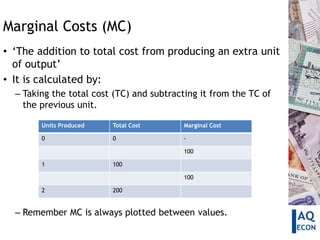
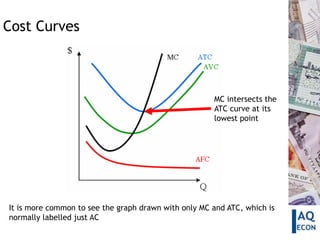
This document defines and explains different types of costs including fixed costs, variable costs, average costs, and marginal costs. It provides examples of fixed costs like rent and salaries. Variable costs vary with output and include raw materials. Average costs are calculated by dividing total costs by units produced. Marginal cost is the change in total cost from producing one additional unit. Cost curves can be used to show the relationship between these different cost measures.