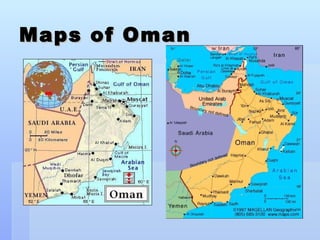
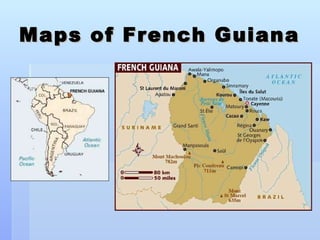
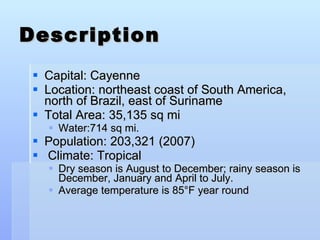
Oman is an arid country located in the Middle East with a population of around 3 million. It has a diverse landscape that includes desert plains, rugged mountains, and beaches. Oman relies heavily on oil exports for its economy but is trying to diversify. The culture places importance on traditions and Islam is the dominant religion.
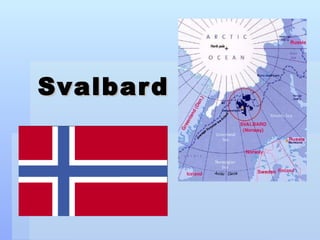
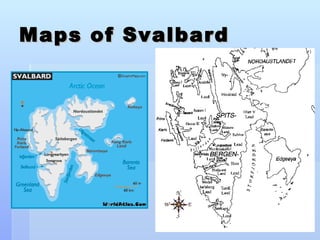
Svalbard is a remote Norwegian archipelago located in the Arctic Ocean with a population under 3,000. Over 60% of the land is covered by glaciers and snow. The climate is Arctic with cold winters. The economy relies on mining and tourism focused on wildlife like polar bears.