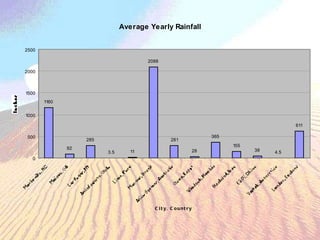
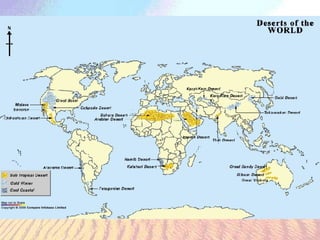
Deserts are dry regions that receive less than 10 inches of rain per year, covering about one-fifth of the Earth's land surface. There are two main types of deserts: hot deserts near the equator with extreme temperature fluctuations, and cold deserts near the poles that are too cold for plant growth. Deserts are areas of extremes, and both plants and animals have adaptations like waxy coatings, deep roots, burrowing, dormancy, and nocturnal behavior to survive the harsh conditions with little water availability. Common deserts include the Sahara desert in Africa, the Atacama desert in South America, and the Mojave and Sonoran deserts in the United States.