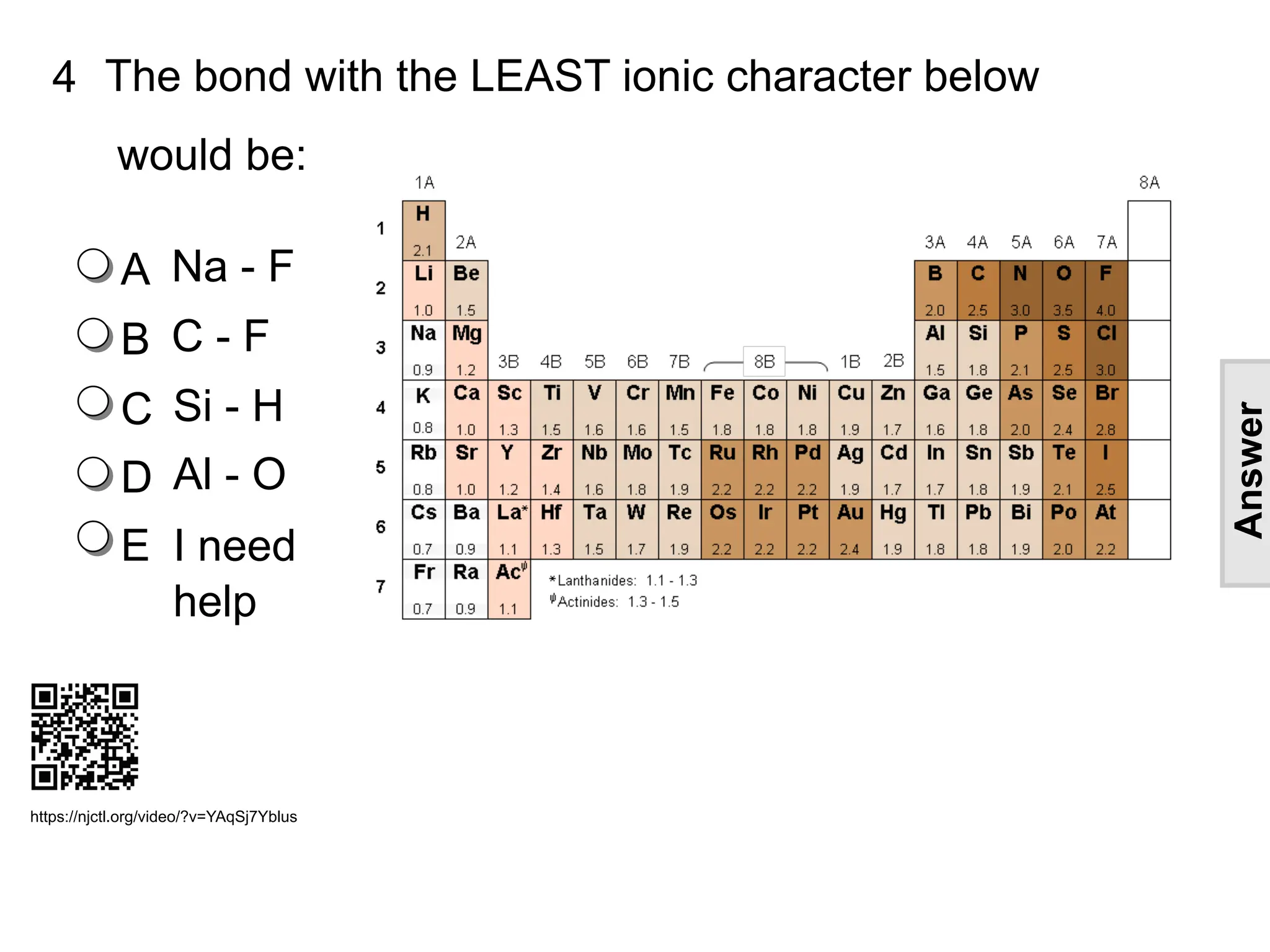
![4 The bond with the LEAST ionic character below
would be:
A Na - F
B C - F
C Si - H
D Al - O
E I need
help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
C
https://njctl.org/video/?v=YAqSj7Yblus](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-24-2048.jpg)

![5 Butter melts on a hot day. What type of compound is it?
A metallic
B ionic
C covalent network
D molecular
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
D
https://njctl.org/video/?v=i5ifRTQUvRs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-26-2048.jpg)

![6 You are given a substance that has a high melting point
and does not conduct electricity, even when you put it in
water. What is it?
A a metal
B an ionic compound
C a covalent network
D a molecule
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
C
https://njctl.org/video/?v=kf_C9WW5TZ8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-28-2048.jpg)

![7 Chlorine monoxide is
A ClO2
B ClO
C OCl
D O2Cl
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
B
https://njctl.org/video/?v=3tP0aqWQR_4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-30-2048.jpg)

![8 Dinitrogen tetroxide is
A NO2
B N2O4
C NO3
D N4O2
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
B
https://njctl.org/video/?v=Erv00aZl39M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-32-2048.jpg)

![9 H2O is
A Hydrogen monoxide
B Dihydrogen monoxide
C Hydrogen oxide
D Hydrogen dioxide
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
B
https://njctl.org/video/?v=eV96TRAN10c](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-34-2048.jpg)

![10 SO3 is
A sulfate
B sulfur oxide
C sulfur trioxide
D sulfite
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
C
https://njctl.org/video/?v=jYpkka4DIKQ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-36-2048.jpg)

![11 P4O10 is
A Phosphorous pentoxide
B Phosphate
C Phosphorous oxide
D Tetraphosphorous decoxide
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
D
https://njctl.org/video/?v=AybvvHso2dw](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-38-2048.jpg)

![12 MgO is
A monomagnesium monoxide
B magnesium monoxide
C magnesium oxide
D monomagnesium oxide
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
C
https://njctl.org/video/?v=Xd4qk_-g-fc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-40-2048.jpg)











![13 How many valence electrons does nitrogen have?
A 2
B 3
C 4
D 5
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
D
https://njctl.org/video/?v=JfPN6yvE-k4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-56-2048.jpg)

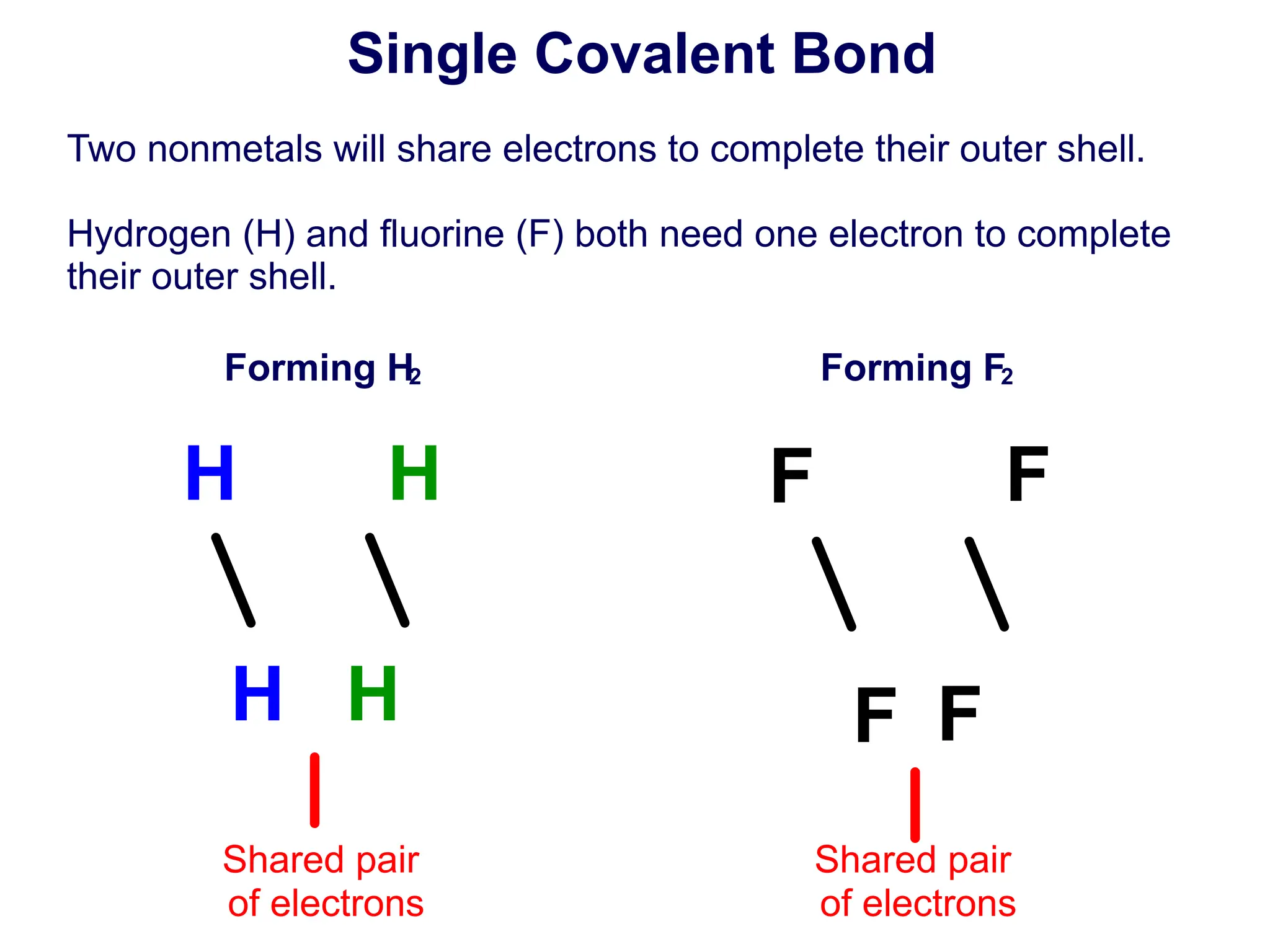
![14 How many electrons are shared by two atoms to
create a single bond?
A 3
B 2
C 4
D 1
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
B
https://njctl.org/video/?v=yqbV2YtF6KU](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-58-2048.jpg)

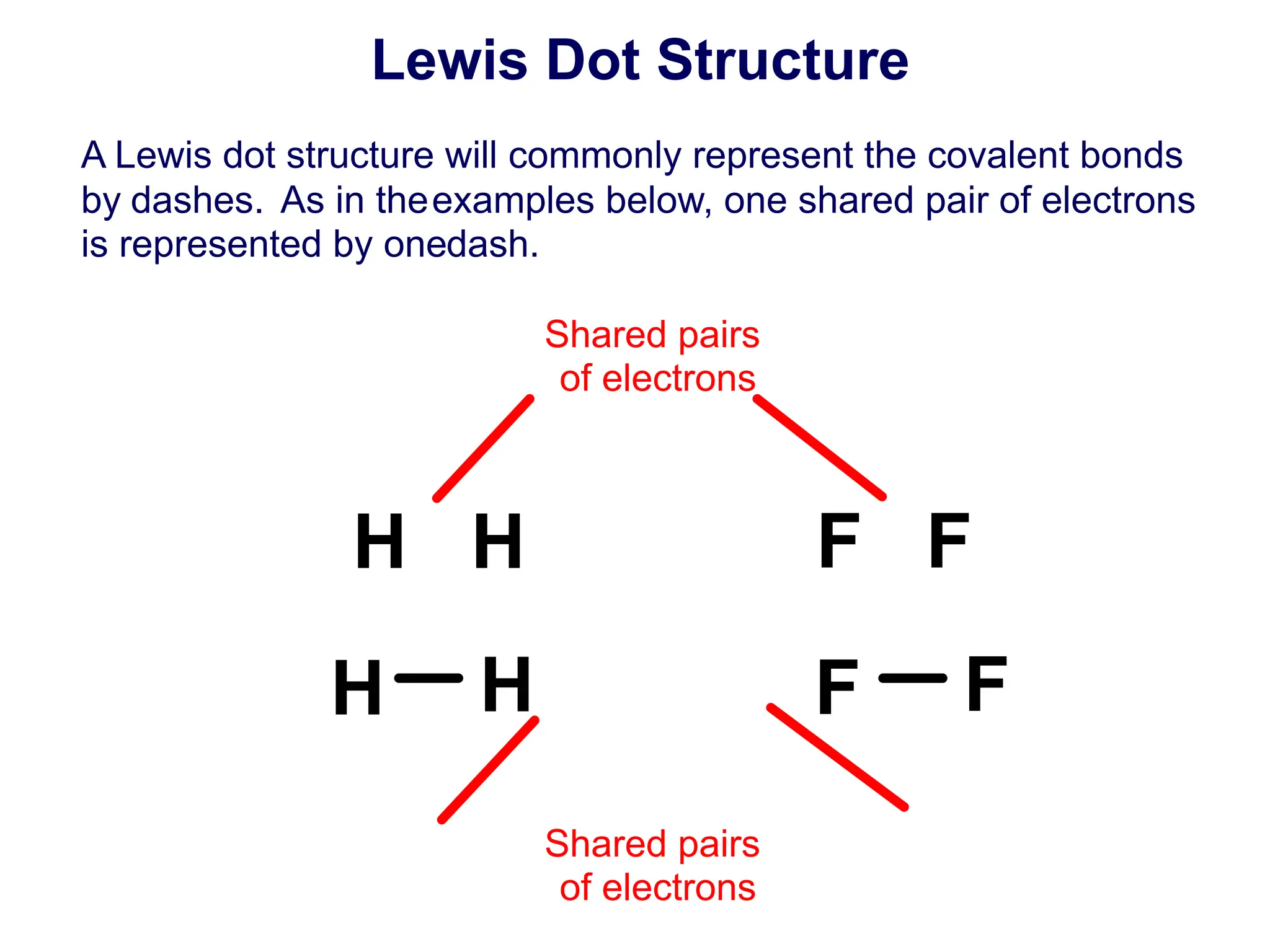
![15 How is a covalent bond represented in a Lewis structure?
A a dash
B a dot
C two dots
D both A and C
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
D
https://njctl.org/video/?v=qpqRuY3TqqQ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-60-2048.jpg)

![16 Which element in H2O is the least electronegative?
A H
B O
C the electronegativities are equal
D H2
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
A
https://njctl.org/video/?v=R9P6-toPzEE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-62-2048.jpg)

![17 How many total valence electrons does H2O have?
A 18
B 8
C 24
D more information is needed
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
B
https://njctl.org/video/?v=N6ocPuZrAbY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-64-2048.jpg)








![18
The Lewis structure for nitrogen is N
A True
B False
C I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
True
https://njctl.org/video/?v=Oa0FPayHqDs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-73-2048.jpg)

![19 Which of the following need fewer than 8 valence
electrons to be stable?
A Boron and Beryllium
B Boron and Helium
C Boron, Beryllium, and Hydrogen
D Boron, Beryllium, Hydrogen and Oxygen
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
C
https://njctl.org/video/?v=YE_CKH0rbC4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-75-2048.jpg)

![20 Which of the following is the correct Lewis Structure for
H2O?
H O H
H H O
H H
O
H H
O
A
B
C
D
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
D
https://njctl.org/video/?v=hZ2Y4durWUk](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-77-2048.jpg)

![21 Which of the following is the correct Lewis Structure
for PH3?
H P H H
H P H
H
H H
P
H
H P H
A
B
C
D
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
B
https://njctl.org/video/?v=oEeXrvlCK1Q](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-79-2048.jpg)

![A
B
C
D
22
H H H H H H C C
C C H
H
H
H
H H
Which of the following is the correct Lewis Structurefor
C2H6?
C C H
H
H H H
H
C C H
H
H H H
H
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
B
https://njctl.org/video/?v=5XD-x96UBmU](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-81-2048.jpg)
















![23 How many electrons are shared by two atoms to
create a double bond?
A 4
B 2
C 8
D 6
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
A
https://njctl.org/video/?v=iU_EKfF_RLI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-98-2048.jpg)

![24 How many electrons are shared by two atoms
to create a triple bond?
A 4
B 2
C 8
D 6
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
D
https://njctl.org/video/?v=qtqfjCwcFoU](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-100-2048.jpg)

![25 As the number of bonds between a pair of atoms
increases, the distance between the atoms:
A increases
B decreases
C remains unchanged
D varies, depending on the atoms
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
B
https://njctl.org/video/?v=d07lxBdPT08](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-102-2048.jpg)

![26 As the number of bonds between a pair of atoms
increases, the strength of the bond between the
atoms:
A increases
B decreases
C remains unchanged
D varies, depending on the atoms
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
A
https://njctl.org/video/?v=EZKmLTRzbwE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-104-2048.jpg)

![27 As the number of bonds between a pair of atoms
increases, the energy of the bond between the
atoms:
A increases
B decreases
C remains unchanged
D varies, depending on the atoms
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
A
https://njctl.org/video/?v=VxU1hKb7TgY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-106-2048.jpg)

![28 Which of the following molecules has a double bond?
A Br2
B BH3
C I2
D O2
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
D
https://njctl.org/video/?v=NVpo2Cx2EBA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-108-2048.jpg)

![29 Which of the following elements is not diatomic in its
elemental state?
A Br2
B S2
C I2
D O2
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
B
https://njctl.org/video/?v=Nt_UDFMPU8A](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-110-2048.jpg)

![30 Which of the following molecules has a triple bond?
A NaCl
B NH3
C N2
D SO2
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
C
https://njctl.org/video/?v=d4_DDTajh94](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-112-2048.jpg)

![31 Using Lewis structure drawings, determine which
molecule below would have the shortest bond length
between atoms.
A O2
B F2
C Cl2
D CO
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
D
https://njctl.org/video/?v=MvFC44e3y84](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-114-2048.jpg)

![32 Which of the following shows the correct Lewis structure
for O3?
A
B
C
D Both A & C
O
O O
O
O
O
O O O
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
D
https://njctl.org/video/?v=N9CtamcQvB8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-116-2048.jpg)



![Lewis Structures for Ions
Drawing the Lewis structure of ions follows the same steps as
molecules. Except f
or an ion, brackets [ ] are added around the
Lewis structure and the charge is indicated.
N H
H
H
H
+
Ammonium Ion
https://njctl.org/video/?v=PiZjj4hQAVc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-120-2048.jpg)





![33 How many valence electrons does CO3
2-
have?
A 22
B 18
C 20
D 24
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
D
https://njctl.org/video/?v=5CiqerILiuo](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-126-2048.jpg)

![34 How many valence electrons does H3O+ have?
A 7
B 8
C 9
D 10
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
B
https://njctl.org/video/?v=NScFSR31Pzc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-128-2048.jpg)

![35 Which of the following is the correct Lewis structure for
the ammonium ion?
A
B
C
D
N H
H
H
H
+
N H
H
H
H
N H
H H
H
N H
H
H
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
B
https://njctl.org/video/?v=PY5PYeUdvzs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-130-2048.jpg)

![36 Which of the following is the correct Lewis structure for
the cyanide ion?
A
B
C
D
C N
-
C N
-
C N
-
All of these are correct
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
A
https://njctl.org/video/?v=KnuuRLS8lk8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-132-2048.jpg)












![37 Which of the following is the correct Lewis structure for
iodine trichloride?
A
B
C
D
I Cl
Cl
Cl
I Cl
Cl
Cl
I Cl
Cl
Cl
I Cl
Cl
Cl
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
A
https://njctl.org/video/?v=7emWqIP0KqM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-145-2048.jpg)

![38 The correct lewis structure for BeCl 2 is:
Cl - Be - Cl
A True
B False
C I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
False
https://njctl.org/video/?v=IjRZF6Kjke4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-147-2048.jpg)

![39 Elements in the first two rows of the periodic table
cannot have expanded octets because their atoms do
not have enough space.
A True
B False
C I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
True
https://njctl.org/video/?v=9p7g669Hfaw](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-149-2048.jpg)

![40 Which compound below contains an atom that is
surrounded by more than an octet of electrons?
A PF5
B CH4
C NBr3
D OF2
E I need help
[This object is a pull tab]
Answer
A
https://njctl.org/video/?v=ctnznW54J-Y](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempresentation-1-covalent-bonding-lewis-diagrams2022-03-02-240201175159-a2add75a/75/Covalent-bonding-Lewis-Diagrams-151-2048.jpg)
