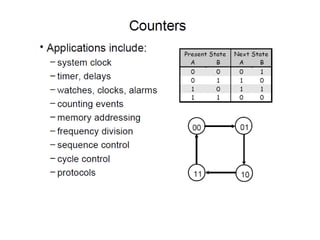
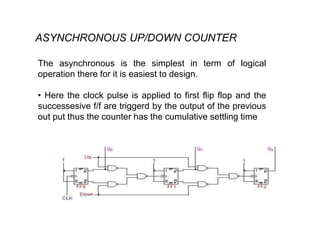
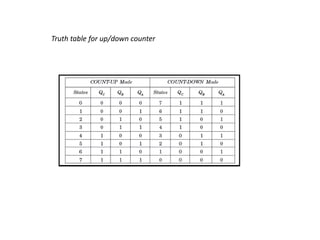
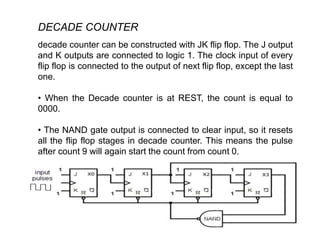
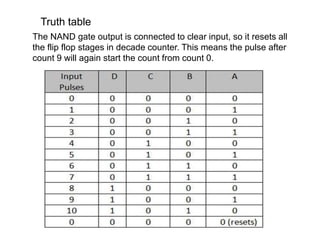
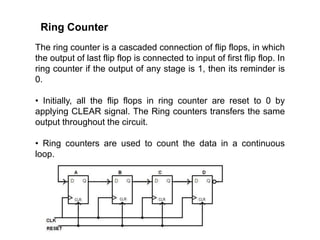
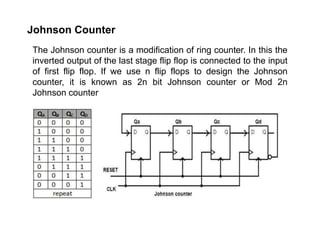
Counters are digital circuits that use flip-flops to count clock pulses. There are different types of counters including synchronous, asynchronous, up/down, decade, ring, and Johnson counters. Synchronous counters are faster but more complex and expensive than asynchronous counters. A decade counter uses JK flip-flops with the J and K inputs connected to logic 1 and the outputs in a cascade to count from 0 to 9 before resetting. A ring counter cascades flip-flops in a loop with the output of the last connected to the input of the first. A Johnson counter is similar but with the inverted output of the last flip-flop connected to the first.