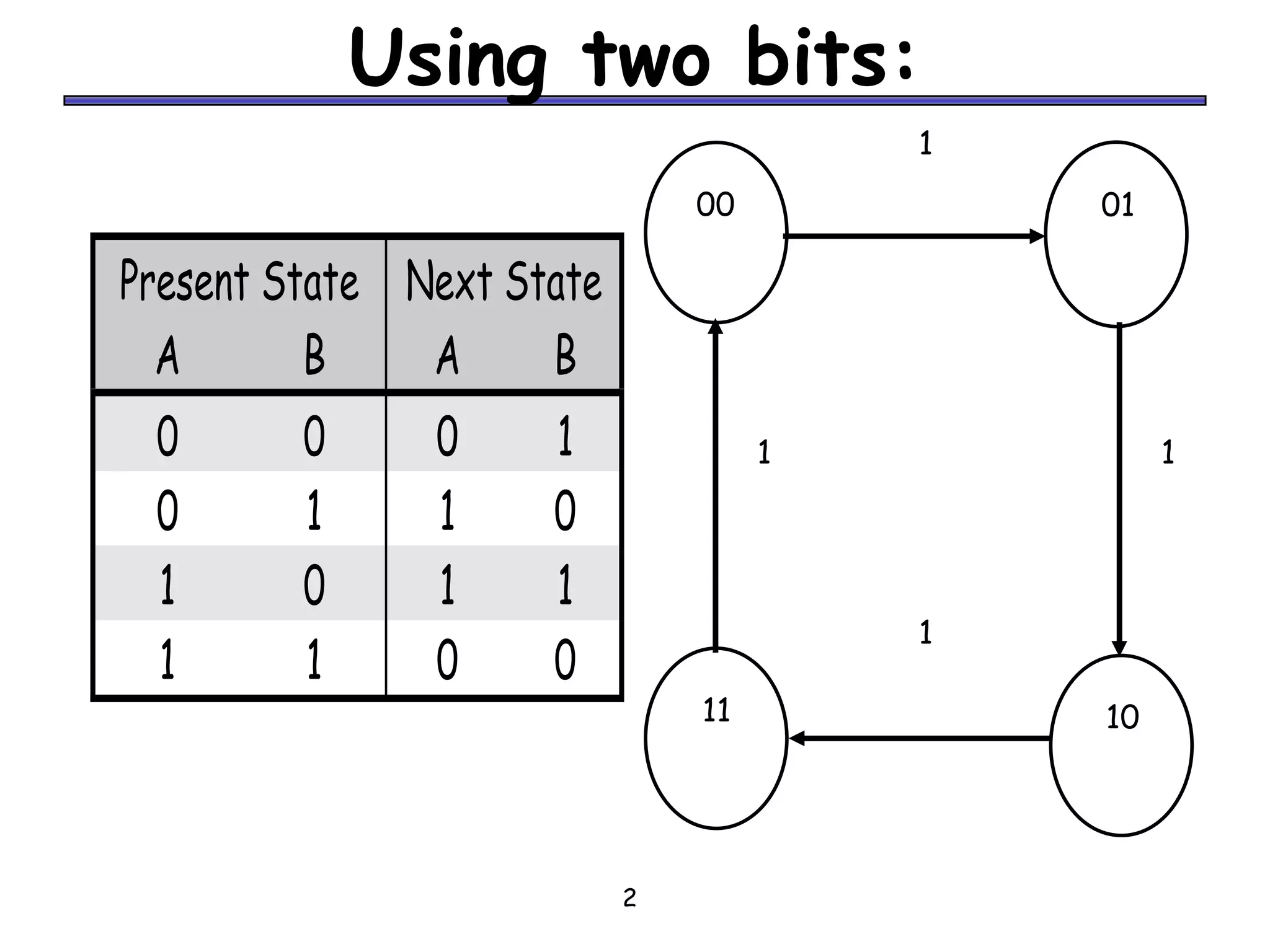
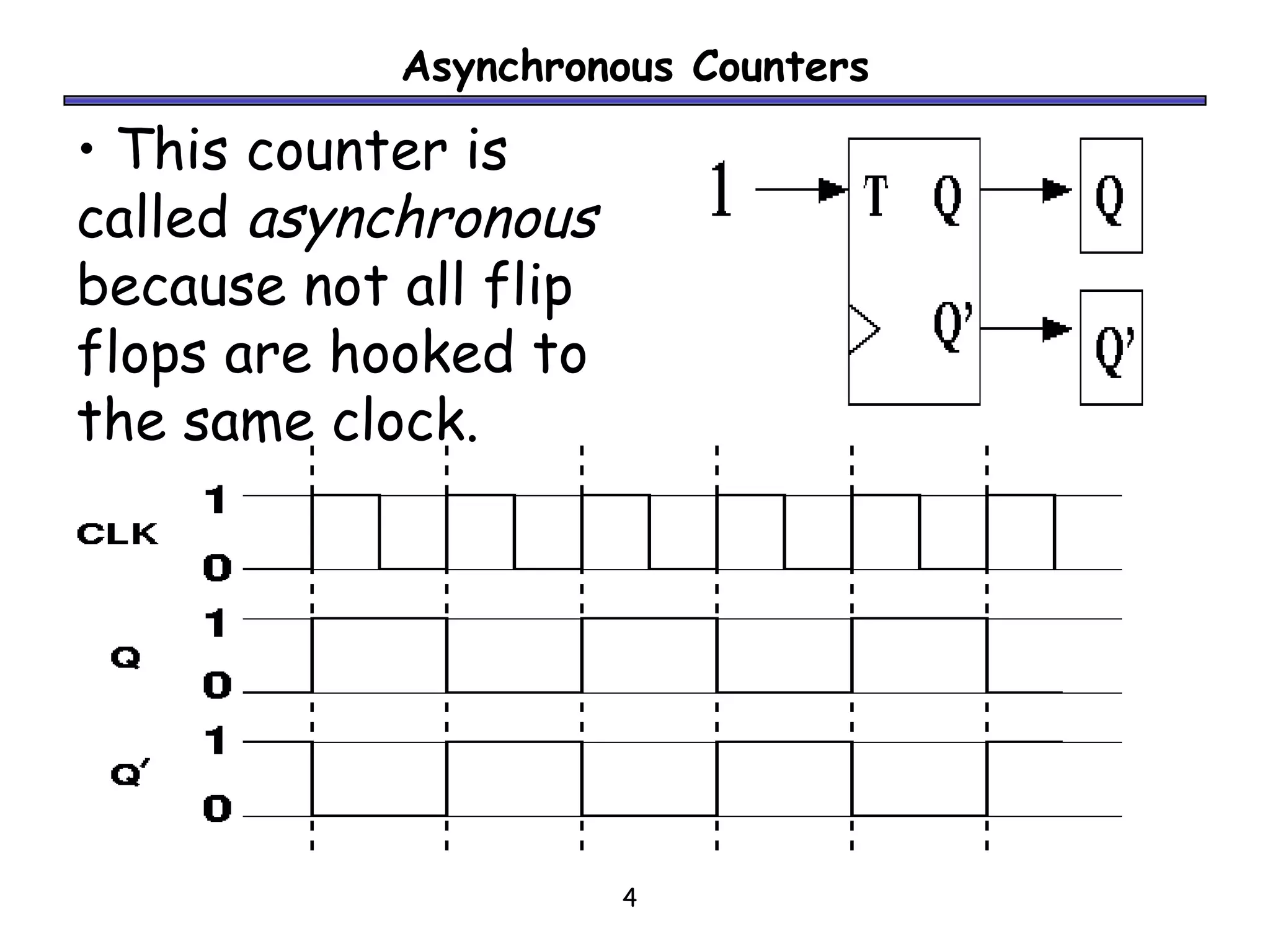
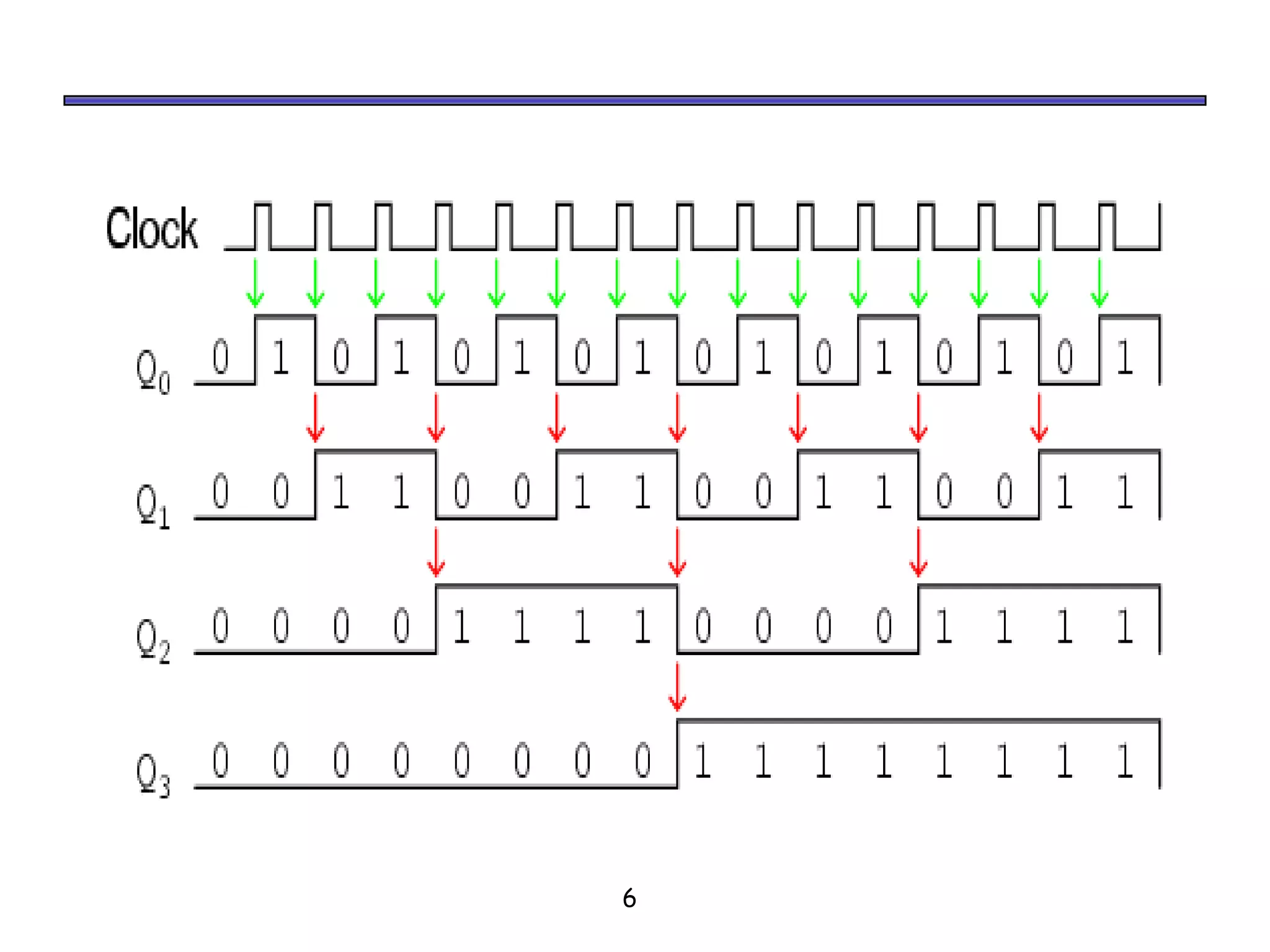
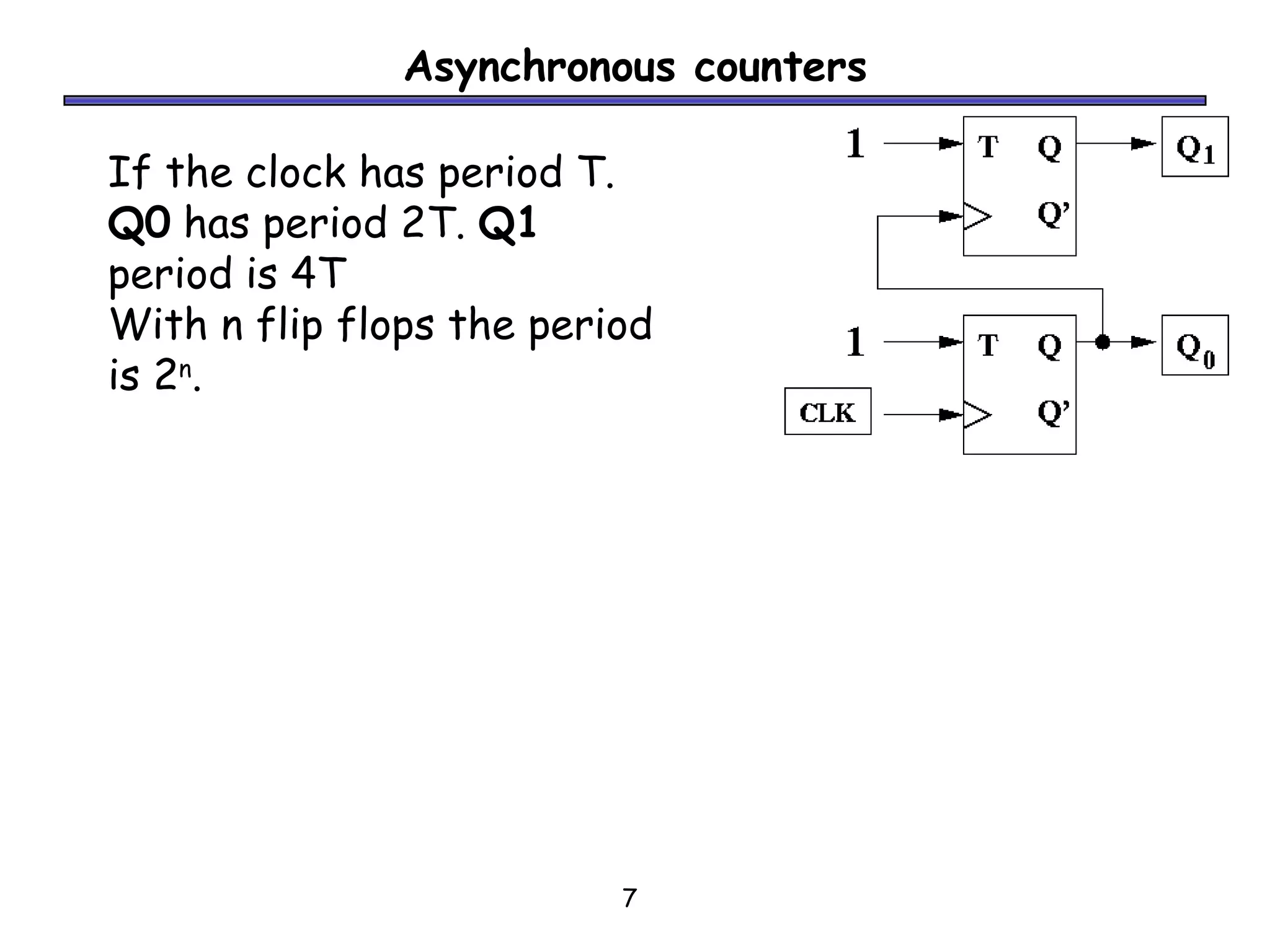
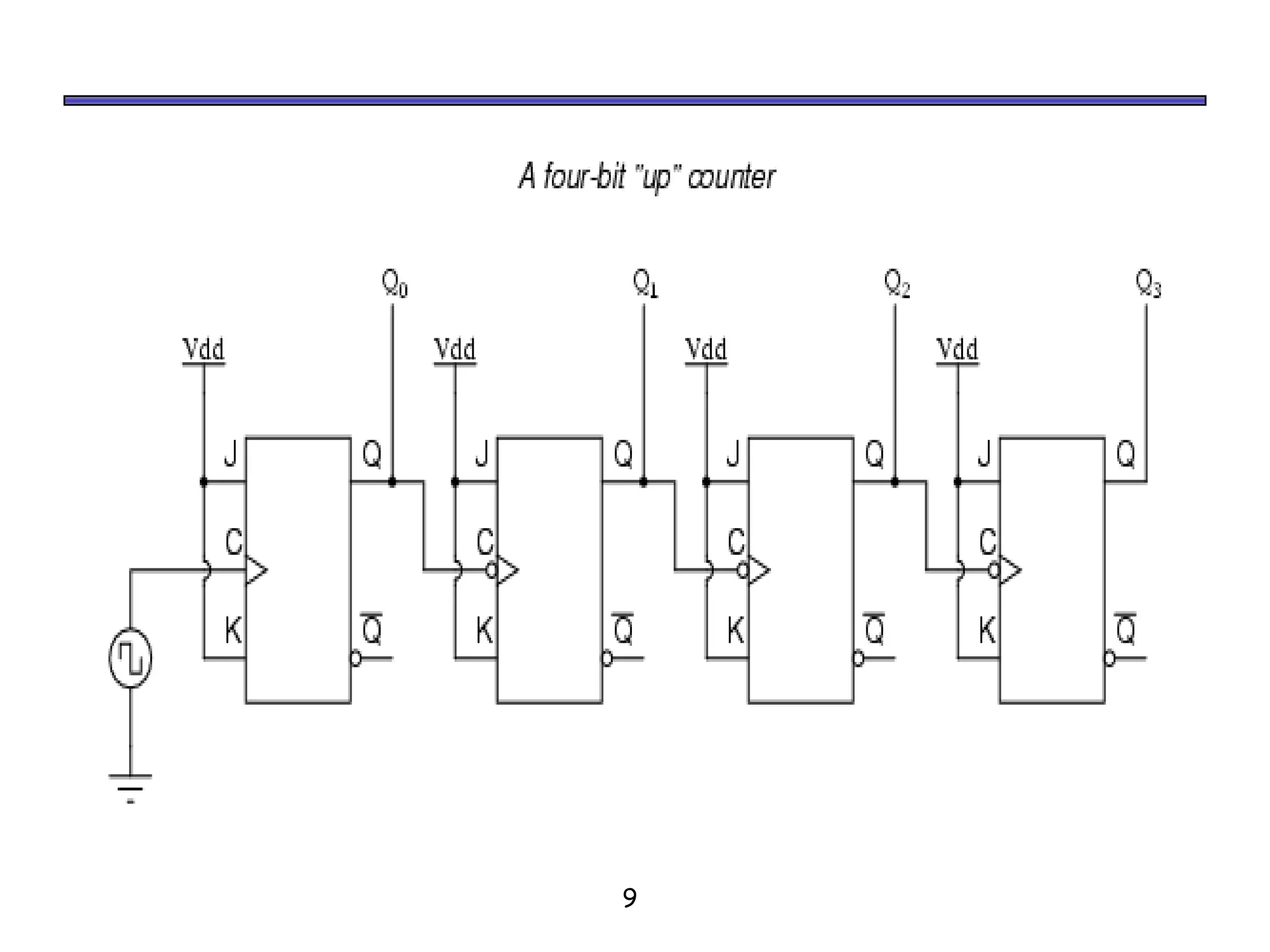
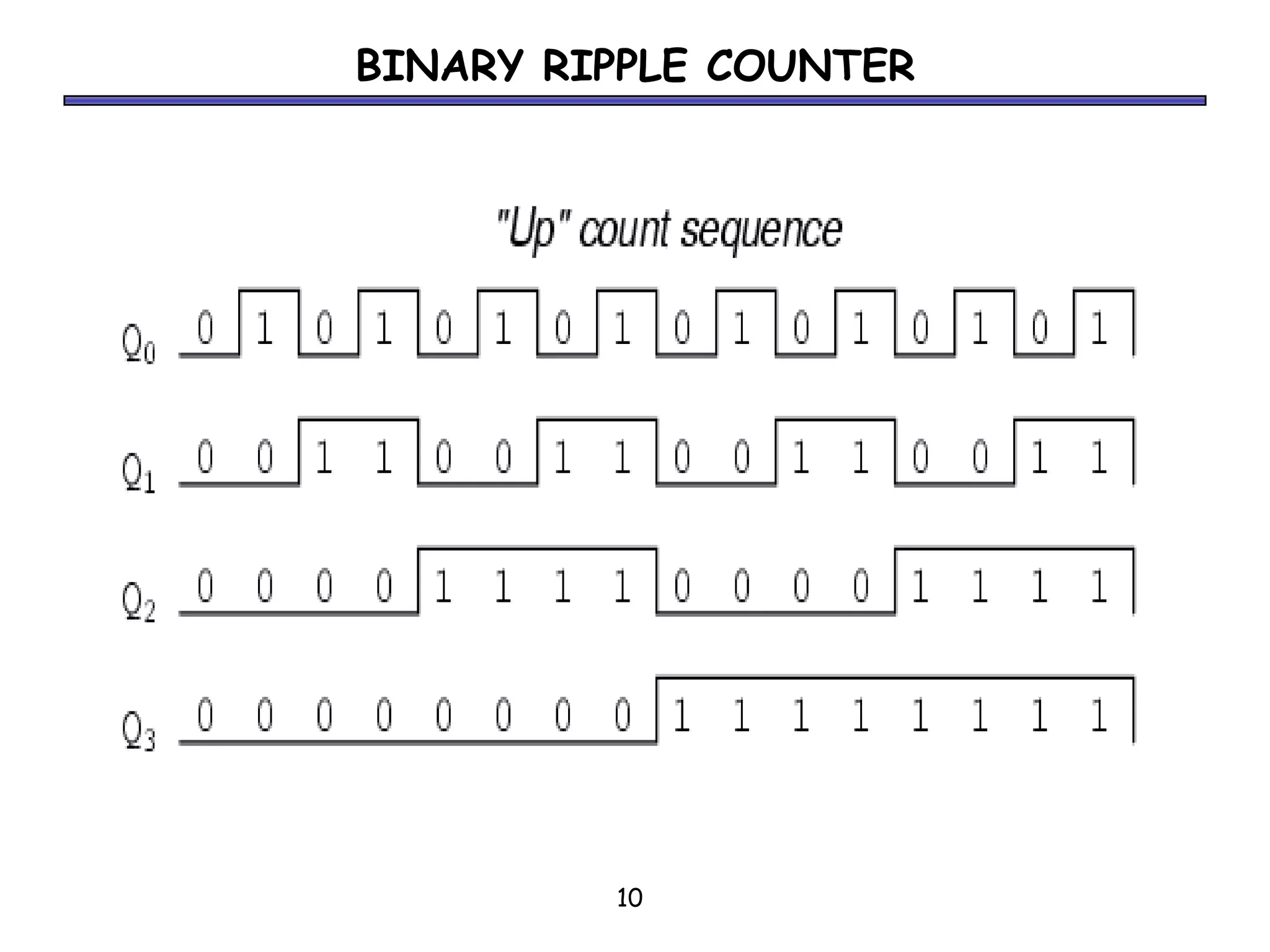
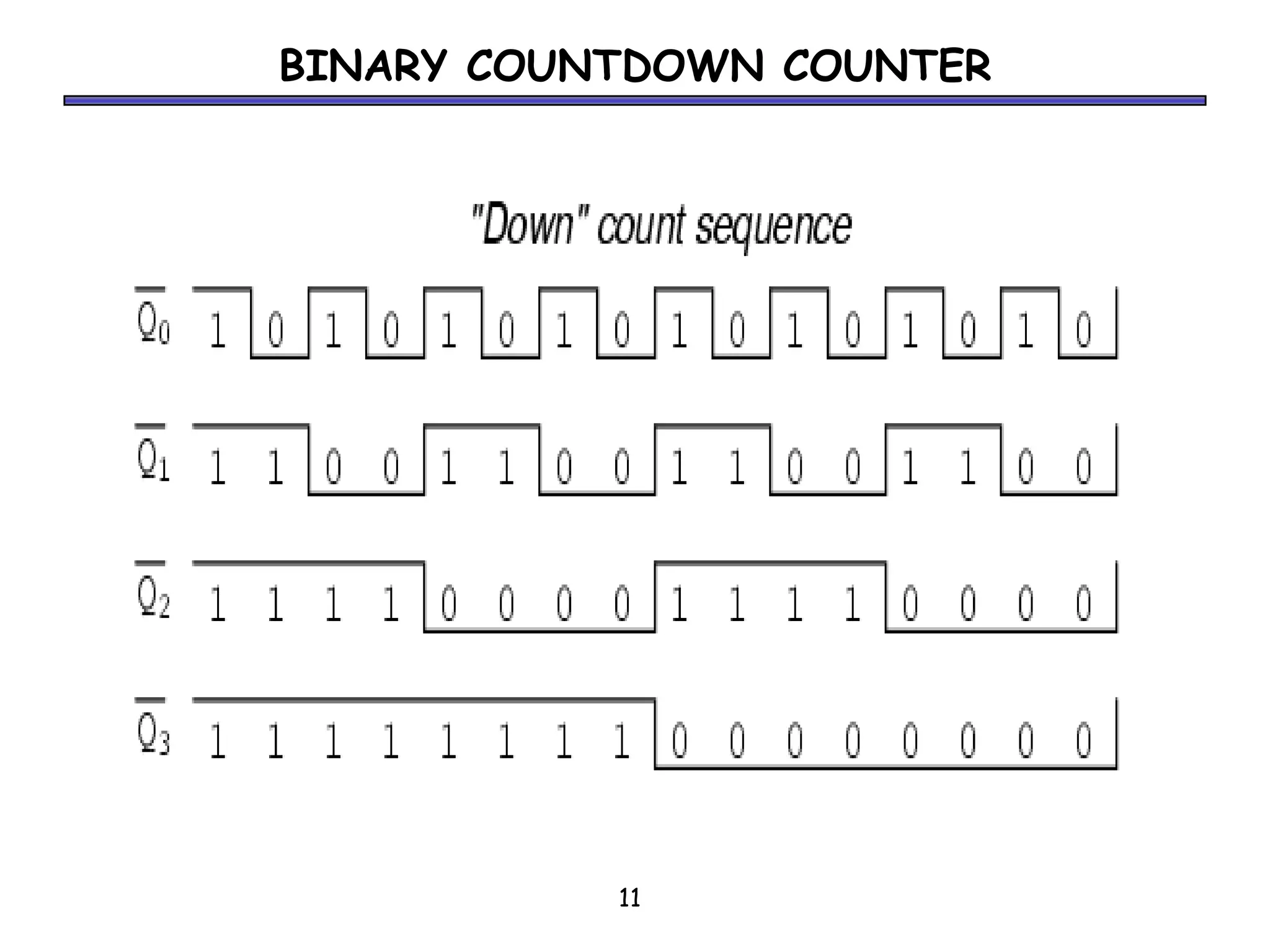
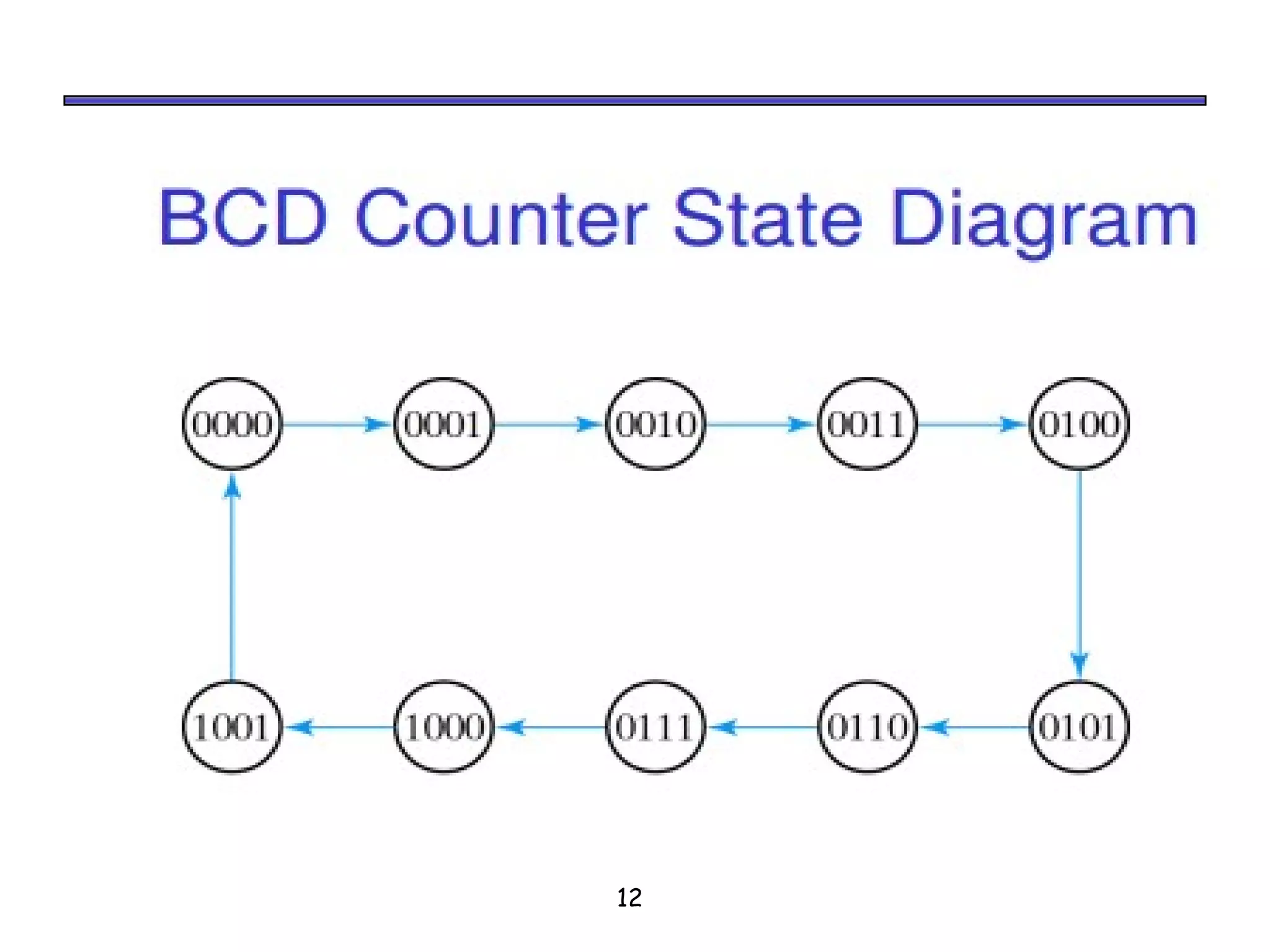
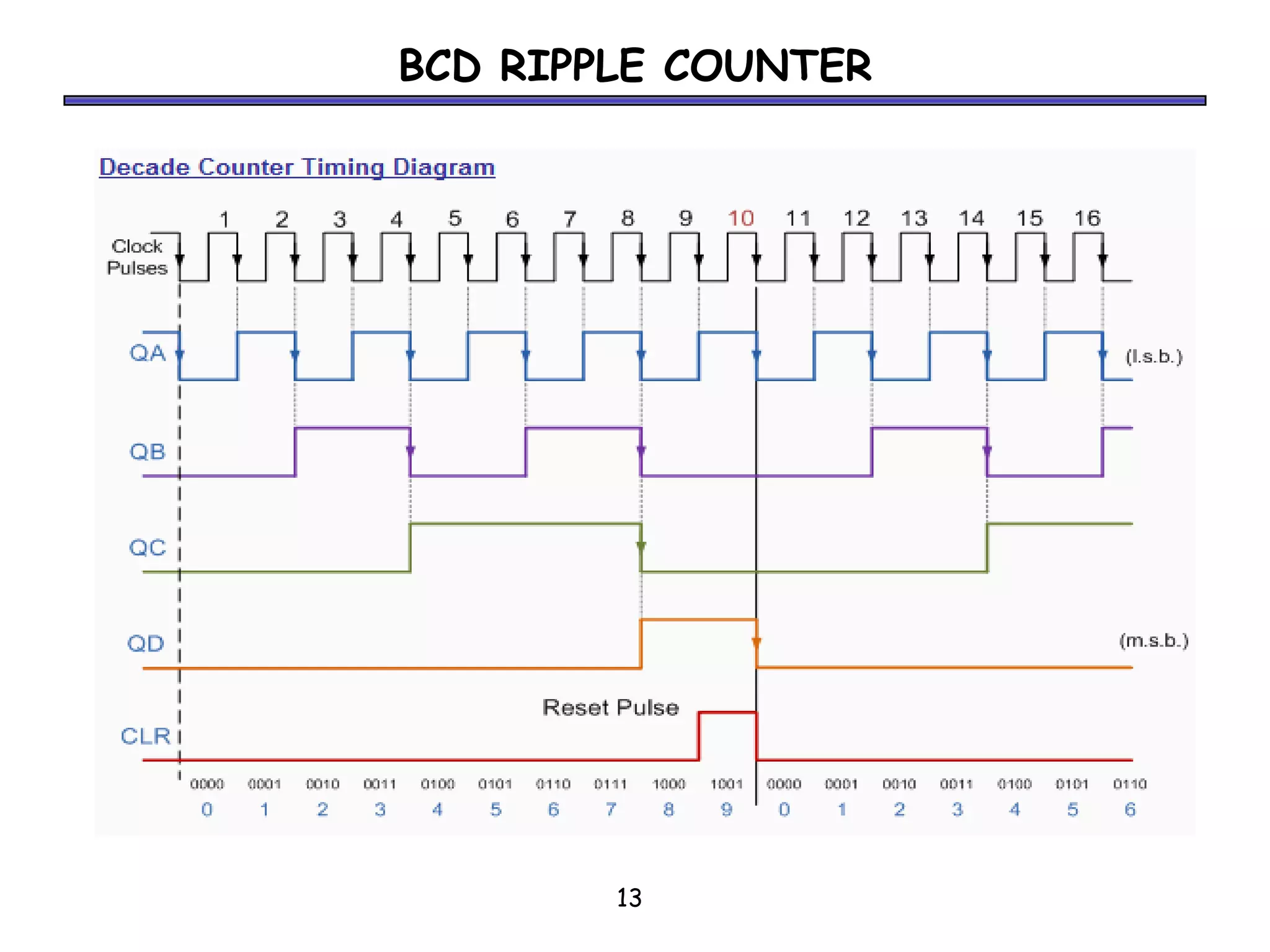
Counters are sequential circuits where the output value increases by one on each clock cycle and wraps around back to zero after reaching the maximum value. Ripple counters are asynchronous counters where the flip-flops are not connected to a common clock, but instead are triggered one after another by each previous flip-flop's output in a ripple effect. This causes the periods of each successive flip-flop to be multiples of the clock period, with the last flip-flop having the largest period of 2n for an n-bit ripple counter.